
A strait is a naturally formed, narrow, typically navigable waterway that connects two larger bodies of water. Most commonly it is a channel of water that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas.

An isthmus is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus.

The River Mersey is a river in the North West of England. Its name is derived from the Anglo-Saxon language and translates as "boundary river". The river may have been the border between the ancient kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria and for centuries it has formed part of the boundary between the historic counties of Lancashire and Cheshire.

An igloo, also known as a snow house or snow hut, is a type of shelter built of snow, typically built when the snow is suitable.
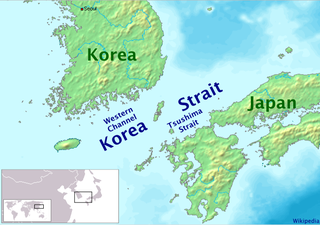
The Korea Strait is a sea passage in East Asia between Korea and Japan, connecting the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan in the northwest Pacific Ocean. The strait is split by the Tsushima Island into the Western Channel and the Tsushima Strait or Eastern Channel.
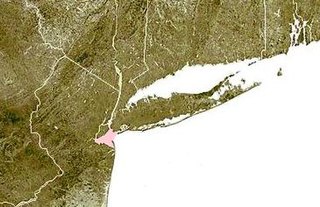
Lower New York Bay is a section of New York Bay south of the Narrows, the relatively narrow strait between the shores of Staten Island and Brooklyn. The southern end of the bay opens directly to the Atlantic Ocean between two spits of land, Sandy Hook, New Jersey, and Rockaway, Queens, on Long Island. The southern portion between Staten Island and New Jersey, at the mouth of the Raritan River, is named Raritan Bay. The Hudson Canyon, the ancient riverbed of the Hudson River which existed during the last ice age when the ocean levels were lower, extends southeast from Lower New York Bay for hundreds of miles into the Atlantic Ocean. The nearby part of the Atlantic Ocean between New Jersey and Long Island is the New York Bight.

The Carquinez Strait is a narrow tidal strait in Northern California. It is part of the tidal estuary of the Sacramento and the San Joaquin rivers as they drain into the San Francisco Bay. The strait is eight miles (13 km) long and connects Suisun Bay, which receives the waters of the combined rivers, with San Pablo Bay, a northern extension of the San Francisco Bay.

In physical geography, a channel is a type of landform consisting of the outline of a path of relatively shallow and narrow body of fluid, most commonly the confine of a river, river delta or strait. The word is cognate to canal, and sometimes takes this form, e.g. the Hood Canal.

A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water, generally on a planet's surface. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more rarely, puddles. A body of water does not have to be still or contained; rivers, streams, canals, and other geographical features where water moves from one place to another are also considered bodies of water.

Tidal race or tidal rapid is a natural occurrence whereby a fast-moving tide passes through a constriction, resulting in the formation of waves, eddies and hazardous currents. The constriction can be a passage where the sides narrow, for example the Gulf of Corryvreckan and the Saltstraumen maelstrom, or an underwater obstruction, such as is found at the Portland Race in the United Kingdom.

In military strategy, a choke point is a geographical feature on land such as a valley, defile or bridge, or maritime passage through a critical waterway such as a strait, which an armed force is forced to pass through in order to reach its objective, sometimes on a substantially narrowed front and therefore greatly decreasing its combat effectiveness by making it harder to bring superior numbers to bear. A choke point can allow a numerically inferior defending force to use the terrain as a force multiplier to thwart or ambush a much larger opponent, as the attacker cannot advance any further without first securing passage through the choke point.

The eaves are the edges of the roof which overhang the face of a wall and, normally, project beyond the side of a building. The eaves form an overhang to throw water clear of the walls and may be highly decorated as part of an architectural style, such as the Chinese dougong bracket systems.

Zion Canyon is a deep and narrow gorge in southwestern Utah, United States, carved by the North Fork of the Virgin River. Nearly the entire canyon is located within the western half of Zion National Park.

Seymour Narrows is a 5-kilometre (3.1 mi) section of the Discovery Passage in British Columbia known for strong tidal currents. Discovery Passage lies between Vancouver Island at Menzies Bay, British Columbia and Quadra Island except at its northern end where the eastern shoreline is Sonora Island. The section known as Seymour Narrows begins about 18 km (11 mi) from the south end of Discovery Passage where it enters the Georgia Strait near Campbell River. For most of the length of the narrows, the channel is about 750 metres (820 yd) wide. Through this narrow channel, currents can reach 15 knots.
The Narrows is a strait in New York City separating Brooklyn and Staten Island.

The levant is an easterly wind that blows in the western Mediterranean Sea and southern France, an example of mountain-gap wind. In Roussillon it is called "llevant" and in Corsica "levante". In the western Mediterranean, particularly when the wind blows through the Strait of Gibraltar, it is called the Viento de Levante or the Levanter. It is also known as the Solano.
This glossary of geography terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in geography and related fields, which describe and identify spatial dimension, geographic locations, topographical features, natural resources, and the collection, analysis, and visualization of geographic data. For related terms, see Glossary of geology and Glossary of environmental science.

A gat is a strait that is constantly eroded by currents flowing back and forth, such as tidal currents. It is usually a relatively narrow but deep, up to 30 m (100 ft) passage between land masses or shallow bars in an area of mudflats. A gat is sometimes a shallower passage on lagoon coasts, including those without any tidal range.

In geology, 3D fold evolution is the study of the full three dimensional structure of a fold as it changes in time. A fold is a common three-dimensional geological structure that is associated with strain deformation under stress. Fold evolution in three dimensions can be broadly divided into two stages, namely fold growth and fold linkage. The evolution depends on fold kinematics, causes of folding, as well as alignment and interaction of the each structure with respect to each other. There are several ways to reconstruct the evolution progress of folds, notably by using depositional evidence, geomorphological evidence and balanced restoration. Understanding the evolution of folds is important because it helps petroleum geologists to gain a better understanding on the distribution of structural traps of hydrocarbon.

















