
Pandorea jasminoides, also known by the common names bower of beauty and bower vine, is a species of flowering plant in the family Bignoniaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a woody climber with pinnate leaves that have three to nine egg-shaped leaflets, and white or pink trumpet-shaped flowers that are red and hairy inside. It is also grown as an ornamental.

Vincetoxicum rossicum is a flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is a perennial herb native to southern Europe and is a highly invasive plant growing in all of the Eastern United States, in the mid west, and southern Ontario and Quebec in Canada. It has several common names including swallowwort, pale swallowwort, and dog-strangling vine; though it does not actually strangle dogs, it can “strangle” native plants and small trees if it is in dense patches. There has historically been much confusion about the genus it belongs to, with authors placing it within Vincetoxicum and others within Cynanchum, but recent molecular and chemical analyses have shown it to belong in the genus Vincetoxicum.

Utricularia dichotoma, commonly known as fairy aprons, is a variable, perennial species of terrestrial bladderwort. It is a widespread species with mauve or purple fan-shaped flowers on a slender stalk and usually grows in wet locations.

Ipomoea leptophylla, the bush morning glory, bush moonflower or manroot, is a flowering plant species in the bindweed family, Convolvulaceae.

Orthoceras strictum, commonly known as the bird's-mouth orchid or horned orchid, is a species of orchid native to eastern and southern Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia. It has between two and five linear leaves and up to nine yellowish green, brownish or blackish flowers with two long, erect to spreading lateral sepals.

Griselinia lucida, commonly known as puka, akapuka or shining broadleaf, is an epiphytic plant native to New Zealand. G. lucida naturally occurs in wet lowland-forests and open or rocky coastal environments mostly in the North Island of New Zealand, and restricted areas of the South Island.

Pterostylis crassicaulis, commonly known as the alpine swan greenhood, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It has a rosette of leaves and up to 18 bluish-green and white flowers with dark green stripes. The flowers have a labellum with a dark green, beak-like appendage. It is similar to P. cycnocephala but is more robust and grows at higher altitudes.

Pterostylis aneba is a species of orchid endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is a recently described and poorly-known greenhood similar to Pterostylis alpina and P. monticola. It has a rosette of fleshy leaves at the base of the plant and a single green and white flower. It grows in alpine and sub-alpine habitats.
Pterostylis bicornis, commonly known as the horned greenhood, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. Non-flowering plants have a rosette of leaves while flowering plants have a similar rosette at the base of a flowering spike with a one or two dark green, white and brown flowers. The flowers have distinctive long, thin horn-like tips.

Pterostylis major is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to New South Wales where it grows on the Northern Tablelands. As with similar greenhoods, the flowering plants differ from those which are not flowering. The non-flowering plants have a rosette of leaves on a short stalk but the flowering plants lack a rosette and have up to eleven well-spaced, bright green flowers with darker stripes, on a flowering stem with stem leaves.
Arthrochilus corinnae, commonly known as the swamp elbow orchid, is a flowering plant in the orchid family (Orchidaceae) and is endemic to the northern part of Cape York in Queensland. It has two or three dull bluish green leaves near its base and up to twelve pale green, insect-like flowers with shiny yellowish glands on its labellum.
Arthrochilus dockrillii, commonly known as the green truffle orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family (Orchidaceae) and is endemic to Tropical North Queensland. It has one or two dark green leaves at its base and up to twenty five greenish, insect-like flowers with red glands on its labellum. This species is known by some authorities as Phoringopsis dockrillii. There is a single record of this species from Papua New Guinea.

Arthrochilus irritabilis, commonly known as clubbed elbow orchid, is a flowering plant in the orchid family (Orchidaceae) and is endemic to Queensland. It has up to five leaves and up to thirty light greenish or reddish, insect-like flower with reddish, hair-like glands on its labellum. There is a single record of this species from Papua New Guinea.
Arthrochilus rosulatus, commonly known as rosetted elbow orchid, is a flowering plant in the orchid family (Orchidaceae) and is endemic to Tropical North Queensland. It has a rosette of bluish green leaves surrounding its base and up to fifteen pale green, insect-like flowers with dark red glands on its labellum.

Hypericum punctatum, the spotted St. John's wort, is a perennial herb native to North America. The yellow-flowered herb occurs throughout eastern North America into southern Canada. The process of microsporogenesis carried out by this plant is prone to errors in chromosomal segregation. It has a diploid number of 14 or 16. Insects are attracted to the plant's pollen and the hypericin in the plant's leaves is toxic to mammals.
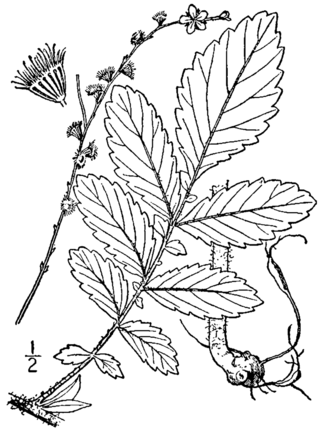
Agrimonia pubescens, the soft agrimony or downy agrimony, is a flowering plant in the genus Agrimonia, a member of the rose family. It grows in dry areas and woodlands.

Bossiaea stephensonii is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to near-coastal areas of New South Wales. It is a small, weakly erect, multi-stemmed shrub with sharply-pointed, mostly elliptic to egg-shaped leaves, and bright yellow and red flowers.
Pomaderris oblongifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Rhamnaceae and is endemic to eastern Victoria. It is a slender shrub with densely hairy young stems, oblong to narrowly egg-shaped leaves and panicles of hairy, greenish to deep maroon flowers.

Chlorocyathus lobulata is a species of plant in the Apocynaceae family. It is native to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. Hendrik J. T. Venter and Rudolf L. Verhoeven, the botanists who first formally described the species named it, using the synonym Raphionacme lobulata, after the distinctive lobes of the corona of its flowers.

Impatiens scapiflora is a species of flowering plant in the family Balsaminaceae. Impatiens scapiflora or Leafless-Stem Balsam is a terrestrial or epiphytic or lithophytic herb endemic to Western Ghats.














