
A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.

Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by Borrelia bacteria, which are spread by ticks in the genus Ixodes. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment, about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems, and tiredness for at least six months.

Borrelia burgdorferi is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus Borrelia, and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. B. burgdorferi sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. Borrelia species are Gram-negative.

The white-footed mouse is a rodent native to North America from Ontario, Quebec, Labrador, and the Maritime Provinces to the southwestern United States and Mexico. In the Maritimes, its only location is a disjunct population in southern Nova Scotia. It is also known as the woodmouse, particularly in Texas.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms.
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia, which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.
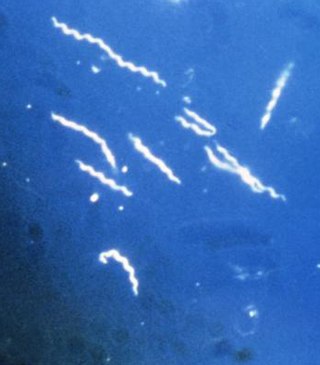
Borrelia is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of Borrelia cause relapsing fever, and are transmitted by ticks or lice, depending on the species of bacteria. A few Borrelia species as Candidatus Borrelia mahuryensis harbor intermediate genetic features between Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia. The genus is named after French biologist Amédée Borrel (1867–1936), who first documented the distinction between a species of Borrelia, B. anserina, and the other known type of spirochete at the time, Treponema pallidum. This bacterium must be viewed using dark-field microscopy, which make the cells appear white against a dark background. Borrelia species are grown in Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium. Of 52 known species of Borrelia, 20 are members of the Lyme disease group, 29 belong to the relapsing fever group, and two are members of a genetically distinct third group typically found in reptiles. A proposal has been made to split the Lyme disease group based on genetic diversity and move them to their own genus, Borelliella, but this change is not widely accepted. This bacterium uses hard and soft ticks and lice as vectors. Testing for the presence of the bacteria in a human includes two-tiered serological testing, including immunoassays and immunoblotting.

Lyme disease, or borreliosis, is caused by spirochetal bacteria from the genus Borrelia, which has 52 known species. Three main species are the main causative agents of the disease in humans, while a number of others have been implicated as possibly pathogenic. Borrelia species in the species complex known to cause Lyme disease are collectively called Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato (s.l.) not to be confused with the single species in that complex Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto which is responsible for nearly all cases of Lyme disease in North America.

Ixodes scapularis is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick, and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It was also named Ixodes dammini until it was shown to be the same species in 1993. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage.

Amblyomma americanum, also known as the lone star tick, the northeastern water tick, or the turkey tick, is a type of tick indigenous to much of the eastern United States and Mexico, that bites painlessly and commonly goes unnoticed, remaining attached to its host for as long as seven days until it is fully engorged with blood. It is a member of the phylum Arthropoda, class Arachnida. The adult lone star tick is sexually dimorphic, named for a silvery-white, star-shaped spot or "lone star" present near the center of the posterior portion of the adult female shield (scutum); adult males conversely have varied white streaks or spots around the margins of their shields.

Southern tick-associated rash illness (STARI) is an emerging infectious disease related to Lyme disease that occurs in southeastern and south-central United States. It is spread by tick bites and it was hypothesized that the illness was caused by the bacteria Borrelia lonestari. However, there is insufficient evidence to declare this Borrelia strain as a causative agent.
Ticks are insects known for attaching to and sucking blood from land-dwelling animals. Ticks fall under the category of 'arthropod', and while they are often thought of in the context of disease transmission, they are also known to cause direct harm to hosts through bites, toxin release, and infestation. Infestation can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe and may even cause death. Hosts can include any number of vertebrates, though humans and livestock are more likely to be the interest of researchers.
Borrelia afzelii is a species of Borrelia a bacterium that can infect various species of vertebrates and invertebrates.

Ixodes uriae, also known as the seabird tick, is a species of parasitic tick known to infest marine birds. It is native to many high latitude areas in the northern and southern hemispheres including Alaska, Canada, Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, England, Scotland, Norway, Finland, the Kola Peninsula, Russia, Patagonia, South Africa and Australia.

Ornithodoros moubata, commonly known as the African hut tampan or the eyeless tampan, is a species of tick in the family Argasidae. It is an ectoparasite and vector of relapsing fever in humans, and African swine fever in pigs.
Borrelia miyamotoi is a bacterium of the spirochete phylum in the genus Borrelia. A zoonotic organism, B. miyamotoi can infect humans through the bite of several species of hard-shell Ixodes ticks, the same kind of ticks that spread B. burgdorferi, the causative bacterium of Lyme disease. Ixodes ticks are also the primary vector in the spread of babesiosis and anaplasmosis.
Borrelia lusitaniae is a bacterium of the spirochete class of the genus Borrelia, which has a diderm (double-membrane) envelope. It is a part of the Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato genospecies and is a Gram-negative bacterium. B. lusitaniae is tick-borne; he type strain is PotiB2. It can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis. A species of tick, Ixodes ricinus, is the host of B. lusitaniae. It is thought to have originated from Portugal and has since spread to parts of Europe and North Africa. Lizards of the family Lacertidae are now believed to be important reservoir hosts of this bacterium.
Borrelia kurtenbachii is a spirochete bacterium; it can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis.
Borrelia andersonii is a spirochete bacterium. It can be pathogenic, being involved in cases of Lyme borreliosis.
Borrelia mayonii is a Gram-negative, host-associated spirochete that is capable of causing Lyme disease. This organism can infect various vertebrate hosts such as humans via the bite of a black legged tick.








