
The six-banded armadillo, also known as the yellow armadillo, is an armadillo found in South America. The sole extant member of its genus, it was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The six-banded armadillo is typically between 40 and 50 centimeters in head-and-body length, and weighs 3.2 to 6.5 kilograms. The carapace is pale yellow to reddish brown, marked by scales of equal length, and scantily covered by buff to white bristle-like hairs. The forefeet have five distinct toes, each with moderately developed claws.
The large vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae.

The small vesper mouse is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. It is one of the hosts of hantavirus, causing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
The delicate vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia and Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 66 and FN = 66.
The Tocantins vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is found in Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 46 and FNa = 66.

Pseudoryzomys simplex, also known as the Brazilian false rice rat or false oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae from south-central South America. It is found in lowland palm savanna and thorn scrub habitats. It is a medium-sized species, weighing about 50 grams (1.8 oz), with gray–brown fur, long and narrow hindfeet, and a tail that is about as long as the head and body. The IUCN has assessed its conservation status as being of least concern, although almost nothing is known about its diet or reproduction.

Vesper mice are rodents belonging to a genus Calomys. They are widely distributed in South America. Some species are notable as the vectors of Argentinian hemorrhagic fever and Bolivian hemorrhagic fever.
Akodon boliviensis, also known as the Bolivian grass mouse or Bolivian akodont, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in the Andes from southeastern Peru through Bolivia into northwestern Argentina.
The crafty vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina and Paraguay.

Hummelinck's vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Aruba, Brazil, Colombia, the Netherlands Antilles, and Venezuela.
The Andean vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.
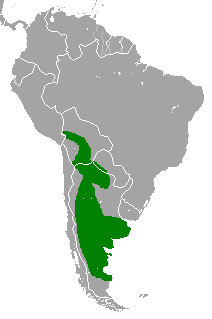
The drylands vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina and Paraguay.
The Peruvian vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only in Peru.
Nephelomys albigularis, also known as the white-throated oryzomys or Tomes's rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Nephelomys of family Cricetidae. Described in 1860, it was the first Nephelomys species to be discovered. It was originally described in the defunct genus Hesperomys as Hesperomys albigularis and considered related to the much smaller H. longicaudatus. By 1894, it was placed in Oryzomys, as Oryzomys albigularis, and associated with what is now Nephelomys meridensis. In the early 1960s, the scope of the species was considerably expanded to include most of the species that are now in Nephelomys, as well as a single name, boliviae, that is currently a synonym of Euryoryzomys nitidus. From 1976 on, several of these were reinstated as separate species.

Akodon caenosus is a rodent in the genus Akodon found in northwestern Argentina and south-central Bolivia. Since its description in 1918, it has been alternatively classified as a separate species or a subspecies of Akodon lutescens. The species Akodon aliquantulus, described from some very small Argentine specimens in 1999, is now recognized as a synonym of A. caenosus.
The caatinga vesper mouse is a rodent species in the family Cricetidae from South America. It is endemic to eastern Brazil, where it is found in open savanna (cerrado) and thorny scrub (caatinga) habitats. Its karyotype has 2n = 66 and FN = 68. It was formerly synonymized with C. callosus, but the latter has 2n = 50 and FN = 66. Karyologic analysis of C. expulsus has shown that the X chromosome is large and submetacentric while the Y chromosome is either acrocentric or submetacentric. Predators include the barn owl. Sexual dimorphism in shape and size occurs; the former is present mainly before the age of 20 days. Males are smaller before age 50 days and larger thereafter, which becomes less prominent after 200 days.
The Córdoba vesper mouse or Córdoba laucha is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is endemic to the area of Córdoba Province, central Argentina, where it is found in the espinal.
The fecund vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is known only from Bolivia, where it is found in the yungas and Tucumano boliviano forest ecoregions at elevations from 600 to 2700 m. It is regarded by some authorities as conspecific with C. boliviae, and by some as conspecific with C. venustus, despite having a karyotype with 2n = 54 while C. venustus generally has a karyotype with 2n = 56.





