Freedom of speech and freedom of the press in Denmark are ensured by § 77 of the constitution:
Danish lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) rights are some of the most extensive in the world. In 2023, ILGA-Europe ranked Denmark as the third most LGBTQ-supportive country in Europe. Polls consistently show that same-sex marriage support is nearly universal amongst the Danish population.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in the Faroe Islands are relatively similar to those of Denmark. The progress of LGBT rights has been slower, however. While same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the Faroe Islands since the 1930s, same-sex couples never had a right to a registered partnership. In April 2016, the Løgting passed legislation legalizing civil same-sex marriage on the Faroes, recognizing same-sex marriages established in Denmark and abroad and allowing same-sex adoption. This was ratified by the Folketing in April 2017. The law went into effect on 1 July 2017.

The Danish Realm, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, or simply Denmark, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of Denmark, who functions as head of state. It consists of metropolitan Denmark—the kingdom's territory in continental Europe and sometimes called "Denmark proper" —and the realm's two autonomous regions: the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic and Greenland in North America. The relationship between the three parts of the Kingdom is known as Rigsfællesskabet.
Laws governing lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) rights are complex and diverse in the Americas, and acceptance of LGBTQ persons varies widely.

A referendum on changing the Danish Act of Succession, the rules governing the succession to the Danish throne, was held in Denmark, the Faroe Islands, and Greenland on 7 June 2009, simultaneously with the election to the European Parliament, in Denmark proper.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in the Faroe Islands since 1 July 2017. Legislation allowing same-sex marriage and adoption by same-sex couples was approved by the Løgting on 29 April 2016. The Danish Parliament approved the necessary legislative adaptations on 25 April 2017, and the law received royal assent on 3 May and went into effect on 1 July 2017.

Danish nationality law is governed by the Constitutional Act and the Consolidated Act of Danish Nationality. Danish nationality can be acquired in one of the following ways:
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Greenland are some of the most extensive in the Americas and the world, relatively similar to those in Denmark proper in Europe. Same-sex sexual activity is legal, with an equal age of consent, and there are some anti-discrimination laws protecting LGBT people. Same-sex couples had access to registered partnerships, which provided them with nearly all of the rights provided to married opposite-sex couples, from 1996 to 2016. On 1 April 2016, a law repealing the registered partnership act and allowing for same-sex marriages to be performed came into effect.
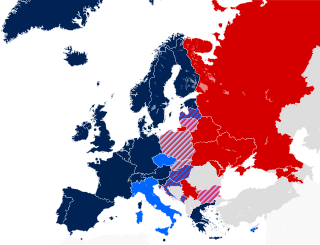
Debate has occurred throughout Europe over proposals to legalise same-sex marriage as well as same-sex civil unions. Currently 33 of the 50 countries and the 8 dependent territories in Europe recognise some type of same-sex union, among them most members of the European Union (24/27). Nearly 43% of the European population lives in jurisdictions where same-sex marriage is legal.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Greenland since 1 April 2016. Same-sex marriage legislation passed the Inatsisartut unanimously on 26 May 2015. Approval by the Folketing followed on 19 January 2016, and the law received royal assent on 3 February. The first same-sex marriage was performed in Nuuk on 1 April.

Same-sex marriage is legal in the following countries: Andorra, Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Denmark, Ecuador, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Luxembourg, Malta, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Uruguay.

The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people are protected under the European Union's (EU) treaties and law. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in all EU member states and discrimination in employment has been banned since 2000. However, EU states have different laws when it comes to any greater protection, same-sex civil union, same-sex marriage, and adoption by same-sex couples.

Adoption by LGBT people in Europe differs in legal recognition from country to country. Full joint adoption or step-child adoption or both is legal in 23 of the 56 European countries, and in all dependent territories.
The Danish educational ceiling is a repealed Danish rule limiting access to multiple higher educations in order to avoid double education.

Aarhus East nominating district is one of the 92 nominating districts that exists for Danish elections following the 2007 municipal reform. It is one of the four nomination districts in Aarhus Municipality, the others being Aarhus South, Aarhus West and Aarhus North. It was created in 1970, with its boundaries being slightly changed in 2007.

Odense East nominating district is one of the 92 nominating districts that exists for Danish elections following the 2007 municipal reform. It is one of the three nomination districts in Odense Municipality, the others being Odense West and Odense South. It was created in 1970 and has maintained its boundaries since then.

Odense West nominating district is one of the 92 nominating districts that exists for Danish elections following the 2007 municipal reform. It is one of the three nomination districts in Odense Municipality, the others being Odense East and Odense South. It was created in 1970 and has maintained its boundaries since then.

Rødovre nominating district is one of the 92 nominating districts that exists for Danish elections following the 2007 municipal reform. It consists of Herlev and Rødovre municipality. It was created in 1966 and has maintained its boundaries since then.

Ballerup nominating district is one of the 92 nominating districts that was created for Danish elections following the 2007 municipal reform. It consists of Ballerup and Glostrup municipality. It was created in 1970, though its boundaries have been changed since then.

















