Luteinizing hormone is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. In females, an acute rise of LH known as an LH surge, triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. It acts synergistically with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
Gonadotropins are glycoprotein hormones secreted by gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary of vertebrates. This family includes the mammalian hormones follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), the placental/chorionic gonadotropins, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG), as well as at least two forms of fish gonadotropins. These hormones are central to the complex endocrine system that regulates normal growth, sexual development, and reproductive function. LH and FSH are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, while hCG and eCG are secreted by the placenta in pregnant women and mares, respectively. The gonadotropins act on the gonads, controlling gamete and sex hormone production.
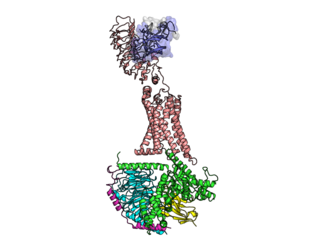
The luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (LHCGR), also lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor (LCGR) or luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR), is a transmembrane receptor found predominantly in the ovary and testis, but also many extragonadal organs such as the uterus and breasts. The receptor interacts with both luteinizing hormone (LH) and chorionic gonadotropins and represents a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Its activation is necessary for the hormonal functioning during reproduction.

Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5(IBF-5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGFBP5 gene. An IGFBP5 gene was recently identified as being important for adaptation to varying water salinity in fish.

Glycoprotein hormones, alpha polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGA gene.

Follitropin subunit beta also known as follicle-stimulating hormone beta subunit (FSH-B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSHB gene. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein.

A-kinase anchor protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AKAP5 gene.

Protein farnesyltransferase/geranylgeranyltransferase type-1 subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FNTA gene.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKACB gene.

Growth hormone 2 (GH2), also known more commonly as placental growth hormone (PGH) or growth hormone variant (GH-V), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GH2 gene. It is produced by and secreted from the placenta during pregnancy, and becomes the predominant form of growth hormone (GH) in the body during this time. Its cogener is growth hormone 1 (GH1), or pituitary growth hormone.

Choriogonadotropin subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGB7 gene.
Progonadoliberin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNRH2 gene.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKIA gene.

Choriogonadotropin subunit beta variant 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGB2 gene.

Troponin C, skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNC2 gene.

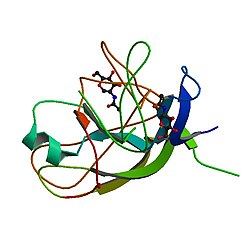
Luteinizing hormone subunit beta also known as lutropin subunit beta or LHβ is a polypeptide that in association with an alpha subunit common to all gonadotropin hormones forms the reproductive signaling molecule luteinizing hormone. In humans it is encoded by the LHB gene.

Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-1 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNG1 gene.

Thyroid stimulating hormone, beta also known as TSHB is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TSHB gene.

Choriogonadotropin subunit beta (CG-beta) also known as chorionic gonadotrophin chain beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGB gene.
Chorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGB5 gene.