
Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated protein N is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPN gene.

Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Sm D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPD2 gene. It belongs to the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein core protein family, and is required for pre-mRNA splicing and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein biogenesis. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.

Splicing factor 3 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SF3A1 gene.

Pinin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PNN gene.

Splicing factor 3A subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SF3A3 gene.
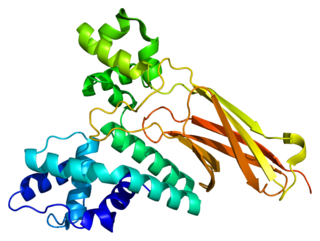
U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 200 kDa helicase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SNRNP200 gene.

Splicing factor 3B subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SF3B3 gene.

Pre-mRNA-processing factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRPF6 gene.

U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPB2 gene.

U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Prp4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRPF4 gene. The removal of introns from nuclear pre-mRNAs occurs on complexes called spliceosomes, which are made up of 4 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) particles and an undefined number of transiently associated splicing factors. PRPF4 is 1 of several proteins that associate with U4 and U6 snRNPs.[supplied by OMIM]

Nucleolar protein 58 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOP58 gene.

H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NHP2 gene.

U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP-associated protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USP39 gene.

Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase H is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPIH gene.

Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX23 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX23 gene.
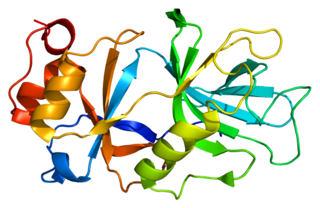
Snurportin1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNUPN gene.

RNA-binding protein 28 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM28 gene. It is a nucleolar component of the spliceosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes.

WW domain-binding protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WBP4 gene.

Zinc finger protein 473 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF473 gene.

In molecular biology, the GYF domain is an approximately 60-amino acid protein domain which contains a conserved GP[YF]xxxx[MV]xxWxxx[GN]YF motif. It was identified in the human intracellular protein termed CD2 binding protein 2 (CD2BP2), which binds to a site containing two tandem PPPGHR segments within the cytoplasmic region of CD2. Binding experiments and mutational analyses have demonstrated the critical importance of the GYF tripeptide in ligand binding. A GYF domain is also found in several other eukaryotic proteins of unknown function. It has been proposed that the GYF domain found in these proteins could also be involved in proline-rich sequence recognition. Resolution of the structure of the CD2BP2 GYF domain by NMR spectroscopy revealed a compact domain with a beta-beta-alpha-beta-beta topology, where the single alpha-helix is tilted away from the twisted, anti-parallel beta-sheet. The conserved residues of the GYF domain create a contiguous patch of predominantly hydrophobic nature which forms an integral part of the ligand-binding site. There is limited homology within the C-terminal 20-30 amino acids of various GYF domains, supporting the idea that this part of the domain is structurally but not functionally important.




























