
Rorquals are the largest group of baleen whales, which comprise the family Balaenopteridae, containing ten extant species in three genera. They include the largest animal that has ever lived, the blue whale, which can reach 180 tonnes, and the fin whale, which reaches 120 tonnes ; even the smallest of the group, the northern minke whale, reaches 9 tonnes.

The minke whale, or lesser rorqual, is a species complex of baleen whale. The two species of minke whale are the common minke whale and the Antarctic minke whale. The minke whale was first described by the Danish naturalist Otto Fabricius in 1780, who assumed it must be an already known species and assigned his specimen to Balaena rostrata, a name given to the northern bottlenose whale by Otto Friedrich Müller in 1776. In 1804, Bernard Germain de Lacépède described a juvenile specimen of Balaenoptera acuto-rostrata. The name is a partial translation of Norwegian minkehval, possibly after a Norwegian whaler named Meincke, who mistook a northern minke whale for a blue whale.

The Antarctic minke whale or southern minke whale is a species of minke whale within the suborder of baleen whales. It is the second smallest rorqual after the common minke whale and the third smallest baleen whale. Although first scientifically described in the mid-19th century, it was not recognized as a distinct species until the 1990s. Once ignored by the whaling industry due to its small size and low oil yield, the Antarctic minke was able to avoid the fate of other baleen whales and maintained a large population into the 21st century, numbering in the hundreds of thousands. Surviving to become the most abundant baleen whale in the world, it is now one of the mainstays of the industry alongside its cosmopolitan counterpart the common minke. It is primarily restricted to the Southern Hemisphere and feeds mainly on euphausiids.

The Chacoan peccary or tagua is the last extant species of the genus Catagonus; it is a peccary found in the Gran Chaco of Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. Approximately 3,000 remain in the world.

Catagonus is a genus of peccaries that contains the living Chacoan peccary and several extinct species. The genus has always been restricted to South America.

Macrolepiota is a genus of white spored, gilled mushrooms of the family Agaricaceae. The best-known member is the parasol mushroom (M. procera). The widespread genus contains about 40 species.

Blastocladiomycota is one of the currently recognized phyla within the kingdom Fungi. Blastocladiomycota was originally the order Blastocladiales within the phylum Chytridiomycota until molecular and zoospore ultrastructural characters were used to demonstrate it was not monophyletic with Chytridiomycota. The order was first erected by Petersen for a single genus, Blastocladia, which was originally considered a member of the oomycetes. Accordingly, members of Blastocladiomycota are often referred to colloquially as "chytrids." However, some feel "chytrid" should refer only to members of Chytridiomycota. Thus, members of Blastocladiomyota are commonly called "blastoclads" by mycologists. Alternatively, members of Blastocladiomycota, Chytridiomycota, and Neocallimastigomycota lumped together as the zoosporic true fungi. Blastocladiomycota contains 5 families and approximately 12 genera. This early diverging branch of kingdom Fungi is the first to exhibit alternation of generations. As well, two (once) popular model organisms—Allomyces macrogynus and Blastocladiella emersonii—belong to this phylum.

Megalographa is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae.
Megalographa bonaerensis is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from southern Brazil and Paraguay southward to northern Argentina and Chile.
Maronite Catholic Eparchy of San Charbel in Buenos Aires is a Maronite Church ecclesiastical territory or eparchy of the Catholic Church in Argentina. It is a suffragan eparchy in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Buenos Aires, a Latin Church archdiocese.

Francisco Javier Muñiz was an Argentine colonel, legislator, and medical doctor. He treated patients and died during the Great Yellow Fever Epidemic of 1871. He was considered the first important naturalist from Argentina.
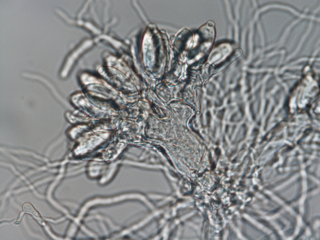
Blastocladia is a genus of aquatic fungi.
Blastocladia angusta is a species of fungus.
Blastocladia arborata is a species of fungus.
Blastocladia caduca is a species of fungus from India.
Blastocladia coronata is a species of fungus from India.

The St. Maron's Cathedral also called Maronite Catholic Cathedral of Buenos Aires is a religious building of the Catholic Church (Maronite) located at 834 Paraguay Street, in the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Not to be confused with the metropolitan cathedral of Latin rite of the Holy Trinity, the cathedral of the military bishopric also of Latin rite or the Armenian Catholic Cathedral of Our Lady of Narek, all in the city of Buenos Aires.
Bessie Bernice Kanouse was an American mycologist. The standard author abbreviation Kanouse is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
Catagonus metropolitanus is an extinct species of peccary known from the Pleistocene of Argentina.
Catagonus carlesi, or Parachoerus carlesi, is an extinct species of peccary that lived in Argentina during the Late Pleistocene.










