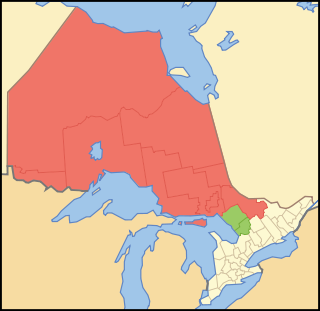
Northern Ontario is a primary geographic and quasi-administrative region of the Canadian province of Ontario, the other primary region being Southern Ontario. Most of the core geographic region is located on part of the Superior Geological Province of the Canadian Shield, a vast rocky plateau located mainly north of Lake Huron, the French River, Lake Nipissing, and the Mattawa River. The statistical region extends south of the Mattawa River to include all of the District of Nipissing. The southern section of this district lies on part of the Grenville Geological Province of the Shield which occupies the transitional area between Northern and Southern Ontario. The extended federal and provincial quasi-administrative regions of Northern Ontario have their own boundaries even further south in the transitional area that vary according to their respective government policies and requirements. Ontario government departments and agencies such as the Growth Plan for Northern Ontario and the Northern Ontario Heritage Fund Corporation define Northern Ontario as all areas north of, and including, the districts of Parry Sound and Nipissing for political purposes, and the federal but not the provincial government also includes the district of Muskoka.

The Regional Municipality of York, also called York Region, is a regional municipality in Southern Ontario, Canada, between Lake Simcoe and Toronto. The region was established after the passing of then Bill 102, An Act to Establish The Regional Municipality of York, in 1970. It replaced the former York County in 1971, and is part of the Greater Toronto Area and the inner ring of the Golden Horseshoe. The regional government is headquartered in Newmarket.

The Ontario Northland Railway is a Canadian railway operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission, a provincial Crown agency of the government of Ontario.

Kirkland Lake is a town and municipality in Timiskaming District of Northeastern Ontario. The 2016 population, according to Statistics Canada, was 7,981.

Sudbury, officially the City of Greater Sudbury, is the largest city in Northern Ontario by population, with a population of 166,004 at the 2021 Canadian Census. By land area, it is the largest in Ontario and the fifth largest in Canada. It is administratively a single-tier municipality and thus is not part of any district, county, or regional municipality. The City of Greater Sudbury is separate from, but entirely surrounded by the Sudbury District. The city is also referred to as "Ville du Grand Sudbury" among Francophones.

Health Sciences North is a teaching hospital in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. HSN offers a variety of programs and services, with regional programs in the areas of cardiac care, oncology, nephrology, trauma and rehabilitation. Patients visit HSN from a wide geographic area across northeastern Ontario.

Collège Boréal d’arts appliqués et de technologie is a French-language college of applied arts and technology serving the Northern and Central Southwestern Ontario area. It is the youngest of the 24 Colleges of Applied Arts and Technology. It achieved the highest graduation rate for the 12th time in 13 years, and for the 9th time in 12 years, it is considered as the highest graduate satisfaction rate among all the community colleges in Ontario. Located in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, Collège Boréal has a total of 42 access centres across 28 cities in the province, including main campuses in Hamilton, Hearst, Kapuskasing, London, Nipissing, Sudbury, Timmins, Toronto, Welland, and Windsor. Collège Boréal began its operations in 1995 as a postsecondary institution. The students are offered technical programs that helps them gain access to a bilingual labour market. In 2002, Collège Boréal opened a campus in Toronto, taking over the programs and services of the defunct Collège des Grands-Lacs. In 2012, the Toronto campus moved to One Yonge Street, and in 2023 to 60 Distillery Lane in the Distillery District in Toronto.

The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is the medical school of the University of Toronto. Founded in 1843, the faculty is based in Downtown Toronto and is one of Canada's oldest institutions of medical studies, being known for the discovery of insulin, stem cells and the site of the first single and double lung transplants in the world.

Northern Ontario School of Medicine University is a public medical university in the Canadian province of Ontario. It is mandated both to educate doctors and to contribute to care in Northern Ontario's urban, rural and remote communities, and has campuses in both Sudbury and Thunder Bay.

Englehart is a town in the Canadian province of Ontario, located on the Blanche River in the Timiskaming District.

Women's College Hospital is a teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is located in downtown Toronto at the north end of Hospital Row, a section of University Avenue where several major hospitals are located. It currently functions as an independent ambulatory care hospital.
The Francophone Association of Municipalities of Ontario is a Canadian political organization of municipalities in the province of Ontario which have significant Franco-Ontarian communities. The organization oversees the maintenance and development of municipal government services in French, and works with other levels of government, as well as organizations in other Canadian provinces, on issues unique to francophone and bilingual communities.

Chamberlain is a township in the Canadian province of Ontario, located within the Timiskaming District.

Charlton and Dack is a municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario, located within the Timiskaming District. Its population in 2016 was 686.

The Englehart River is a river in Timiskaming District in northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is in the Saint Lawrence River drainage basin and is a right tributary of the Blanche River.

The Blanche River is a river in the Saint Lawrence River drainage basin in Timiskaming District in northeastern Ontario, Canada. The river is a tributary of Lake Timiskaming and its name is from the French for the colour "white".
John Oliver is a politician in Ontario, Canada. He is a former Liberal member of the House of Commons of Canada who was elected in 2015 in the riding of Oakville. He served one term and chose not to run for re-election.

The Sinai Health System is a hospital system which serves Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It comprises two hospitals, Mount Sinai Hospital and Hennick Bridgepoint Hospital, both affiliated with the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine.
Contact North is a distance education network in the Canadian province of Ontario, with 112 online learning centres throughout the province. Based principally in Sudbury and Thunder Bay, the network partners with Ontario's 24 public colleges, 22 public universities and 250 public literacy and essential skills and training providers to help Ontarians in over 600 communities across the province participate in education and training opportunities without leaving their own community.



















