
Point Reyes National Seashore is a 71,028-acre (287.44 km2) park preserve located on the Point Reyes Peninsula in Marin County, California. As a national seashore, it is maintained by the US National Park Service as an important nature preserve. Some existing agricultural uses are allowed to continue within the park. Clem Miller, a US Congressman from Marin County, wrote and introduced the bill for the establishment of Point Reyes National Seashore in 1962 to protect the peninsula from development which was proposed at the time for the slopes above Drake's Bay.

The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges that stretch 1,500 km (930 mi) from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific Coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from 150 to 3,300 m.

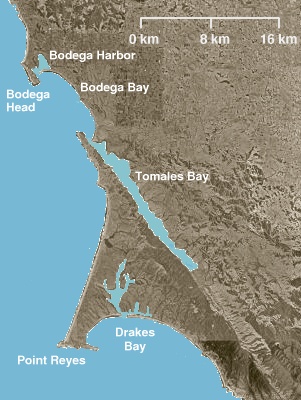
Drakes Bay is a 4 mi (6 km) wide bay named so by U.S. surveyor George Davidson in 1875 along the Point Reyes National Seashore on the coast of northern California in the United States, approximately 30 mi (50 km) northwest of San Francisco at approximately 38 degrees north latitude. The bay is approximately 8 mi (13 km) wide. It is formed on the lee side of the coastal current by Point Reyes. The bay is named after Sir Francis Drake and has long been considered Drake's most likely landing spot on the west coast of North America during his circumnavigation of the world by sea in 1579. An alternative name for this bay is Puerto De Los Reyes.

Point Reyes is a prominent cape and popular Northern California tourist destination on the Pacific coast. Located in Marin County, it is approximately 30 miles (50 km) west-northwest of San Francisco. The term is often applied to the Point Reyes Peninsula, the region bounded by Tomales Bay on the northeast and Bolinas Lagoon on the southeast. The headland is protected as part of Point Reyes National Seashore.

Tomales Bay is a long, narrow inlet of the Pacific Ocean in Marin County in northern California in the United States. It is approximately 15 mi (24 km) long and averages nearly 1.0 mi (1.6 km) wide, effectively separating the Point Reyes Peninsula from the mainland of Marin County. It is located approximately 30 mi (48 km) northwest of San Francisco. The bay forms the eastern boundary of Point Reyes National Seashore. Tomales Bay is recognized for protection by the California Bays and Estuaries Policy. On its northern end, it opens out onto Bodega Bay, which shelters it from the direct current of the Pacific. The bay is formed along a submerged portion of the San Andreas Fault.

Bodega Bay is a shallow, rocky inlet of the Pacific Ocean on the coast of northern California in the United States. It is approximately 5 mi (8 km) across and is located approximately 40 mi (60 km) northwest of San Francisco and 20 mi (32 km) west of Santa Rosa. The bay straddles the boundary between Sonoma County to the north and Marin County to the south. The bay is a marine habitat used for navigation, recreation, and commercial and sport fishing.

Bodega Harbor is a small, shallow, natural harbor on the Pacific coast of northern California in the United States, approximately 40 mi (64 km) northwest of San Francisco. The harbor is approximately 2 sq mi (5.2 km2) in area.

The Santa Lucia Mountains or Santa Lucia Range is a rugged mountain range in coastal central California, running from Carmel southeast for 140 miles (230 km) to the Cuyama River in San Luis Obispo County. The range is never more than 11 miles (18 km) from the coast. The range forms the steepest coastal slope in the contiguous United States. Cone Peak at 5,158 feet (1,572 m) tall and three miles (5 km) from the coast, is the highest peak in proximity to the ocean in the lower 48 United States. The range was a barrier to exploring the coast of central California for early Spanish explorers.

The Farallon Islands, or Farallones, are a group of islands and sea stacks in the Gulf of the Farallones, off the coast of San Francisco, California, United States. The islands are also sometimes referred to by mariners as the Devil's Teeth Islands, in reference to the many treacherous underwater shoals in their vicinity. The islands lie 30 miles (48 km) outside the Golden Gate and 20 miles (32 km) south of Point Reyes, and are visible from the mainland on clear days. The islands are part of the City and County of San Francisco. The only inhabited portion of the islands is on Southeast Farallon Island (SEFI), where researchers from Point Blue Conservation Science and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service stay. The islands are closed to the public.

Goat Rock Beach is a sand beach in northwestern Sonoma County, California, United States. This landform is a sub-unit of Sonoma Coast State Beach, owned and managed by the State of California. At the northern terminus of Goat Rock Beach is the mouth of the Russian River, and the southern end of this crescent shaped expanse is the massive Goat Rock, an iconic outcrop of the Sonoma Coast, which is barely attached to the mainland by a narrow isthmus.

