Related Research Articles

Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. About 29% of Earth's surface is land consisting of continents and islands. The remaining 71% is covered with water, mostly by oceans but also lakes, rivers and other fresh water, which together constitute the hydrosphere. Much of Earth's polar regions are covered in ice. Earth's outer layer is divided into several rigid tectonic plates that migrate across the surface over many millions of years. Earth's interior remains active with a solid iron inner core, a liquid outer core that generates Earth's magnetic field, and a convecting mantle that drives plate tectonics.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn, form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the second-most populous country, the seventh-largest country by land area, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as:

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethicist, who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and in turn inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in 1914 in South Africa, is now used throughout the world.

In Newtonian mechanics, linear momentum, translational momentum, or simply momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity, then the object's momentum is:
In SI units, momentum is measured in kilogram meters per second (kg⋅m/s).
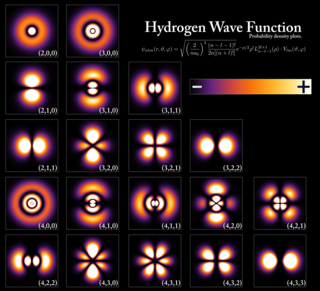
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

Krishna is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of the god Vishnu and also as the supreme God in his own right. He is the god of compassion, tenderness, love and is one of the most popular and widely revered among Indian divinities. Krishna's birthday is celebrated every year by Hindus on Krishna Janmashtami according to the lunisolar Hindu calendar, which falls in late August or early September of the Gregorian calendar. Krishna is usually depicted with a flute in his hand.
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that, together, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. More precisely, the first law defines the force qualitatively, the second law offers a quantitative measure of the force, and the third asserts that a single isolated force does not exist. These three laws have been expressed in several ways, over nearly three centuries, and can be summarised as follows:

In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualise its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton's laws of motion.

Jesus, also referred to as Jesus of Nazareth or Jesus Christ, was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah prophesied in the Old Testament.

The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States or America, is a country primarily located in central North America, between Canada and Mexico. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five self-governing territories, and several other island possessions. At 3.8 million square miles, it is the world's third- or fourth-largest country by total area. With a population of over 328 million, it is the third most populous country in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city is New York City.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi), is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
English is a West Germanic language first spoken in early medieval England which eventually became the leading language of international discourse in today's world. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea. English is most closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, while its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse, as well as Latin and French.

Animals are multicellular eukaryotic organisms that form the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from 8.5 micrometres (0.00033 in) to 33.6 metres (110 ft). They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The kingdom Animalia includes humans but in colloquial use the term animal often refers only to non-human animals. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology.

A penis is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do not bear a penis in every animal species, and in those species in which the male does bear a so-called penis, the penises in the various species are not necessarily homologous.

R.E.M. was an American rock band from Athens, Georgia, formed in 1980 by drummer Bill Berry, guitarist Peter Buck, bassist Mike Mills, and lead vocalist Michael Stipe who were students at the University of Georgia. Liner notes from some of the band's albums list attorney Bertis Downs and manager Jefferson Holt as non-musical members. One of the first alternative rock bands, R.E.M. was noted for Buck's ringing, arpeggiated guitar style; Stipe's distinctive vocal quality, unique stage presence, and obscure lyrics; Mills's melodic basslines and backing vocals; and Berry's tight, economical drumming style. In the early 1990s, other alternative rock acts such as Nirvana and Pavement viewed R.E.M. as a pioneer of the genre. After Berry left the band in 1997, the band continued its career in the 2000s with mixed critical and commercial success. The band broke up amicably in 2011 with members devoting time to solo projects after having sold more than 90 million albums worldwide and becoming one of the world's best-selling music artists.

In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns. For example, the dimension of the matrix below is 2 × 3, because there are two rows and three columns:
Bizionia is a strictly aerobic genus from the family of Flavobacteriaceae which produce carotenoids. Bizionia is named after Bartolomeo Bizio.
References
- 1 2 Parte, A.C. "Bizionia". LPSN .
- 1 2 3 "Bizionia algoritergicola". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ George M., Garrity (2011). Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology (2nd ed.). New York: Springer Science + Business Media. ISBN 0-387-68572-3.
- ↑ Atlas, edited by Asim K. Bej, Jackie Aislabie, Ronald M. (2010). Polar microbiology the ecology, biodiversity, and bioremediation potential of microorganisms in extremely cold environments. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 1-420-08388-0.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)