
The Erie Canal is a canal in New York, United States that is part of the east–west, cross-state route of the New York State Canal System. Originally, it ran 363 miles (584 km) from where Albany meets the Hudson River to where Buffalo meets Lake Erie. It was built to create a navigable water route from New York City and the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes. When completed in 1825, it was the second longest canal in the world and greatly affected the development and economy of New York, New York City, and the United States.
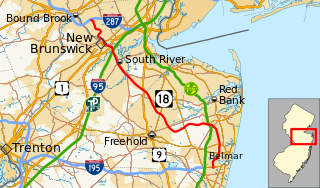
Route 18 is a 42.8-mile-long (68.9 km) state highway in the US state of New Jersey. It begins at an intersection with Route 138 in Wall Township and ends at Interstate 287 (I-287) in Piscataway. Much of the route is a limited-access freeway, including the entire portion in Monmouth County and much of the northern end through New Brunswick and Piscataway. The remainder of the route is a multi-lane divided highway. Route 18 was formerly designated as Route S28, a prefixed spur of State Highway Route 28 through Middlesex and Monmouth counties. The designation, assigned in the 1927 renumbering, remained until a second renumbering in 1953. At that point, Route 18 was designated onto the alignment.

The Raritan River is a major river of central New Jersey in the United States. Its watershed drains much of the mountainous area of the central part of the state, emptying into the Raritan Bay on the Atlantic Ocean.

The Delaware and Raritan Canal is a canal in central New Jersey, United States, built in the 1830s, that served to connect the Delaware River to the Raritan River. It was an efficient and reliable means of transportation of freight between Philadelphia and New York City, especially coal from the anthracite fields in eastern Pennsylvania. The canal allowed shippers to cut many miles off the existing route from the Pennsylvania coal fields, down the Delaware, around Cape May, and up along the Atlantic Ocean coast to New York City.

The Shropshire Union Canal is a navigable canal in England. The Llangollen and Montgomery canals are the modern names of branches of the Shropshire Union (SU) system and lie partially in Wales.

The Ocmulgee River (ok-MUHL-gee) is a western tributary of the Altamaha River, approximately 255 mi (410 km) long, in the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the westernmost major tributary of the Altamaha.
The Grand Junction Canal is a canal in England from Braunston in Northamptonshire to the River Thames at Brentford, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the Midlands to London, by-passing the upper reaches of the River Thames near Oxford, thus shortening the journey.

The Oconee River is a 220-mile-long (350 km) river which has its origin in Hall County, Georgia, and terminates where it joins the Ocmulgee River to form the Altamaha River near Lumber City at the borders of Montgomery County, Wheeler County, and Jeff Davis County. South of Athens, two forks, known as the North Oconee River and Middle Oconee River, converge to form the Oconee River. Milledgeville, the former capital city of Georgia, lies on the Oconee River.

Coburg Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, in England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Queens Dock to the north, Brunswick Dock to the south.

Southeast Georgia's Lower Coastal Plain is a subregion that encompasses the lowest-lying areas of the Atlantic coastal plain in the state, containing barrier islands, marshes, and swampy lowlands, as well as flat plains and low terraces. It differs from Georgia's Upper Coastal Plain in that it is lower in elevation with less relief and wetter soils. The United States Environmental Protection Agency defines the Lower Coastal Plain as an ecoregion, part of the larger, interstate Southern Coastal Plain.
The Atlantic and Gulf Railroad was chartered in February 1856 by act of the Georgia General Assembly. It was also known as the Main Trunk Railroad. It traversed south Georgia from Screven to Bainbridge, Georgia. Construction began in early January 1859. Its construction was halted by the American Civil War. Construction began again after the end of the war and the line was completed to Bainbridge, Georgia by late December 1867. The route never reached all the way to the Gulf of Mexico as it had originally had intended. The company went bankrupt in 1877 and was bought in 1879 by Henry B. Plant and became incorporated into his Plant System. Its main line is currently operated by CSX Transportation. Throughout its history, the Atlantic and Gulf was closely associated with the Savannah and Albany Railroad Company and its successor the Savannah, Albany, and Gulf Railroad.
In Georgia folklore, the Altamaha-ha is a legendary creature, alleged to inhabit the myriad small streams and abandoned rice fields near the mouth of the Altamaha River in southeastern Georgia, United States. Sightings are particularly reported around Darien and elsewhere in McIntosh County.
The Battle of Altamaha Bridge, also known as the Battle for the Doctortown Railroad Trestle, was an American Civil War engagement fought December 19, 1864, in Wayne County, Georgia, during Sherman's March to the Sea. The Confederate victory prevented Federal forces from destroying a vital railroad bridge during Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman's siege of Savannah, keeping open Confederate supply lines to the city.

