
A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener.

Gliotoxin is a sulfur-containing mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by several species of fungi, especially those of marine origin. It is the most prominent member of the epipolythiopiperazines, a large class of natural products featuring a diketopiperazine with di- or polysulfide linkage. These highly bioactive compounds have been the subject of numerous studies aimed at new therapeutics. Gliotoxin was originally isolated from Gliocladium fimbriatum, and was named accordingly. It is an epipolythiodioxopiperazine metabolite that is one of the most abundantly produced metabolites in human invasive Aspergillosis (IA).

Spirotryprostatin B is an indolic alkaloid found in the Aspergillus fumigatus fungus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. Spirotryprostatin B and several other indolic alkaloids have been found to have anti-mitotic properties, and as such they have become of great interest as anti-cancer drugs. Because of this, the total syntheses of these compounds is a major pursuit of organic chemists, and a number of different syntheses have been published in the chemical literature.

Spirotryprostatin A is an indolic alkaloid from the 2,5-Diketopiperazine class of natural products found in the Aspergillus fumigatus fungus. Spirotryprostatin A and several other indolic alkaloids have been found to have anti-mitotic properties, and as such they have become of great interest as anti-cancer drugs. Because of this, the total syntheses of these compounds is a major pursuit of organic chemists, and a number of different syntheses have been published in the chemical literature.

Aplaviroc is a CCR5 entry inhibitor that belongs to a class of 2,5-diketopiperazines developed for the treatment of HIV infection. It was developed by GlaxoSmithKline.
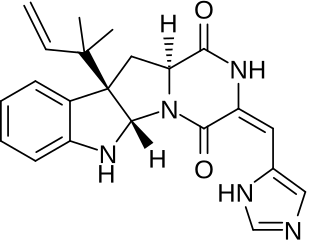
Roquefortine C is a mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by various fungi, particularly species from the genus Penicillium. It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used as a source of proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes during maturation of the blue-veined cheeses, Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton and Gorgonzola.

Brevianamides are indole alkaloids that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced as secondary metabolites of fungi in the genus Penicillium and Aspergillus. Structurally similar to paraherquamides, they are a small class compounds that contain a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazoctane ring system. One of the major secondary metabolites in Penicillium spores, they are responsible for inflammatory response in lung cells.

BQ-123, also known as cyclo(-D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu-), is a cyclic pentapeptide that was first isolated from a fermentation broth of Streptomyces misakiensis in 1991. NMR studies indicate that the polypeptide backbone consists of a type II beta turn and an inverse gamma turn. The side-chains adopt different orientations depending on the solvent used. The proline carbonyl oxygen atom located at the onset of a beta turn is a sodium ion binding site. It has a high affinity for sodium ions and can coordinate up to three of them. Studies have shown that BQ123 is effective in reversing Ischemia-induced acute renal failure, and it has been suggested that this might be because BQ123 increases reabsorption of sodium ions in the proximal tubule cells.
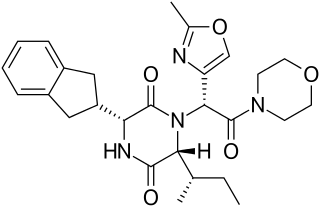
Retosiban also known as GSK-221,149-A is an oral drug which acts as an oxytocin receptor antagonist. It is being developed by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of preterm labour. Retosiban has high affinity for the oxytocin receptor and has greater than 1400-fold selectivity over the related vasopressin receptors
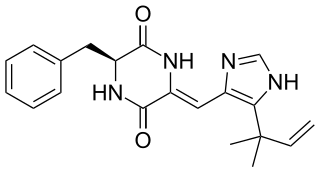
Phenylahistin is a metabolite produced by the fungus Aspergillus ustus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines featuring a dehydrohistidine residue that exhibit important biological activities, such as anti-cancer or neurotoxic effects.
2,5-Diketopiperazine is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2C(O))2. The compound features a six-membered ring containing two amide groups at opposite positions in the ring. It was first compound containing a peptide bond to be characterized by X-ray crystallography in 1938. It is the parent of a large class of 2,5-Diketopiperazines (2,5-DKPs) with the formula (NHCH2(R)C(O))2 (R = H, CH3, etc.). They are ubiquitous peptide in nature. They are often found in fermentation broths and yeast cultures as well as embedded in larger more complex architectures in a variety of natural products as well as several drugs. In addition, they are often produced as degradation products of polypeptides, especially in processed foods and beverages. They have also been identified in the contents of comets.

