
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK5R1 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NEK2 gene.

Ninein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NIN gene. Ninein, together with its paralog Ninein-like protein is one of the proteins important for centrosomal function. This protein is important for positioning and anchoring the microtubules minus-ends in epithelial cells. Localization of this protein to the centrosome requires three leucine zippers in the central coiled-coil domain. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been reported.

Centromere protein J is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CENPJ gene. It is also known as centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP). During cell division, this protein plays a structural role in the maintenance of centrosome integrity and normal spindle morphology, and it is involved in microtubule disassembly at the centrosome. This protein can function as a transcriptional coactivator in the Stat5 signaling pathway and also as a coactivator of NF-kappaB-mediated transcription, likely via its interaction with the coactivator p300/CREB-binding protein.

CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDK5RAP3 gene.

Centrosome-associated protein 350 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP350 gene.

CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDK5RAP1 gene.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK5R2 gene.

Centrosomal protein of 68 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP68 gene. CEP68 is required for centrosome cohesion. It decorates fibres emanating from the proximal ends of centrioles. During mitosis, CEP68 dissociates from centrosomes. CEP68 and rootletin depend both on each other for centriole association, and both also require CEP250 for their function.

Myomegalin, also known as phosphodiesterase 4D-interacting protein or cardiomyopathy-associated protein 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDE4DIP gene. It has roles in the formation of microtubules from the centrosome. Its name derives from the fact that it is highly expressed in units of tubular myofibrils known as sarcomeres and is a large protein, at 2,324 amino acids. It was first characterised in 2000.

Centriolar coiled-coil protein of 110 kDa also known as centrosomal protein of 110 kDa or CP110 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCP110 gene. It is a cell cycle-dependent CDK substrate and regulates centrosome duplication. CP110 suppresses a cilia assembly program.

Cyclin dependent kinase 5 is a protein, and more specifically an enzyme, that is encoded by the Cdk5 gene. It was discovered 15 years ago and it is saliently expressed in post-mitotic central nervous system neurons (CNS).

Centrosomal protein of 135 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP135 gene. It is part of the centrosome throughout the cell cycle, being distributed in the pericentriolar material. CEP135 is required for the centriolar localization of CEP250.

Rootletin also known as ciliary rootlet coiled-coil protein (CROCC) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CROCC gene. Rootletin is a component of the ciliary rootlet, and, together with CEP68 and CEP250, is required for centrosome cohesion.

Centrosomal protein of 192 kDa, also known as Cep192, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP192 gene. It is the homolog of the C. elegans and D. melanogaster gene SPD-2.

Centrosomal protein of 164 kDa, also known as CEP164, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP164 gene. Its function appears two be twofold: CEP164 is required for primary cilium formation. Furthermore, it is an important component in the response to DNA damage by UV light.

Centrosomal protein of 76 kDa, also known as CEP76, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP76 gene.

Centrosomal protein of 78 kDa, also known as Cep78, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP78 gene.

Centrosomal protein of 152 kDa, also known as Cep152, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP152 gene. It is the ortholog of the Drosophila melanogaster gene asterless (asl) and both are required for centriole duplication.
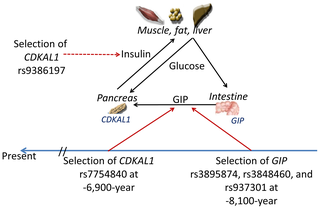
CDKAL1 is a gene in the methylthiotransferase family. The complete physiological function and implications of this have not been fully determined. CDKAL1 is known to code for CDK5, a regulatory subunit-associated protein 1. This protein CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1 is found broadly across tissue types including neuronal tissues and pancreatic beta cells. CDKAL1 is suspected to be involved in the CDK5/p35 pathway, in which p35 is the activator for CDK5 which regulates several neuronal functions.






















