Related Research Articles

The order Lamiales are an order in the asterid group of dicotyledonous flowering plants. It includes about 23,810 species, 1,059 genera, and is divided into about 25 families. These families include Acanthaceae, Bignoniaceae, Byblidaceae, Calceolariaceae, Carlemanniaceae, Gesneriaceae, Lamiaceae, Lentibulariaceae, Linderniaceae, Martyniaceae, Mazaceae, Oleaceae, Orobanchaceae, Paulowniaceae, Pedaliaceae, Peltantheraceae, Phrymaceae, Plantaginaceae, Plocospermataceae, Schlegeliaceae, Scrophulariaceae, Stilbaceae, Tetrachondraceae, Thomandersiaceae, Verbenaceae.
Brucellosis is a zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.
Chlamydia pecorum, also known as Chlamydophila pecorum is a species of Chlamydiaceae that originated from ruminants, such as cattle, sheep and goats. It has also infected koalas and swine. C. pecorum strains are serologically and pathogenically diverse.
In, molecular genetics, an ORFeome refers to the complete set of open reading frames (ORFs) in a genome. The term may also be used to describe a set of cloned ORFs. ORFs correspond to the protein coding sequences (CDS) of genes. ORFs can be found in genome sequences by computer programs such as GENSCAN and then amplified by PCR. While this is relatively trivial in bacteria the problem is non-trivial in eukaryotic genomes because of the presence of introns and exons as well as splice variants.

Whippomorpha or Cetancodonta is a group of artiodactyls that contains all living cetaceans and hippopotamuses. All Whippomorphs are descendants of the last common ancestor of Hippopotamus amphibius and Tursiops truncatus. This makes it a crown group. Whippomorpha is a suborder within the order Artiodactyla. The placement of Whippomorpha within Artiodactyla is a matter of some contention, as hippopotamuses were previously considered to be more closely related to Suidae (pigs) and Tayassuidae (peccaries). Most contemporary scientific phylogenetic and morphological research studies link hippopotamuses with cetaceans, and genetic evidence has overwhelmingly supported an evolutionary relationship between Hippopotamidae and Cetacea. Modern Whippomorphs all share a number of behavioural and physiological traits; such as a dense layer of subcutaneous fat and largely hairless bodies. They exhibit amphibious and aquatic behaviors and possess similar auditory structures.

Flavobacterium columnare is a thin Gram-negative rod bacterium of the genus Flavobacterium. The name derives from the way in which the organism grows in rhizoid columnar formations.

The inquisitive shrew mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is only known from Yunnan province of China, although its range is thought to extend over the border into Myanmar.

