
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the eastern border area of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-speaking peoples, Teso people also known as Iteso or people of Teso, Karo peoples, Luo peoples, Ateker peoples, Kalenjin peoples, Karamojong people also known as the Karamojong or Karimojong, Datooga, Dinka, Nuer, Atwot, Lotuko, and the Maa-speaking peoples.

The Kakwa people are a Nilotic ethnic group and part of the Karo people found in north-western Uganda, south-western South Sudan, and north-eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, particularly to the west of the White Nile river.

The Luo, are several ethnically and linguistically related Nilotic ethnic groups that inhabit an area ranging from Egypt and Sudan to South Sudan and Ethiopia, through Northern Uganda and eastern Congo (DRC), into western Kenya, and the Mara Region of Tanzania. Their Luo languages belong to the western branch of the Nilotic language family.
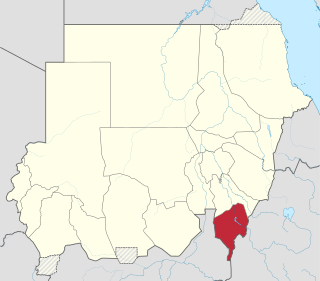
Blue Nile State is one of the eighteen states of the Republic of the Sudan. It was established by presidential decree nº 3 in 1992 and it is named after the Blue Nile River.
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Bor to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

The Nilotic languages are a group of related languages spoken across a wide area between South Sudan and Tanzania by the Nilotic peoples.
The Western Nilotic languages are one of the three primary branches of the Nilotic languages, along with the Eastern Nilotic languages and Southern Nilotic languages; Themselves belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subfamily of Nilo-Saharan. The about 22 Western Nilotic languages are spoken in an area ranging from southwestern Ethiopia and South Sudan via northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo and northern Uganda to southwestern Kenya.

The Shilluk is a major Luo Nilotic ethnic group that resides in the northeastern Upper Nile state of South Sudan on both banks of the Nile River in Malakal. Before the Second Sudanese Civil War, the Shilluk also lived in settlements on the northern bank of the Sobat River, close to where the Sobat joins the Nile.

The Anyuak, also known as Anyuaa and Anywaa, are a Luo Nilotic ethnic group inhabiting parts of East Africa. The Anuak belong to the larger Luo family group. Their language is referred to as Dha-Anywaa. They primarily reside in the Gambela Region of western Ethiopia, and South Sudan. Group members number between 200,000 and 300,000 people worldwide. Many of the Anyuak people now follow Christianity. It is one of the first of the Nilotic groups to become almost entirely Christian, following the Shilluk people.
Dinka is a Nilotic dialect cluster spoken by the Dinka people, a major ethnic group of South Sudan. There are several main varieties, such as Padang, Rek, Agaar, Ciec, Apaak, Aliep, Bor, Hol, Nyarweng, Twic East and Twic Mayardit, which are distinct enough to require separate literary standards. Jaang, Jieng or Muonyjieng is used as a general term to cover all Dinka languages. Recently Akutmɛ̈t Latueŋ Thuɔŋjäŋ has proposed a unified written grammar of Dinka.

The Luo of Kenya and Tanzania are a Nilotic ethnic group native to western Kenya and the Mara Region of northern Tanzania in East Africa. The Luo are the fourth-largest ethnic group (10.65%) in Kenya, after the Kikuyu (17.13%), the Luhya (14.35%) and the Kalenjin (13.37%). The Tanzanian Luo population was estimated at 1.1 million in 2001 and 3.4 million in 2020. They are part of a larger group of related Luo peoples who inhabit an area ranging from South Sudan, southwestern Ethiopia, northern and eastern Uganda, southwestern Kenya, and northern Tanzania.
Jumjum or Mabaan is an ethnic group in South Sudan. Most of its members are Muslims. The number of persons in this group is at about 92,000. They speak Mabaan, a Luo Nilotic language. They live in the Upper Nile.

The Jur River is a river in western South Sudan, flowing through the Bahr el Ghazal and Equatoria regions. About 485 kilometres (301 mi) long, it flows north and northeast, joining the Bahr el Ghazal River on the western side of the Sudd wetlands. The Jur River is part of the Nile basin, as the Bahr al-Ghazal flows into the White Nile.
The Jur Mananger are a Luo Nilotic ethnic group numbering 20,000 to 30,000 people living in Gogrial District of South Sudan. They speak a Western Nilotic language related to Luo and Shilluk.

South Sudan is home to around 60 indigenous ethnic groups and 80 linguistic partitions among a 2021 population of around 11 million. Historically, most ethnic groups were lacking in formal Western political institutions, with land held by the community and elders acting as problem solvers and adjudicators. Today, most ethnic groups still embrace a cattle culture in which livestock is the main measure of wealth and used for bride wealth.
Luo language or Lwo language may refer to:
Southern Burun is a Western Nilotic language of Sudan. It is a dialect continuum with Burun proper, Mabaan/Ulu, and Jumjum.
The Luwo are a Nilotic ethnic group that live in the western parts of South Sudan. They are part of a larger group of ethno-linguistically related Luo peoples of East Africa. They speak the Luwo language which is a Northern Luo language.
The Nilotic peoples are a collection of ethnic groups indigenous to Nile Valley in East Africa.











