
The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the Firth of Clyde between Ayrshire and Argyll and Bute. There are about forty islands and skerries, of which only four are inhabited and only nine larger than 40 hectares. The largest and most populous are Arran and Bute, and Great Cumbrae and Holy Island are also served by dedicated ferry routes. Unlike the four larger Scottish archipelagos, none of the isles in this group are connected to one another or to the mainland by bridges.

Lismore is an island of some 2,351 hectares in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The climate is damp and mild, with over 166 centimetres (65 in) of rain recorded annually. This fertile, low-lying island was once a major centre of Celtic Christianity, with a 6th-century monastery associated with Saint Moluag, and later became the seat of the medieval Bishop of Argyll. There are numerous ruined structures including a broch and two 13th-century castles.

Sutherland is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire to the south and the Atlantic to the north and west. Like its southern neighbour Ross-shire, Sutherland has some of the most dramatic scenery in the whole of Europe, especially on its western fringe where the mountains meet the sea. These include high sea cliffs, and very old mountains composed of Precambrian and Cambrian rocks.
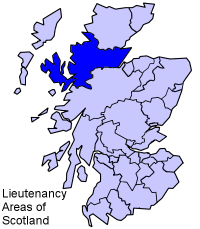
Ross and Cromarty, sometimes referred to as Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, is a variously defined area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. There is a registration county and a lieutenancy area in current use, the latter of which is 8,019 square kilometres in extent. Historically there has also been a constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, a local government county, a district of the Highland local government region and a management area of the Highland Council. The local government county is now divided between two local government areas: the Highland area and Na h-Eileanan Siar. Ross and Cromarty border Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south.

Argyll, sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland.

The Shiant Islands or Shiant Isles are a privately owned island group in the Minch, east of Harris in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. They are five miles southeast of the Isle of Lewis.

The Kyles of Bute form a narrow sea channel that separates the northern end of the Isle of Bute from the Cowal peninsula in Argyll and Bute, on the Scottish mainland. The surrounding hillsides are roughly wooded, and overlooked by rocky tops and areas of moorland.

Ronay is an island in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, which lies a short distance off the east coast of Grimsay.
Loch Torridon is a sea loch on the west coast of Scotland in the Northwest Highlands. The loch was created by glacial processes and is in total around 15 miles (25 km) long. It has two sections: Upper Loch Torridon to landward, east of Rubha na h-Airde Ghlaise, at which point it joins Loch Sheildaig; and the main western section of Loch Torridon proper. Loch a' Chracaich and Loch Beag are small inlets on the southern shores of the outer Loch, which joins the Inner Sound between the headlands of Rubha na Fearna to the south and Red Point to the north.

Ross-shire is a historic county in the Scottish Highlands. The county borders Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south, as well as having a complex border with Cromartyshire – a county consisting of numerous enclaves or exclaves scattered throughout Ross-shire's territory. Ross-shire includes most of Ross along with Lewis in the Outer Hebrides. Dingwall is the traditional county town. The area of Ross-shire is based on that of the historic province of Ross, but with the exclusion of the many enclaves that form Cromartyshire.

Loch Ailort is a sea loch in Morar, Lochaber, Highland, Scotland. Loch Ailort is a shallow V shaped loch, with the small Ardnish Peninsula on the north side, and the large southwest facing Moidart Peninsula to the south. Loch Ailort is bounded in the northeast by the settlement of the same name, Lochailort and in the west, opening out into the Sound of Arisaig. To the north of the loch lies Loch nan Uamh.

Na h-Eileanan Iasgaich comprise a small uninhabited archipelago in Loch Boisdale, in the south east of the island of South Uist, in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. The individual islands are separated from one another at high tide, but connected to one another at low tide,. They are around 50 ha in extent and over 20m at their highest point. Their boundaries are ill-defined.

Bernera Island or simply Bernera is a tidal island off Lismore, in Argyll, Scotland.
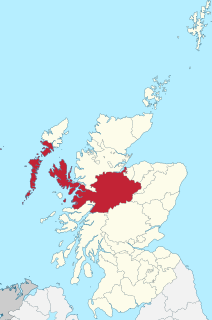
Inverness-shire is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. Covering much of the Highlands and Outer Hebrides, it is Scotland's largest county, though one of the smallest in population, with 67,733 people or 1.34% of the Scottish population.
Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba is the national advisory partnership for Gaelic place names in Scotland. Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba are based at Sabhal Mòr Ostaig on Skye.

Eileanan Chearabhaigh is a collection of small uninhabited tidal islands off the south east coast of Benbecula in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The English language name Keiravagh Islands is sometimes used.

Loch Sween is a sea loch located near Lochgilphead, Argyll and Bute, Scotland. Castle Sween is located on the southern shore towards the seaward end of the loch. The village of Tayvallich, a favoured haven for water craft as it sits at the head of sheltered Loch a' Bhealaich, lies on the northern shore.

Loch Buidhe is a fresh water loch on Rannoch Moor, Argyll and Bute within Highland council area, Scotland..

















