Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

The Carbon Trust was developed and launched in the UK over 1999–2001 as part of the development of the Climate Change Levy (CCL), a tax on business energy use that still operates today. The Carbon Trust was originally funded by around £50m of UK tax revenue generated from the Levy to help businesses reduce energy costs and therefore offset the additional cost of paying the CCL. The establishment of the Carbon Trust was announced in the 2000 UK White Paper "Climate Change - the UK Programme". It was launched alongside the introduction of the CCL in March–April 2001.
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.

Carbon offsetting is a trading mechanism that allows entities such as governments, individuals, or businesses to compensate for (i.e. “offset”) their greenhouse gas emissions by supporting projects that reduce, avoid, or remove emissions elsewhere. In other words, carbon offsets focus on offsetting emissions through investments in emission reduction projects. When an entity invests in a carbon offsetting program, it receives carbon credits, i.e "tokens" used to account for net climate benefits from one entity to another. A carbon credit or offset credit can be bought or sold after certification by a government or independent certification body. One carbon offset or credit represents a reduction, avoidance or removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide or its carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e).
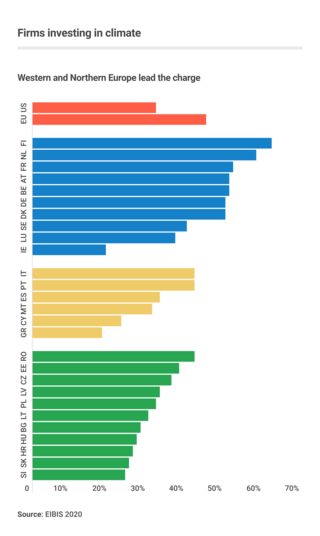
Business action on climate change includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.

Clean technology, in short cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.

A sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus will also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register, a visual artist, first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.
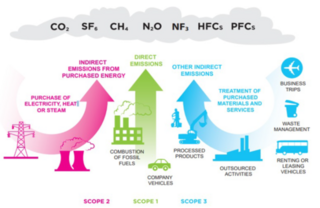
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.
The Gold Standard (GS), or Gold Standard for the Global Goals, is a standard and logo certification mark program, for non-governmental emission reductions projects in the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), the Voluntary Carbon Market and other climate and development interventions. It is published and administered by the Gold Standard Foundation, a non-profit foundation headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It was designed with an intent to ensure that carbon credits are real, verifiable, and that projects make measurable contributions to sustainable development. The objective of the GS is to add branding, with a quality label, to carbon credits generated by projects which can then be bought and traded by countries that have a binding legal commitment according to the Kyoto Protocol, businesses, or other organizations for carbon offsetting purposes.

Clean fuel may refer to type of fuel used for transport or a type of fuel used for cooking and lighting. With regards to cooking, the Sustainable Development Goal 7 aims to "Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all." Clean fuel there is defined by the emission rate targets and specific fuel recommendations included in the normative guidance WHO guidelines for indoor air quality. Clean fuel is one component of sustainable energy.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However, the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020, 27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation, 25% from electricity, 24% from industry, 13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021, the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States, as well as worldwide.

ClimateCare is a profit for purpose environmental and social impact company known for its role providing carbon offset services, with a particular focus on using carbon and other results based finance to support its 'Climate+Care Projects'. It also provides businesses and governments with sustainable development programmes, environmental and social impact measurement and project development.
The International Carbon Reduction and Offset Alliance (ICROA) is an industry trade group for providers of voluntary carbon offsets. It was established in 2008, and aims to promote industry self-regulation based on its ICROA Code of Best Practices. Members produce an annual report demonstrating compliance with the ICROA Code.
PAS 2060 is a specification detailing how to demonstrate carbon neutrality produced and published by the British Standards Institution.

The Climate and Development Knowledge Network (CDKN) works to enhance the quality of life for the poorest and most vulnerable to climate change. CDKN does this by combining research, advisory services and knowledge management in support of locally owned and managed policy processes. It works in partnership with decision-makers in the public, private and non-governmental sectors nationally, regionally and globally.
South Pole is a Swiss carbon finance consultancy founded in 2006 in Zurich, Switzerland. South Pole's business covers project and technology finance, data and advisory on sustainability risks and opportunities, as well as the development of environmental commodities such as carbon and renewable energy credits. The company has 23 offices across Europe, Africa, Asia Pacific, North America and South America.
Atmosfair is an independent German non-profit organization which offers offsets for greenhouse gases emitted by aircraft, cruise ships, long-distance coaches, and events. The organization, founded in 2005, develops and finances small-scale energy efficiency and renewable energy projects in developing countries, which lead to reduced carbon emissions. Atmosfair has repeatedly won acclaim for operating with a high degree of transparency and accountability, as well as efficient use of funds.

Sustainable Development Goal 13 is to limit and adapt to climate change. It is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The official mission statement of this goal is to "Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts". SDG 13 and SDG 7 on clean energy are closely related and complementary.
Klima is a carbon offsetting mobile application created by Climate Labs GmbH with headquarters in Berlin. The company was formed in 2019 and is the third to have been founded jointly by serial entrepreneurs Markus Gilles, Andreas Pursian-Ehrlich, and Jonas Brandau. Klima's mission is "to turn carbon neutrality into a mass movement and unleash the power of individual action at scale."

Global net zero emissions describes the state where emissions of carbon dioxide due to human activities and removals of these gases are in balance over a given period. It is often called simply net zero. In some cases, emissions refers to emissions of all greenhouse gases, and in others it refers only to emissions of carbon dioxide. To reach net zero targets requires actions to reduce emissions. One example would be by shifting from fossil fuel energy to sustainable energy sources. Organizations often offset their residual emissions by buying carbon credits.