Fort King George State Historic Site is a fort located in the U.S. state of Georgia in McIntosh County, adjacent to Darien. The fort was built in 1721 along what is now known as the Darien River and served as the southernmost outpost of the British Empire in the Americas until 1727. The fort was constructed in what was then considered part of the colony of South Carolina, but was territory later settled as Georgia. It was part of a defensive line intended to encourage settlement along the colony's southern frontier, from the Savannah River to the Altamaha River. Great Britain, France, and Spain were competing to control the American Southeast, especially the Savannah-Altamaha River region.

The recorded History of Brunswick, Georgia dates to 1738, when a 1,000-acre (4 km2) plantation was established along the Turtle River. By 1789, the city was recognized by President George Washington as having been one of five original ports of entry for the American colonies. In 1797, Brunswick's prominence was further recognized when it became the county seat of Glynn County, a status it retains to this day. During the later stages of the Civil War, with the approach of the Union Army, much of the city was abandoned and burned. Economic prosperity eventually returned, when a large lumber mill was constructed in the area. By the late 19th-century, despite yellow fever epidemics and occasional hurricanes, business in Brunswick was thriving, due to port business for cotton, lumber, naval stores, and oysters. During this period, Brunswick also enjoyed a tourist trade, stimulated by nearby Jekyll Island, which had become a posh, exclusive getaway for some of the era's most influential people. World War I stimulated ship building activity in Brunswick. But it was not until World War II that the economy boomed, when 16,000 workers were employed to produce ninety-nine Liberty ships and "Knot" ships. During the war, Brunswick's Glynco Naval Air Station was, for a time, the largest blimp base in the world. Since the end of World War II, the city has enjoyed a period of moderate economic activity, centered on its deep natural port, which is the western-most harbor on the eastern seaboard. In recent years, in recognition of a thriving local enterprise, Brunswick has declared itself to be the "Shrimp Capital of the World".
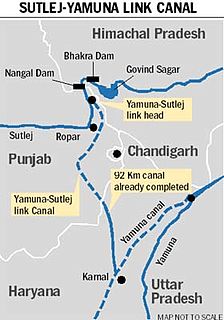
Satluj Yamuna Link Canal or SYL as it is popularly known, is a proposed 214-kilometer (133 mi) long canal in India to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. However, the proposal met obstacles and was referred to the Supreme Court of India. It defines river water sharing between the states of Punjab and Haryana. Captain Abhimanyu, Finance Minister of Haryana, while presenting the Government of Haryana 2018-19 budget in March 2018 announced that the INR 100 crore funds have been for completion of the construction of SYL.

Brunswick Mill, Ancoats is a former cotton spinning mill in Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mill was built around 1840, part of a group of mills built along the Ashton Canal, and at that time it was one of the country's largest mills. It was built round a quadrangle, a seven-storey block facing the canal. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. Production finished in 1967.

The Three Rivers Regional Library System (TRRL) is a public library system that serves the counties of Brantley, Camden, Charlton, Long, McIntosh, and Wayne, Georgia. The administrative office of the system is located in Jesup, Georgia.


