Sonoma Coast State Park is a State of California property in Sonoma County consisting of public access use on lands adjoining the Pacific Ocean. This extent of beach runs from a coastal point about 4 miles (6 km) north of Jenner and continues for approximately 17 miles (27 km) to the south to terminate at Bodega Head. The property lies along State Route 1 and consists of a number of named beaches including Arched Rock Beach, Gleason Beach and Goat Rock Beach. The ecosystem consists of alternating sandy beaches and rocky shoreline, with a marine terrace extending above the entire extent with an upland California coastal prairie habitat.
Tomales High School is located in the town of Tomales, California, United States. It is the comprehensive high school of the Shoreline Unified School District. It serves the western Marin and Sonoma County communities, stretching from the towns of Point Reyes Station and Inverness along Tomales Bay, running north past the fishing port of Bodega Bay to the mouth of the Russian River, a distance of nearly 50 miles (80 km), and widening 13 miles (21 km) east from the west coast. Tomales High School draws its students from approximately 450 square miles (1,200 km2). Tomales High School was recognized as a California Distinguished School in 2011.

The Salinian Block or Salinian terrane is a geologic terrane which lies west of the main trace of the San Andreas Fault system in California. It is bounded on the south by the Big Pine Fault in Ventura County and on the west by the Nacimiento Fault. It was named for the Salinas Valley in Monterey County, California.

Duncans Point is a cape on the Pacific Coast of northern California in the United States. It is located in Sonoma County at 38.393°N 123.0947°W, approximately 45 miles (70 km) northwest of San Francisco and approximately 20 miles (30 km) west of Santa Rosa.

Doran Regional Park is a regional park south of Bodega Bay, California, U.S.A. that is maintained by the Sonoma County Regional Parks Department. It covers an area of 127 acres (51 ha). It is located at 38.314°N 123.0428°W on the sand spit separating Bodega Harbor from Bodega Bay. The park address is 201 Doran Beach Road, Bodega Bay, CA.

The Bodega Bay Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed Northern California nuclear power facility that was stopped by local activism in the 1960s and never built. The foundations, located 2 miles (3.2 km) west of the active San Andreas Fault, were being dug at the time the plant was cancelled. The action has been termed "the birth of the anti-nuclear movement."

Bodega Head State Marine Reserve (SMR) and Bodega Head State Marine Conservation Area (SMCA) are two adjoining marine protected areas off Bodega Bay in Sonoma County on California’s north-central coast. The combined area of these marine protected areas is 21.64 square miles (56.0 km2), with 9.3 square miles (24 km2) in the SMR, and 12.34square miles in the SMCA. Bodega Head SMR prohibits the take of all living marine resources. Bodega Head SMCA prohibits the take of all living marine resources, except the recreational and commercial take of pelagic finfish with troll fishing gear or seine, Dungeness crab by trap, and market squid by hand-held dip net and round haul net.
Estero de Limantour State Marine Reserve (SMR) and Drakes Estero State Marine Conservation Area (SMCA) are two adjoining marine protected areas along the Point Reyes National Seashore in Marin County on California’s north central coast. These marine protected areas cover a combined 4.04 square miles (10.5 km2), with 1.49 square miles (3.9 km2) in the SMR and 2.55 square miles (6.6 km2) in the SMCA. Drakes Estero SMCA prohibits the take of all living marine resources from Drakes Estero except the recreational take of clams and formerly the commercial aquaculture of shellfish pursuant to a disputed state water bottom lease and permit, which has been the subject of ongoing legal proceedings since 2012, when the lease was allowed to expire.

Point Reyes State Marine Reserve (SMR) and Point Reyes State Marine Conservation Area (SMCA) are two adjoining marine protected areas that extend offshore of Point Reyes Headlands and within Drakes Bay in Marin County on California’s north central coast. The combined area of these marine protected areas is 21.49 square miles, with 9.38 in the SMR, and 12.11 in the adjacent SMCA. Point Reyes SMR prohibits the take of all living marine resources. Point Reyes SMCA prohibits the take of all living marine resources, except the recreational and commercial take of Dungeness crab by pot and salmon by trolling.
From 1577 to 1580 Sir Francis Drake circumnavigated the world. In 1579 as part of this voyage he landed on the west coast of North America which consequently has drawn the attention of scores of historians, geographers, linguists, anthropologists and other professionals. In addition, many history buffs have sought to locate Drake's New Albion. The established site for Drake's 1579 landing at New Albion is at Drake's Cove in Drakes Bay in Marin County, California. More than a score of ideas for an alternative to Drake's New Albion claim have been put forth which cover the coast from Alaska to Baja California Sur, Mexico. These ideas span the eighteenth through the early twenty-first centuries.

















