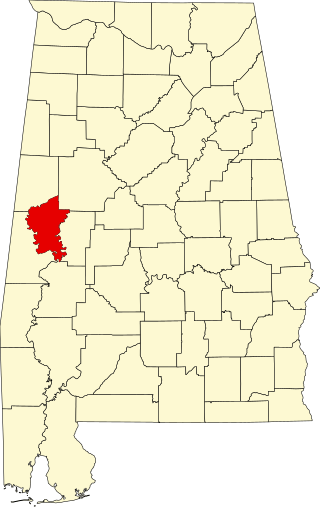
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Greene County, Alabama.
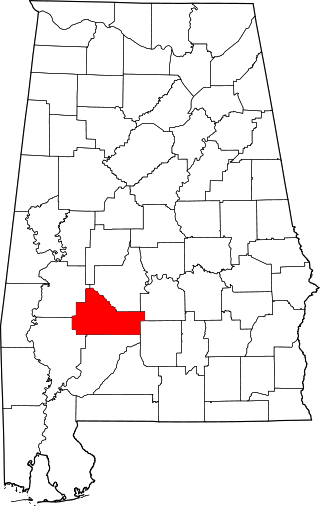
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Wilcox County, Alabama.
Beech Island is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Aiken County, South Carolina, United States. It was first listed as a CDP in the 2020 census with a population of 1,421.

Glenville is an unincorporated community in Russell County, Alabama, United States which used to be in Barbour County. During the Civil War, Company "H" of the 15th Regiment Alabama Infantry was raised from Barbour and Dale counties and called the "Glenville Guards". The Glennville Historic District, containing the antebellum core of the community, is a historic district listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.
Holy Trinity is an unincorporated community in Russell County, Alabama, United States. It is about 20 miles south of Columbus, Georgia, on State Route 165 and is the location of Apalachicola Fort Site, a National Historic Landmark.

Brown Chapel A.M.E. Church is a church at 410 Martin Luther King Jr. Boulevard in Selma, Alabama, United States. This church was a starting point for the Selma to Montgomery marches in 1965 and, as the meeting place and offices of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) during the Selma Movement, played a major role in the events that led to the adoption of the Voting Rights Act of 1965. The nation's reaction to Selma's "Bloody Sunday" march is widely credited with making the passage of the Voting Rights Act politically viable in the United States Congress.
Prairieville is an unincorporated community in Hale County, Alabama, United States.

Gainestown is an unincorporated community on the Alabama River in Clarke County, Alabama, United States. It was named for George Strother Gaines, who was the senior United States Indian agent in the region; he established a trading post here in 1809 for business with the Choctaw, the predominant tribe.

Verbena, also known as Summerfield, is an unincorporated community in southeastern Chilton County, Alabama, United States. Named for the indigenous flower, Verbena developed into a popular resort location for the more affluent citizenry of Montgomery, the state's capital, during the yellow fever outbreaks of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Many stately homes, some of which have undergone recent renovation and restoration, line the streets of the town as a reminder of this historic past.
Coy is an unincorporated community in Wilcox County, Alabama, United States. Coy is located in a bend of the Alabama River and is home to several historic plantations. The most notable of these is Dry Fork Plantation, included on the National Register of Historic Places.

Pleasant Hill is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama.
Summerfield, also known as Valley Creek, is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama. Summerfield has one historic district included on the National Register of Historic Places, the Summerfield District. Most of the community was annexed into Valley Grande following its incorporation as a city in 2003. Summerfield was the home of the Centenary Institute, a school operated by the Methodist Episcopal Church, South, from 1829 until the 1880s.
Minter is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama, United States. Minter has one site included on the National Register of Historic Places, the Street Manual Training School.
Sardis, also known as Berlin, is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama, United States.
Richmond, also known as Warrenton, is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama, United States. Richmond gained its name from Richmond County, New York, the birthplace for several early settlers, most notably the Crocherons. Richmond has one site included on the National Register of Historic Places, the Street Manual Training School. Elm Bluff Plantation, owned by John Jay Crocheron, is nearby in Elm Bluff.

Carlowville is an unincorporated community in Dallas County, Alabama. A portion of Carlowville was designated as the Carlowville Historic District on the National Register of Historic Places on January 18, 1978, the Carlowville Historic District.
Wheeler is an unincorporated community in Lawrence County, Alabama, United States. Wheeler had a post office at one time, but it no longer exists. Wheeler has two sites on the National Register of Historic Places, the Tidewater-type cottage known as Bride's Hill and the former home of Joseph Wheeler, Pond Spring.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Mobile, Alabama.

George Bigelow Rogers (1870–1945) was an American architect, best known for the wide variety of buildings that he designed in Mobile, Alabama, including mansions in historic European styles and other private residences, churches and public buildings, and the first 11-story skyscraper in Mobile and the Southeast United States. Many of his structures have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
St. Clair Springs is an unincorporated community and historic district in St. Clair County, Alabama, United States.












