
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome.

Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.
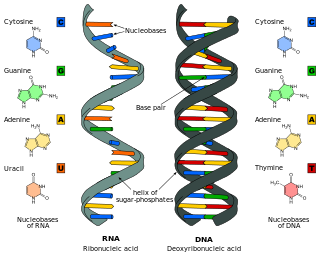
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA.

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself or by forming a template for the production of proteins. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.
A buffer solution is a solution where the pH does not change significantly on dilution or if an acid or base is added at constant temperature. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. In nature, there are many living systems that use buffering for pH regulation. For example, the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood, and bicarbonate also acts as a buffer in the ocean.
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small fragments of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression, or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules.
Gene knockdown is an experimental technique by which the expression of one or more of an organism's genes is reduced. The reduction can occur either through genetic modification or by treatment with a reagent such as a short DNA or RNA oligonucleotide that has a sequence complementary to either gene or an mRNA transcript.

A Morpholino, also known as a Morpholino oligomer and as a phosphorodiamidate Morpholino oligomer (PMO), is a type of oligomer molecule used in molecular biology to modify gene expression. Its molecular structure contains DNA bases attached to a backbone of methylenemorpholine rings linked through phosphorodiamidate groups. Morpholinos block access of other molecules to small specific sequences of the base-pairing surfaces of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Morpholinos are used as research tools for reverse genetics by knocking down gene function.

Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), also called diethyl dicarbonate, is used in the laboratory to inactivate RNase enzymes in water and on laboratory utensils. It does so by the covalent modification of histidine, lysine, cysteine, and tyrosine residues.

Lithium acetate (CH3COOLi) is a salt of lithium and acetic acid. It is often abbreviated as LiOAc.
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) is a buffer solution commonly used in biological research. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride and, in some formulations, potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH. The osmolarity and ion concentrations of the solutions match those of the human body (isotonic).
Good's buffers are twenty buffering agents for biochemical and biological research selected and described by Norman Good and colleagues during 1966–1980. Most of the buffers were new zwitterionic compounds prepared and tested by Good and coworkers for the first time, though some were known compounds previously overlooked by biologists. Before Good's work, few hydrogen ion buffers between pH 6 and 8 had been accessible to biologists, and very inappropriate, toxic, reactive and inefficient buffers had often been used. Many Good's buffers became and remain crucial tools in modern biological laboratories.
In chemical thermodynamics, conformational entropy is the entropy associated with the number of conformations of a molecule. The concept is most commonly applied to biological macromolecules such as proteins and RNA, but also be used for polysaccharides and other molecules. To calculate the conformational entropy, the possible conformations of the molecule may first be discretized into a finite number of states, usually characterized by unique combinations of certain structural parameters, each of which has been assigned an energy. In proteins, backbone dihedral angles and side chain rotamers are commonly used as parameters, and in RNA the base pairing pattern may be used. These characteristics are used to define the degrees of freedom. The conformational entropy associated with a particular structure or state, such as an alpha-helix, a folded or an unfolded protein structure, is then dependent on the probability of the occupancy of that structure.

MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) is a chemical compound that contains a morpholine ring. It has a molecular weight of 195.2 g/mol and the chemical formula is C6H13NO4S. Synonyms include: 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid; 2-(4-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid; 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid; 2-(4-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid; MES; MES hydrate; and morpholine-4-ethanesulfonic acid hydrate. MOPS is a similar pH buffering compound which contains a propanesulfonic moiety instead of an ethanesulfonic one.

Nuclease S1 is an endonuclease enzyme that splits single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and RNA into oligo- or mononucleotides. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, cytoplasmic, also known as Tyrosine-tRNA ligase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the YARS gene.

Monocarboxylate transporter 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC16A4 gene.
LB buffer, also known as lithium borate buffer, is a buffer solution used in agarose electrophoresis, typically for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It is made up of Lithium borate.

Aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) is a chemical compound that readily polymerizes in aqueous solution, forming a stable free radical that inhibits protein-nucleic acid interactions. It is a potent inhibitor of ribonuclease and topoisomerase II by preventing the binding of the nucleic acid to the enzyme. It stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation processes including the Jak2/STAT5 pathway in NB2 lymphoma cells, ErbB4 in neuroblastoma cells, and MAP kinases, Shc proteins, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase and phospholipase Cγ in PC12 cells. It also inhibits apoptosis. It prevents down-regulation of Ca2+-impermeable GluR2 receptors and inhibits calpain, a Ca2+-activated protease that is activated during apoptosis.

Vinylsulfonic acid is the organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHSO3H. It is the simplest unsaturated sulfonic acid. The C=C double bond is a site of high reactivity. Polymerization gives polyvinylsulfonic acid, especially when used as a comonomer with functionalized vinyl and (meth)acrylic acid compounds. It is a colorless, water-soluble liquid, although commercial samples can appear yellow or even red.