Hybridization and polyploidy are common phenomena in ferns, and the genus Dryopteris is known to be one of the most freely-hybridizing fern genera. North American botanists recognized early that there were close relationships between many of the species of Dryopteris on the continent, and that these relationships reflected hybrid ancestry. The complex includes six sexual diploid parents, six sexual allopolyploids, and numerous sterile hybrids at various ploidal levels.
Lawsonia intracellularis is a species of bacterium. It is obligately intracellular and was isolated from intestines of pigs with proliferative enteropathy disease.
Cronobacter turicensis is a bacterium. It is usually food-borne and pathogenic. It is named after Turicum, the Latin name of Zurich, as the type strain originates from there. Its type strain is strain 3032. This strain was first isolated from a fatal case of neonatal meningitis. C. Turicensis strains are indole negative but malonate, dulcitol and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside positive.
Cronobacter dublinensis is a bacterium. Its name pertains to Dublin, the origin of the type strain. The type strain is originally from a milk powder manufacturing facility. C. dublinensis sp. nov. is dulcitol negative and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside positive and generally positive for indole production.
Cronobacter muytjensii is a bacterium. It is named after Harry Muytjens. Its type strain is ATCC 51329T. It is indole, dulcitol, and malonate positive but palatinose and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside negative.
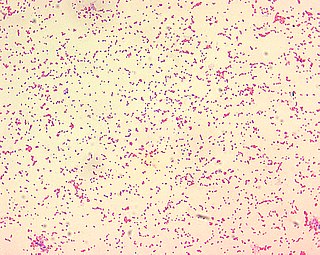
Brucella ceti is a gram negative bacterial pathogen of the Brucellaceae family that causes brucellosis in cetaceans. Brucella ceti has been found in both classes of cetaceans, mysticetes and odontocetes. Brucellosis in some dolphins and porpoises can result in serious clinical signs including fetal abortions, male infertility, neurobrucellosis, cardiopathies, bone and skin lesions, stranding events, and death.
Cronobacter malonaticus, formerly considered a subspecies of Cronobacter sakazakii, is a bacterium. Its type strain is CDC 1058-77T.
Brucella microti is a species of bacteria first isolated from the common vole, Microtus arvalis. Its genome has been sequenced. It is Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming, and coccoid, with the type strain CCM 4915T. It is pathogenic.
Brucella inopinata is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, non-spore-forming coccoid bacterium, first isolated from a breast implant infection site. Its type strain is BO1T. It is a potential cause of brucellosis.
Sarcocystis calchasi is an apicomplexan parasite. It has been identified to be the cause of Pigeon protozoal encephalitis (PPE) in the intermediate hosts, domestic pigeons. PPE is a central-nervous disease of domestic pigeons. Initially there have been reports of this parasite in Germany, with an outbreak in 2008 and in 2011 in the United States. Sarcocystis calchasi is transmitted by the definitive host Accipter hawks.

Cooperia oncophora is one of the most common intestinal parasitic nematodes in cattle in temperate regions. Infections with C. oncophora may result in mild clinical symptoms, but can lead to weight loss and damage of the small intestine, especially when co-infections with other nematodes such as O. ostertagi occur. Infections are usually treated with broad-spectrum anthelmintics such as benzimidazole, but resistance to these drugs has developed in the last decades and is now very common. C. oncophora has a direct life cycle. Infective larvae are ingested by the host. The larvae grow to adults, which reproduce in the small intestines. Eggs are shed onto the pasture with the faeces, which leads to new infections. Co-infections with other gastro-intestinal nematodes such as O. ostertagi and H. contortus are common.

Cooperia is a genus of nematode from the Cooperiidae family that is one of the most common intestinal parasitic nematodes in cattle in temperate regions. Infections with Cooperia may result in mild clinical symptoms, but can lead to weight loss and damage of the small intestine, especially when co-infections with other nematodes such as Ostertagia ostertagi occur. Infections are usually treated with broad-spectrum anthelmintics such as benzimidazole, but resistance to these drugs has developed in the last decades and is now very common. Cooperia has a direct life cycle. Infective larvae are ingested by the host. The larvae grow to adults, which reproduce in the small intestines. Eggs are shed onto the pasture with the faeces, which leads to new infections. Co-infections with other gastro-intestinal nematodes such as O. ostertagi and Haemonchus contortus are common.
Dioicy is a sexual system where archegonia and antheridia are produced on separate gametophytes. It is one of the two main sexual systems in bryophytes, the other being monoicy. Both dioicous and monoicous gametophytes produce gametes in gametangia by mitosis rather than meiosis, so that sperm and eggs are genetically identical with their parent gametophyte.
References
- ↑ NCBI Taxonomy Browser: Brucella pinnipedialis.
- ↑ Foster, G.; Osterman, B. S.; Godfroid, J.; Jacques, I.; Cloeckaert, A. (2007). "Brucella ceti sp. nov. and Brucella pinnipedialis sp. nov. for Brucella strains with cetaceans and seals as their preferred hosts". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 57 (11): 2688–2693. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65269-0 . ISSN 1466-5026. PMID 17978241.
- ↑ Nymo, Ingebjørg H; Tryland, Morten; Godfroid, Jacques (2011). "A review of Brucella infection in marine mammals, with special emphasis on Brucella pinnipedialis in the hooded seal (Cystophora cristata)". Veterinary Research. 42 (1): 93. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-93 . ISSN 1297-9716. PMC 3161862 . PMID 21819589.