This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(October 2024) |
A body orifice is any opening in the body of an animal.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(October 2024) |
A body orifice is any opening in the body of an animal.
In a typical mammalian body such as the human body, the external body orifices are:
Other animals may have some other body orifices:
Internal orifices include the orifices of the outflow tracts of the heart, between the heart valves.

In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it leaves the uterus.

A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species.
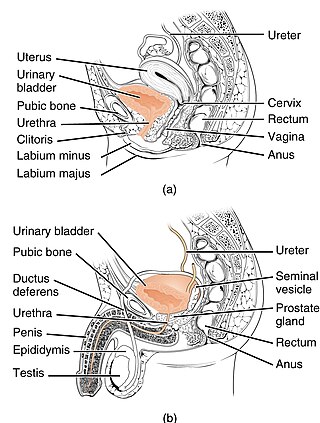
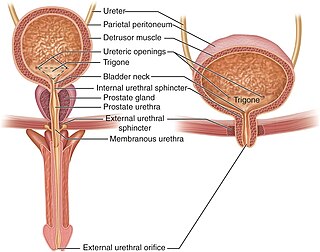
The urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which placental mammals urinate and ejaculate. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the urethra also transports semen but is separate from the urinary tract.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.

A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In anatomy, a meatus is a natural body opening or canal.
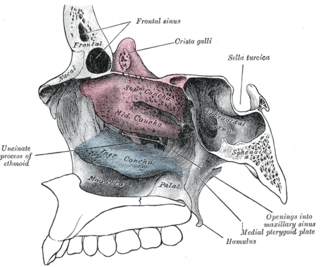
In anatomy, a nasal concha, also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various other animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name. A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal passages in vertebrates.
The urogenital opening is where bodily waste and reproductive fluids are expelled to the environment outside of the body cavity. In some organisms, including monotremes, birds and some fish, discharge from the urological, digestive, and reproductive systems empty into a common sac called the cloaca.
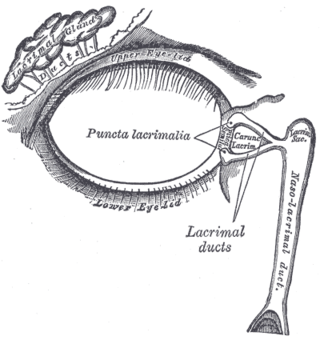
The nasolacrimal duct carries tears from the lacrimal sac of the eye into the nasal cavity. The duct begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The opening of the nasolacrimal duct into the inferior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity is partially covered by a mucosal fold.

The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.
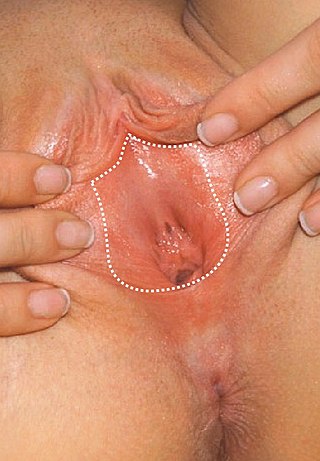
The vulval vestibule is the part of the vulva between the labia minora. At the innermost part are the vaginal introitus and urinary meatus. The Bartholin's and Skene's glands each have two openings to the vestibule on the inside. The outer edge, marked by a coloration difference in the tissues, is called Hart's line, named after David Berry Hart.

The pneumostome or breathing pore is a respiratory opening of the external body anatomy of an air-breathing land slug or land snail. It is a part of the respiratory system of gastropods.
In embryology, Carnegie stages are a standardized system of 23 stages used to provide a unified developmental chronology of the vertebrate embryo.

The spongy urethra is the longest part of the male urethra, and is contained in the corpus spongiosum of the penis.
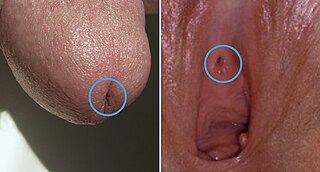
The urinary meatus, also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening in the penis or vulva where urine exits the urethra during urination. It is where semen exits the penis during ejaculation. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch.

A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the nose for respiration. Where the nostrils pass through the nasal cavity they widen, are known as nasal fossae, and contain turbinates and olfactory mucosa. The nasal cavity also connects to the paranasal sinuses. From the nasal cavity, the nostrils continue into the pharynx, a switch track valve connecting the respiratory and digestive systems.

Townsend's big-eared bat is a species of vesper bat.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.