A diketopiperazine (DKP), also known as a dioxopiperazine or piperazinedione, is a class of organic compounds related to piperazine but containing two amide linkages. DKP's are the smallest known class of cyclic peptide. Despite their name, they are not ketones, but amides. Three regioisomers are possible, differing in the locations of the carbonyl groups.

(−)-Aurantiamine is a blue fluorescence metabolite produced by the fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum, the most common fungi found in cereals. (−)-Aurantiamine belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines featuring a dehydrohistidine residue that exhibit important biological activities, such as anti-cancer or neurotoxic effects. It is the isopropyl analog of the microtubule binding agent (−)-phenylahistin but is 40 times less active than the latter on P388 cell proliferation. The total asymmetric synthesis of (−)-aurantiamine has been described.

Fumitremorgins are tremorogenic metabolites of Aspergillus and Penicillium, that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines.
Fellutanine A, B, C and D are bio-active diketopiperazine alkaloids isolated from the cultures of Penicillium fellutanum, that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. Originally they were thought to be based on the "trans" cyclic dipetide cyclo(L-Trp-D-Trp) but were later shown to be based on the "cis" cyclic dipetide cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp). This was also confirmed when fellutanine A, B and C were isolated from Penicillium simplicissimum. The fellutanines A−C, are non-annulated analogues of cyclo(L-Trp-L-Trp), but unlike their diannulated analogue fellutanine D are not cytotoxic.

Verruculogen is a mycotoxin produced by certain strains of aspergillus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. It is an annulated analogue of cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) which belongs to the most abundant and structurally diverse class of tryptophan-proline 2,5-diketopiperazine natural products. It produces tremors in mice due to its neurotoxic properties. It also tested positive in a Salmonella/mammalian microsome assay and was shown to be genotoxic. It is a potent blocker of calcium-activated potassium channels.
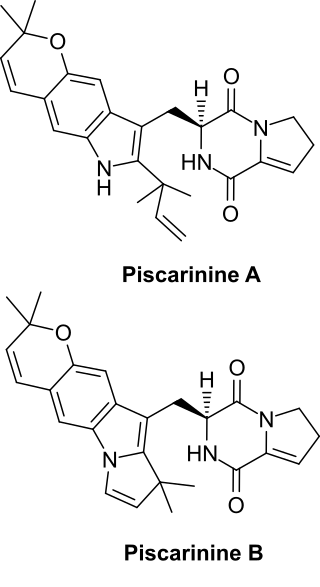
Piscarinines are bioactive alkaloid isolates of Penicillium piscarium NKM F-961 and Penicillium piscarium Westling that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. The cytotoxic dehydroproline tryptophan derivatives piscarinines A and B were shown to be active against the prostate cancer cell line LNCAP.

Stephacidin A and B are antitumor alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus ochraceus that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. This unusual family of fungal metabolites are complex bridged 2,5-diketopiperazine alkaloids that possess a unique bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane core ring system and are constituted mainly from tryptophan, proline, and substituted proline derivatives where the olefinic unit of the isoprene moiety has been formally oxidatively cyclized across the α-carbon atoms of a 2,5-diketopiperazine ring. The molecular architecture of stephacidin B, formally a dimer of avrainvillamide, reveals a complex dimeric prenylated N-hydroxyindole alkaloid that contains 15 rings and 9 stereogenic centers and is one of the most complex indole alkaloids isolated from fungi. Stephacidin B rapidly converts into the electrophilic monomer avrainvillamide in cell culture, and there is evidence that the monomer avrainvillamide interacts with intracellular thiol-containing proteins, most likely by covalent modification.

(-)-Versicolamide B and (+)-Versicolamide B are spiroindole alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. The versicolamides are structurally complex spiro-cyclized versions of prenylated cyclo(L-Trp-L-Pro) derivatives which possess a unique spiro-fusion to a pyrrolidine at the 3-position of the oxindole core together with the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system. While (-)-versicolamide B was isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus sp. the enantiomer (+)-versicolamide B was isolated from the terrestrial fungi Aspergillus versicolor NRRL. The total asymmetric syntheses of both enantiomers have been achieved and the implications of their biosynthesis have been investigated.
Fungal isolates have been researched for decades. Because fungi often exist in thin mycelial monolayers, with no protective shell, immune system, and limited mobility, they have developed the ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. Researchers have discovered fungal isolates with anticancer, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and other bio-active properties. The first statins, β-Lactam antibiotics, as well as a few important antifungals, were discovered in fungi.
















