Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration.

Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, proliferation, and survival of certain target neurons. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it was one of the first to be described. Since it was first isolated by Nobel Laureates Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen in 1956, numerous biological processes involving NGF have been identified, two of them being the survival of pancreatic beta cells and the regulation of the immune system.
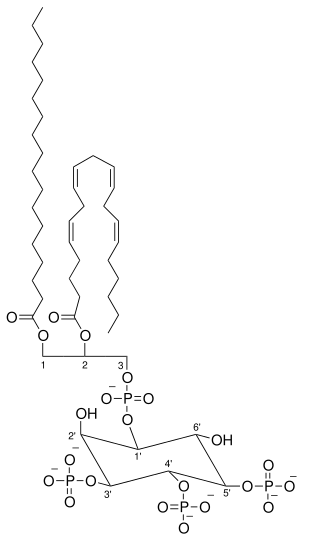
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3), abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI 3-kinases) phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is a phospholipid that resides on the plasma membrane.
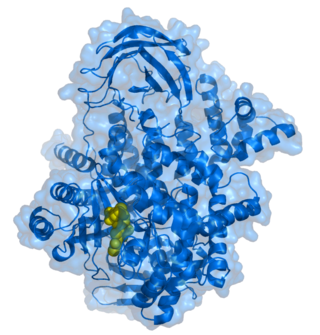
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.

GRB2-associated-binding protein 2 also known as GAB2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GAB2 gene.

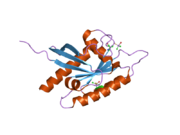
RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT1 gene. This enzyme belongs to the AKT subfamily of serine/threonine kinases that contain SH2 protein domains. It is commonly referred to as PKB, or by both names as "Akt/PKB".

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.
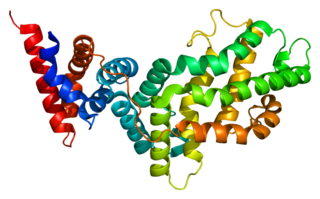
RAS p21 protein activator 1 or RasGAP, also known as RASA1, is a 120-kDa cytosolic human protein that provides two principal activities:

RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT3 gene.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (S6K1), also known as p70S6 kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KB1 gene. It is a serine/threonine kinase that acts downstream of PIP3 and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 in the PI3 kinase pathway. As the name suggests, its target substrate is the S6 ribosomal protein. Phosphorylation of S6 induces protein synthesis at the ribosome.

RhoC is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RHOC.
Activated CDC42 kinase 1, also known as ACK1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TNK2 gene. TNK2 gene encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, ACK1, that binds to multiple receptor tyrosine kinases e.g. EGFR, MERTK, AXL, HER2 and insulin receptor (IR). ACK1 also interacts with Cdc42Hs in its GTP-bound form and inhibits both the intrinsic and GTPase-activating protein (GAP)-stimulated GTPase activity of Cdc42Hs. This binding is mediated by a unique sequence of 47 amino acids C-terminal to an SH3 domain. The protein may be involved in a regulatory mechanism that sustains the GTP-bound active form of Cdc42Hs and which is directly linked to a tyrosine phosphorylation signal transduction pathway. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified from this gene, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined.

Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4KB gene.

Band 4.1-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPB41L1 gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RASA3 gene.

Arf-GAP with GTPase, ANK repeat and PH domain-containing protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGAP1 gene.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.
Lewis C. Cantley is an American cell biologist and biochemist who has made significant advances to the understanding of cancer metabolism. Among his most notable contributions are the discovery and study of the enzyme PI-3-kinase, now known to be important to understanding cancer and diabetes mellitus. He is currently Meyer Director and Professor of Cancer Biology at the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City. He was formerly a professor in the Departments of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the Director of Cancer Research at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. In 2016, he was elected Chairman of the Board for the Hope Funds for Cancer Research.