
Meta-analysis is the statistical combination of the results of multiple studies addressing a similar research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, this statistical approach involves extracting effect sizes and variance measures from various studies. Meta-analyses are integral in supporting research grant proposals, shaping treatment guidelines, and influencing health policies. They are also pivotal in summarizing existing research to guide future studies, thereby cementing their role as a fundamental methodology in metascience.

Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution, patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.

Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical, and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behavior occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.
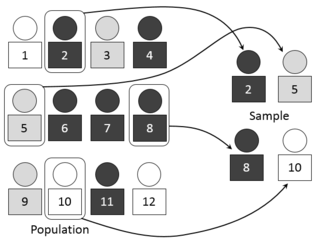
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population and statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection compared to recording data from the entire population, and thus, it can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population.
Survey methodology is "the study of survey methods". As a field of applied statistics concentrating on human-research surveys, survey methodology studies the sampling of individual units from a population and associated techniques of survey data collection, such as questionnaire construction and methods for improving the number and accuracy of responses to surveys. Survey methodology targets instruments or procedures that ask one or more questions that may or may not be answered.

The Lancet, one of the oldest scientific medical journals in the world, published two peer-reviewed studies on the effect of the 2003 invasion of Iraq and subsequent occupation on the Iraqi mortality rate. The first was published in 2004; the second in 2006. The studies estimate the number of excess deaths caused by the occupation, both direct and indirect.
The American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) is a professional organization of more than 2,000 public opinion and survey research professionals in the United States and from around the world, with members from academia, media, government, the non-profit sector and private industry. AAPOR publishes three academic journals: Public Opinion Quarterly, Survey Practice and the Journal of Survey Statistics and Methodology. It holds an annual research conference and maintains a "Code of Professional Ethics and Practices", for survey research which all members agree to follow. The association's founders include pioneering pollsters Archibald Crossley, George Gallup, and Elmo Roper.
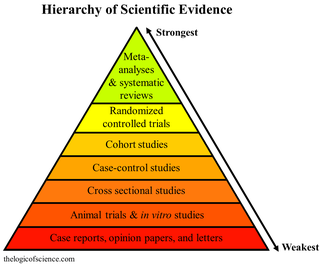
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic, then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.

In survey research, response rate, also known as completion rate or return rate, is the number of people who answered the survey divided by the number of people in the sample. It is usually expressed in the form of a percentage. The term is also used in direct marketing to refer to the number of people who responded to an offer.
In statistics, (between-) study heterogeneity is a phenomenon that commonly occurs when attempting to undertake a meta-analysis. In a simplistic scenario, studies whose results are to be combined in the meta-analysis would all be undertaken in the same way and to the same experimental protocols. Differences between outcomes would only be due to measurement error. Study heterogeneity denotes the variability in outcomes that goes beyond what would be expected due to measurement error alone.

In research of human subjects, a survey is a list of questions aimed for extracting specific data from a particular group of people. Surveys may be conducted by phone, mail, via the internet, and also in person in public spaces. Surveys are used to gather or gain knowledge in fields such as social research and demography.
Priscilla K. Coleman is a retired Professor of Human Development and Family Studies in the School of Family and Consumer Sciences at Bowling Green State University, Ohio. She is the author of a number of disputed academic papers, which claim to have found a statistical correlation or causal relationship between abortion and mental health problems.
A cluster-randomised controlled trial is a type of randomised controlled trial in which groups of subjects are randomised. Cluster randomised controlled trials are also known as cluster-randomised trials, group-randomised trials, and place-randomized trials. Cluster-randomised controlled trials are used when there is a strong reason for randomising treatment and control groups over randomising participants.
In statistics, the Sobel test is a method of testing the significance of a mediation effect. The test is based on the work of Michael E. Sobel, and is an application of the delta method. In mediation, the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable is hypothesized to be an indirect effect that exists due to the influence of a third variable. As a result when the mediator is included in a regression analysis model with the independent variable, the effect of the independent variable is reduced and the effect of the mediator remains significant. The Sobel test is basically a specialized t test that provides a method to determine whether the reduction in the effect of the independent variable, after including the mediator in the model, is a significant reduction and therefore whether the mediation effect is statistically significant.
The interviewer effect is the distortion of response to an interviewer-administered data collection effort which results from differential reactions to the social style and personality of interviewers or to their presentation of particular questions. The use of fixed-wording questions is one method of reducing interviewer bias. Anthropological research and case-studies are also affected by the problem, which is exacerbated by the self-fulfilling prophecy, when the researcher is also the interviewer it is also any effect on data gathered from interviewing people that is caused by the behavior or characteristics of the interviewer.

The replication crisis is an ongoing methodological crisis in which the results of many scientific studies are difficult or impossible to reproduce. Because the reproducibility of empirical results is an essential part of the scientific method, such failures undermine the credibility of theories building on them and potentially call into question substantial parts of scientific knowledge.
Patricia A. Berglund is a researcher at the University of Michigan's Institute for Social Research. She was included in the 2014, 2015 and 2016 Clarivate Analytics lists of "highly cited researchers" in the fields of psychiatry and psychology.

Equivalence tests are a variety of hypothesis tests used to draw statistical inferences from observed data. In these tests, the null hypothesis is defined as an effect large enough to be deemed interesting, specified by an equivalence bound. The alternative hypothesis is any effect that is less extreme than said equivalence bound. The observed data are statistically compared against the equivalence bounds. If the statistical test indicates the observed data is surprising, assuming that true effects are at least as extreme as the equivalence bounds, a Neyman-Pearson approach to statistical inferences can be used to reject effect sizes larger than the equivalence bounds with a pre-specified Type 1 error rate.
Floyd J (Jack) Fowler Jr. is an American researcher, academic and author. He is a Senior Research Fellow at Center for Survey Research at the University of Massachusetts Boston. He is an early contributor to research on patient-reported outcomes after treatment for various conditions including benign prostate disease, benign uterine conditions and prostate cancer. He also led survey projects to understand the causes and consequences of variation in the way medical care is delivered.

Joseph Waksberg was an American statistician. While at the United States Census Bureau and Westat, he developed methods for area sampling and telephone sampling and made contributions in many areas of surveys and censuses.










