Related Research Articles

The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people is an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide.

A cowboy is an animal herder who tends cattle on ranches in North America, traditionally on horseback, and often performs a multitude of other ranch-related tasks. Cattle drives ensure the herds health in finding pasture and bring them to market. The historic American cowboy of the late 19th century arose from the vaquero traditions of northern Mexico and became a figure of special significance and legend. A subtype, called a wrangler, specifically tends the horses used to work cattle. In addition to ranch work, some cowboys work for or participate in rodeos. Cowgirls, first defined as such in the late 19th century, had a less-well documented historical role, but in the modern world work at identical tasks and have obtained considerable respect for their achievements. Cattle handlers in many other parts of the world, particularly South America and stockmen and jackaroos in Australia, perform work similar to the cowboy.
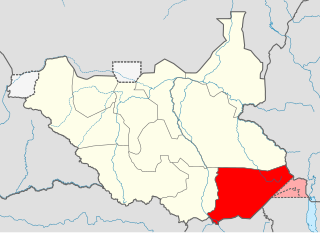
Eastern Equatoria is a state in South Sudan. It has an area of 73,472 km2. The capital City is Torit. On October 1, 1972, the state was divided into Imatong and Namorunyang states and was re-established by a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020.
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Bor to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

The Herero are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting parts of Southern Africa. There were an estimated 250,000 Herero people in Namibia in 2013. They speak Otjiherero, a Bantu language. Though the Herero primarily reside in Namibia, there are also significant populations in Botswana and Angola, and a small number in South Africa. The Hereros in Botswana and South Africa are there because of displacement during the 1904 - 1908 genocide committed by the German Empire.

Kraal is an Afrikaans and Dutch word, also used in South African English, for an enclosure for cattle or other livestock, located within a Southern African settlement or village surrounded by a fence of thorn-bush branches, a palisade, mud wall, or other fencing, roughly circular in form. It is similar to a boma in eastern or central Africa.

The Karamojong or Karimojong are a Nilotic ethnic group. They are agro-pastoral herders living mainly in the north-east of Uganda. Their language is also known as ngaKarimojong and is part of the Nilotic language family. Their population is estimated at 475,000 people.
The Nyakyusa are a Bantu ethnolinguistic group who live in the fertile mountains of southern Mbeya Region of Tanzania and the Northern Region of Malawi. They speak the Nyakyusa language, a member of the Bantu language family. In 1993 the Nyakyusa population was estimated to number 1,050,000, with 750,000 living in Tanzania. Nyakyusa are marked as highly educated and eager agriculturists. The Nyakyusa are colonising people where success and survival depended on individual effort. Nyakyusa have managed to collect vast wealth from trade and agriculture than any tribe in Tanzania..

The Murle are a Surmic ethnic group inhabiting the Pibor County and Boma area in Greater Pibor Administrative Area, South Sudan, as well as parts of southwestern Ethiopia. They have also been referred as Beir by the Dinka and as Jebe by the Luo and Nuer, among others. The Murle speak the Murle language, which is part of the Surmic language family. The language cluster includes some adjoining groups in Sudan, as well as some non-contiguous Surmic populations in southwestern Ethiopia.

The Toposa are an ethnic group in South Sudan, living in the Greater Kapoeta region of the erstwhile Eastern Equatoria state. They have traditionally lived by herding cattle, sheep and goats, and in the past were involved in the ivory trade. They have a tradition of constant low-level warfare, usually cattle raids, against their neighbors.
Jiye may refer to:
The Teso–Turkana languages are a group of closely related Eastern Nilotic languages spoken in southeastern South Sudan, northeastern Uganda, northwestern Kenya, and southwestern Ethiopia. In effect they form a dialect cluster consisting of c.2 million people. According to Gerrit Dimmendaal, most of these languages – Karimojong, Jie, Toposa, Turkana, and Nyangatom – are mutually intelligible, and for the most part differ only in regard to tone. Teso belongs to the same broad group but is not described as being as closely related to Turkana as the others.

Tilothu, also spelled Tilauthu or Tilothu, is a village and corresponding community development block in Rohtas district, Bihar, India. It is located 15 km from Dehri-on-Sone on the west bank of the Son River. As of 2011, the population of Tilouthu was 16,402, in 2,745 families, while the corresponding block population was 109,249.
Wateni is a rural commune in the Cercle of Sikasso in the Sikasso Region of southern Mali. The commune covers an area of 211 square kilometers and includes ten villages. In the 2009 census it had a population of 6,701. The village of N'Tjila, the administrative center (chef-lieu) of the commune, is 94 km west-northwest of Sikasso.

Cattle Depot Artist Village is located on 63 Ma Tau Kok Road, Ma Tau Kok, Kowloon, Hong Kong. The site was originally used as a slaughterhouse from 1908 to 1999. It was renovated and developed into a village for artists in 2001. It is now home to around 20 art groups.
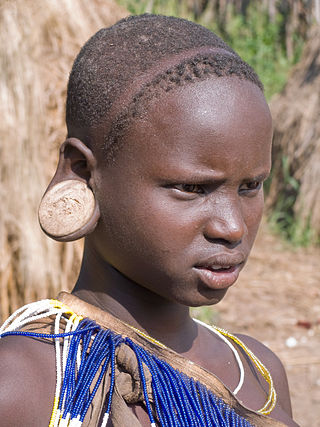
Suri is a collective name for three ethnic groups mainly living in Suri woreda, in southwestern Ethiopia. They share many similarities politically, territorially, culturally and economically but speak different languages. They all speak South East Surmic languages within the Nilo-Saharan language family, which includes the Mun, Majang, and Me'en people's languages.

The Dodoth are an ethnic group in north eastern Uganda. They belong to the Karamojong Cluster, which also includes the Karamojong and Jie people. Their language is a dialect of the Karamojong language. Their population is estimated at 129,102.

Kapoeta East County is an administrative region of Eastern Equatoria state in South Sudan, bordered by Kenya to the south, Ethiopia to the east and Jonglei state to the west. It is part of the Greater Kapoeta region of the state. The largest ethnic group is the Toposa people. The principal town is Narus. The county includes the disputed Ilemi triangle, controlled by Kenya. The emblem of the county is a horned bull, with big humps and a large tail.
The Battle at Fort Utah was a violent attack in 1850 in which 90 Mormon militiamen surrounded an encampment of Timpanogos families on the Provo River one winter morning, and laid siege for two days, eventually shooting between 40 and 100 Native American men and one woman with guns and a cannon during the attack as well as during the pursuit and capture of the two groups that fled the last night. One militiaman died from return fire during the siege. Of the Timpanogos people who fled in the night, one group escaped southward, and the other ran east to Rock Canyon. Both groups were captured, however, and the men were executed. Over 40 Timpanogos children, women, and a few men were taken as prisoners to nearby Fort Utah. They were later taken northward to the Salt Lake Valley and sold as slaves to church members there. The bodies of up to 50 Timpanogos men were beheaded by some of the settlers and their heads put on display at the fort as a warning to the mostly women and children prisoners inside.

Rustampur is a village in Rahi block of Rae Bareli district, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located 7 km from Rae Bareli, the district headquarters. As of 2011, it has a total population of 4,546 people, in 843 households. It has one primary school and one primary health centre. It serves as the headquarters of a nyaya panchayat which also includes 12 other villages.
References
- ↑ "Jiye". gurtong. Archived from the original on January 29, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ↑ Glottolog
- ↑ Olson, James Stuart; Meur, Charles (1996). The Peoples of Africa: An Ethnohistorical Dictionary. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 255. ISBN 978-0-313-27918-8.