Related Research Articles

Koryaks are an Indigenous people of the Russian Far East, who live immediately north of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Kamchatka Krai and inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea. The cultural borders of the Koryaks include Tigilsk in the south and the Anadyr basin in the north.

Porridge is a food made by heating or boiling ground, crushed or chopped starchy plants, typically grain, in milk or water. It is often cooked or served with added flavourings such as sugar, honey, fruit, or syrup to make a sweet cereal, or it can be mixed with spices, meat, or vegetables to make a savoury dish. It is usually served hot in a bowl, depending on its consistency. Oat porridge, or oatmeal, is one of the most common types of porridge. Gruel is a thinner version of porridge and congee is a savoury variation of porridge of Asian origin.
The Lugbara live in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda , and South Sudan. Their number totaled approximately 240,000, with around 180,000 residing in north-western Uganda, with the remaining population spread across bordering areas of the modern-day Democratic Republic of Congo and South Sudan. The Lugbara people speak in a Sudanese language. The basic social and economic unit found in Lugbara culture is a lineage group under the authority of a male genealogical elder called ba wara, meaning "big man". These lineage groups, often referred to as sub-tribes, typically lived in a village built atop a hillside or ridge. In addition to the male elder, other religious leaders include diviners, oracles, and rain men.

The Samburu are a Nilotic people of north-central Kenya. Samburu are semi-nomadic pastoralists who herd mainly cattle but also keep sheep, goats and camels. The name they use for themselves is Lokop or Loikop, a term which may have a variety of meanings which Samburu themselves do not agree on. Many assert that it refers to them as "owners of the land" though others present a very different interpretation of the term. Samburu speak the Samburu dialect of the Maa language, which is a Nilotic language. The Maa language is also spoken by other 22 sub tribes of the Maa community otherwise known as the Maasai. Many Western anthropologists tried to carve out and create the Samburu tribe as a community of its own, unaffiliated to its parent Maasai community, a narrative that seems that many Samburu people today hold. There are many game parks in the area, one of the most well known is Samburu National Reserve. The Samburu sub tribe is the third largest in the Maa community of Kenya and Tanzania, after the Kisonko (Isikirari) of Tanzania and Purko of Kenya and Tanzania.
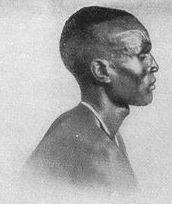
The Dinka people are a Nilotic ethnic group native to South Sudan. The Dinka mostly live along the Nile, from Mangalla-Jonglei to Renk, in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, Upper Nile, and the Abyei Area of the Ngok Dinka in South Sudan.

The Nuer people are a Nilotic ethnic group concentrated in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. They also live in the Ethiopian region of Gambella. The Nuer speak the Nuer language, which belongs to the Nilotic language family. They are the second largest ethnic group in South Sudan. The Nuer people are pastoralists who herd cattle for a living. Their cattle serve as companions and define their lifestyle. The Nuer call themselves "Naath".

South African cuisine reflects the diverse range of culinary traditions embodied by the various communities that inhabit the country. Among the indigenous peoples of South Africa, the Khoisan foraged over 300 species of edible food plants, such as the rooibos shrub legume, whose culinary value continues to exert a salient influence on South African cuisine. Subsequent encounters with Bantu pastoralists facilitated the emergence of cultivated crops and domestic cattle, which supplemented traditional Khoisan techniques of meat preservation. In addition, Bantu-speaking communities forged an extensive repertoire of culinary ingredients and dishes, many of which are still consumed today in traditional settlements and urban entrepôts alike.

