
The tusk shells or tooth shells, technically the Scaphopoda, are members of a class of shelled marine mollusc with worldwide distribution, and are the only class of exclusively infaunal marine molluscs. Shells of species within this class range from about 0.5 to 15 cm in length. Members of the order Dentaliida tend to be significantly larger than those of the order Gadilida.

The Centriscidae are a family of fishes from the order Syngnathiformes which includes the snipefishes, shrimpfishes, and bellowfishes. A small family, consisting of only about a dozen marine species, they are of an unusual appearance, as reflected by their common names. The species in this family are restricted to relatively shallow, tropical parts of the Indo-Pacific.
This glossary of ichthyology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in ichthyology, the study of fishes.
The armoured frog, or armoured mist frog, is a species of tree frog in the torrent frog complex, a group restricted to north-eastern Queensland, Australia.

The dwarf lanternshark is a little-known species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae and is the smallest shark in the world, reaching a maximum known length of 20 cm (7.9 in). It is known to be present only on the upper continental slopes off Colombia and Venezuela, at a depth of 283–439 m (928–1,440 ft). This species can be identified by its small size at maturity, long flattened head, and pattern of black ventral markings and a mid-dorsal line. Like other members of its genus, it is capable of producing light from a distinctive array of photophores. Reproduction is aplacental viviparous, with females gestating two or three young at a time. The dwarf lanternshark is not significant to commercial fisheries, but could be threatened by mortality from bycatch; the degree of impact from human activities on its population is unknown.

Ariadne ariadne, the angled castor, is a species of nymphalid butterfly found in Asia.

Acrochordonichthys is a genus of catfishes of the family Akysidae. It includes ten species.
Cherax parvus is a species of crayfish in the family Parastacidae. It is only known from its type locality – the Upper Tully River catchment in the Cardwell Range of north-eastern Queensland – and is listed as data deficient on the IUCN Red List. It was discovered in a rainforest catchment in a highland of northeastern Queensland during a Queensland Museum expedition to the upper Tully River area in November 1992. It is one of the smallest species in the genus. No species of Cherax has been considered endemic to wet upland or highland areas before it was discovered; most previous records were from elevations less than 400 meters. It also has several morphological features unique to the genus, and does not appear closely related to any extant species, suggesting a long period of geographic isolation.

The club-foot whiting, Sillaginopodys chondropus,, the only member of the genus Sillaginopodys, is a coastal marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that inhabits a wide range including west Africa, India and the northern Indonesian Archipelago. The species is unique in the morphology of the pelvic spine and fin, making identification of the species easier than most of its relatives. The species is of minor commercial importance, taken by seine net and marketed fresh throughout its range.

Mauritia arabica, common name the Arabian cowry, is a species of cowry, a sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries.
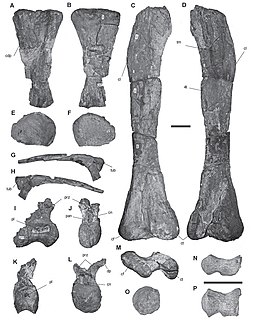
Atacamatitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period.
Valdiviathyris quenstedti is a small species of brachiopods with a maximum size of about 0.3 inches or 7.6 millimetres wide.
Salvatoria koorineclavata is a species belonging to the phylum Annelida, a group known as the segmented worms. A related species in Australia has been described as Brania clavata and subsequently as Salvatoria clavata. While similar, the Australian species has a longer pharynx and proventricle; at the same time, blades of chaetae are present in the Australian species, with longer and upwards curved spines, which are straight in S. clavata; its pharyngeal tooth is located more anteriorly than in S. clavata. Other global species, like those in the genus Brania, are also similar to S. koorineclavata. Salvatoria californiensis has similar chaetae, with shorter spines and less developed teeth. Its acicula lacks a defined acute tip, and the proventricle is quite shorter, running through 5 segments in S. koorineclavata, with fewer rows of muscle cells. The species name comes from an Aboriginal word, Koorine, meaning "daughter", due to the similarity of the Australian species to the European species of S. clavata.

Sphaerosyllis levantina is a species belonging to the phylum Annelida, a group known as the segmented worms. It was first described from Haifa Bay in the eastern Mediterranean. It is similar to Sphaerosyllis hystrix, and is thought to show a cosmopolitan distribution. Its name derives from its type locality, levantina being the feminine form of a neo-Latin adjective meaning "pertaining to the region where the sun raises"; the adjective is feminine to agree with the feminine genus name, Syllis being a river nymph in Greek mythology.
Sphaerosyllis voluntariorum is a species belonging to the phylum Annelida, a group known as the segmented worms. This species is closely related to Sphaerosyllis bifurcata, Sphaerosyllis bifurcatoides and Sphaerosyllis rotundipapillata, all endemic species to Australia, characterized by having large dorsal papillae, sometimes trilobed, and with shafts of compound chaetae distally bifid. S. voluntariorum is more densely papillated on its anterior segments and has a long subdistal spine on the ventral simple chaetae. This species' name alludes to the volunteers of the Marine Invertebrate section of The Australian Museum, who sorted specimens of syllids that led to the description of this animal.
Sphaerosyllis goorabantennata is a species belonging to the phylum Annelida, a group known as the segmented worms. Sphaerosyllis goorabantennata is distinct by its small size, small and unevenly distributed papillae, as well as by its particularly long antennae and tentacular cirri. Sphaerosyllis minima and S. minima magnapapillata are also small, but their antennae and tentacular cirri are significantly shorter, like its cogenerate species. The species' name is derived from the Aboriginal word gooraba, meaning "big", alluding to its long antennae.
Gymnotus choco, commonly known as the cuchillo, is an electric knifefish. G. choco is distinguished from its cogenerate species group by a color pattern possessing pale yellow bands oriented obliquely, wherein the interband margins are wavy or even irregular; one to three Y-shaped dark bands occur on its body's posterior section; and its pale bands do not extend above the fish's lateral line on its body's anterior two-thirds. G. choco is most similar to G. paraguensis from the Pantanal in Brazil and Paraguay. From the latter, it is distinguished by having a narrower mouth, a more cylindrical body, and a longer preanal distance.
Parapionosyllis winnunga is a species belonging to the phylum Annelida, a group known as the segmented worms. Parapionosyllis winnunga is characterized by the shape of the blades of its compound chaetae, which have a long subdistal spine, in turn much longer than in other cogenerate species. Its species name is derived from the Aboriginal word winnunga, meaning "small".
Celsinotum candango is a species of crustaceans. Its epithet comes from the name applied to people that built the city of Brasilia and was subsequently used for its inhabitants. The species was found in Lagoa do Henrique, a freshwater pond in the Brasília National Park. Its body is high and rounded, with a low dorsal keel. Its last 5–8 ventral setae ventral setae thick and spiniform, carrying 1–3 setules on their posterior margin. Its head shield and head pores are the same as its cogenerate species, as is its labrum, antenna and antennule and thoracic limbs. Celsinotum candango other species of the genus in the proportions of its postabdomen, given the postanal portion is 1.2–1.3 times longer than the anal one in all other species. It differs from Australian species by its less developed keel, the lateral head pores which are located close to midline, a longer spine on the basal segment of the antenna exopodite, and by the presence of very big projections on the latter. The Brazilian C. Laticaudatum differs from C. candango by having a longer spine on the basal segment of the antenna exopodite, in the shape of its postabdomen, and in postabdominal denticles, which in this species are long and single.

Yungia aurantiaca is a species of flatworm in the family Pseudocerotidae. It is found in the temperate northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.









