
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions for local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils, and five are administered by unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities that also perform the functions of regional councils. The Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation.

Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. There are 67 territorial authorities: 13 city councils, 53 district councils and the Chatham Islands Council. District councils serve a combination of rural and urban communities, while city councils administer the larger urban areas. Five territorial authorities also perform the functions of a regional council and thus are unitary authorities. The Chatham Islands Council is a sui generis territorial authority that is similar to a unitary authority.

The provinces of the Colony of New Zealand existed as a form of sub-national government. Initially established in 1846 when New Zealand was a Crown colony without responsible government, two provinces were established. Each province had its own legislative council and Governor. With the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 the provinces were recreated around the six planned settlements or "colonies". By 1873 the number of provinces had increased to nine, but they had become less isolated from each other and demands for centralised government arose. In 1875 the New Zealand Parliament decided to abolish the provincial governments, and they came to an end in November 1876. They were superseded by counties, which were later replaced by territorial authorities.

Triennial elections for all 74 cities, districts, twelve regional councils and all district health boards in New Zealand were held on 9 October 2004. Most councils were elected using the first-past-the-post method, but ten were elected using the single transferable vote (STV) method. It was the first time that the STV method was available; the change came through successful lobbying by Rod Donald.
The following lists events that happened during 1896 in New Zealand.
The 1928 Chatham Cup was the sixth annual nationwide knockout football competition in New Zealand.
The 1933 Chatham Cup was the 11th annual nationwide knockout football competition in New Zealand.
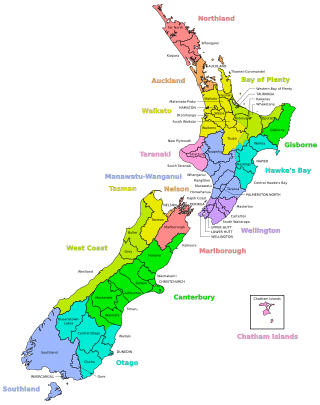
A district in New Zealand is a territorial authority area governed by a district council as a second-tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. They were formed as a result of the local government reforms in 1989. There are 53 districts in New Zealand, and they do not include the 12 city councils, the Auckland Council, and the Chatham Islands Council. District councils serve a combination of rural and urban communities, while city councils administer the larger urban areas. Three districts are unitary authorities also performing the functions of a regional council.

The 2010 New Zealand local elections were triennial elections to select local government officials and district health board members. All elections are conducted by postal ballot, with election day being Saturday 9 October 2010.

New Zealand has a unitary system of government in which the authority of the central government defines sub-national entities. Local government in New Zealand has only the powers conferred upon it by the New Zealand Parliament. In general, local authorities are responsible for enabling democratic local decision-making and promoting the social, economic, environmental, and cultural well-being of their communities, as well as more specific functions for which they have delegated authority.
The New Zealand Centre for Sustainable Cities states that it is an inter-disciplinary research centre "dedicated to providing the research base for innovative solutions to the economic, social, environmental and cultural development" of New Zealand urban centres. It states "87% of New Zealanders live in cities. The health and well-being of a significant proportion of population is reliant on developing environments that take into account the connections between transport, design, energy, health and governance and other issues."

The 2016 New Zealand local elections were triennial local elections to select local government officials and District Health Board members. Under section 10 of the Local Electoral Act 2001, a "general election of members of every local authority or community board must be held on the second Saturday in October in every third year" from the date the Act came into effect in 2001, meaning 8 October 2016.
The 2016 Chatham Cup was New Zealand's 89th annual knockout football competition.
Climate emergency declarations have been made by multiple jurisdictions in New Zealand, including national, regional and territorial authorities. The first New Zealand´s jurisdictions began to declare climate emergencies in 2019.

The 2022 New Zealand local elections were triennial elections held in New Zealand on Saturday 8 October 2022. Voting began by postal vote on 16 September and ended at noon on 8 October 2022.

Star Flats refers to a form of medium-density state housing in New Zealand. The flats were designed in the late 1950s by Ministry of Works architect Neville Burren, working under the Ministry's Housing Division's chief architect Frederick Newman. They were built from 1958 and throughout the 1960s. Each building was named after a star.