The Culture of Africa is varied and manifold, consisting of a mixture of countries with various tribes depicting their unique characteristic and trait from the continent of Africa. It is a product of the diverse populations that inhabit the continent of Africa and the African diaspora. Generally, Culture can be defined as a collective mass of distinctive qualities belonging to a certain group of people. These qualities include laws, morals, beliefs, knowledge, art, customs, and any other attributes belonging to a member of that society. Culture is the way of life of a group of people.
African cuisine is a staple of the continent's culture, and its history is entwined with the story of the native people of Africa. The foods that native Africans eat have been influenced by their religions, as well as by their climates and lifestyles. The first Africans to inhabit the continent were hunter-gatherers who ate what they could find in nature. As agriculture became more common in Africa, so did agriculture-based diets.

The Turkana are a Nilotic people native to the Turkana County in northwest Kenya, a semi-arid climate region bordering Lake Turkana in the east, Pokot, Rendille and Samburu people to the south, Uganda to the west, to the South Sudan and Ethiopia to the north.

Ugali, also known as posho, nsima, and other names, is a type of corn meal made from maize or corn flour in several African countries, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi, Botswana and South Africa It is cooked in boiling water or milk until it reaches a stiff or firm dough-like consistency. In 2017, the dish was added to the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, one of a few foods in the list.

The Kuku are a Nilotic tribe of the Karo people from South Sudan. They inhabit the agricultural lands of Kajo Keji County in Central Equatoria State. The Kuku speak a Kuku dialect, also called BaKuku.

Culture of Somaliland encompasses a wide range of Somali activity and Islamic structures that give Somaliland a rich cultural and historical heritage. Nomadic and Arab Islamic cultural significance have also played a key role in Somaliland's cultural history.

The cuisine of Botswana is unique but shares some characteristics with other cuisines of Southern Africa. Examples of Setswana food include pap, samp, vetkoek, bogobe and mophane worms. A food unique to Botswana is seswaa, salted mashed-up meat.

The Lugbara are a Central Sudanic ethnic group who live primarily in the West Nile region of Uganda, in the adjoining area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) with a few living in South Sudan. They speak the Lugbara language, a Central Sudanic language similar to the language spoken by the Madi, with whom they also share many cultural similarities.

Libyan culture is a blend of many influences, due to its exposure to many historical eras. Libya was an Italian colony for over four decades, which also had a great impact on the country's culture. Once an isolated society, Libyans succeeded in preserving their traditional folk customs alive today, now recognized by many as the most "pure" extant form of Arab culture found outside the Arabian Peninsula. Libyan culture places strong emphasis on family, tribal bonds, loyalty, solidarity and faithfulness.

The Daasanach are an ethnic group inhabiting parts of Ethiopia, Kenya, and South Sudan. Their main homeland is in the Debub Omo Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region, adjacent to Lake Turkana. According to the 2007 national census, they number 48,067 people, of whom 1,481 are urban dwellers.

The Lopit people are a Nilotic ethnic group found in Eastern Equatoria State, South Sudan. Traditionally, they refer to themselves as donge (plural) or dongioni (singular). The Lopit number 160,000 to 200,000 people living in the Lopit area, in the Lopit mountains which extend from the east to the north of Torit.
The Rubatab people constitute one of many Sunni riverine tribes of Northern Sudan. They inhabit the region of the Fourth Cataract of the Nile. Similar to their neighbouring tribes, the mid-stream Manasir and the downstream Shaiqiyah (الشايقيّة), the Rubatab are an Arab tribe in the Northeastern Sudan, with an archaic Arabic mother tongue. Their tribal homeland traditionally stretches north of Berber, Sudan until the famed town of Abu Hamad. The Rubatab border the Ababda people, the Bishari tribe, and the Manasir.

Chadian cuisine is the cooking traditions, practices, foods and dishes associated with the Republic of Chad. Chadians use a medium variety of grains, vegetables, fruits and meats. Commonly consumed grains include millet, sorghum, and rice as staple foods. Commonly eaten vegetables include okra and cassava. A variety of fruits are also eaten. Meats include mutton, chicken, pork, goat, fish, lamb and beef. The day's main meal is typically consumed in the evening on a large communal plate, with men and women usually eating in separate areas. This meal is typically served on the ground upon a mat, with people sitting and eating around it.