San Marino, officially the Most Serene Republic of San Marino and also known as the Republic of San Marino, is the oldest existing representative republic and the European state with the smallest population, apart from Vatican City. It is the larger of the two microstates surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern side of the Apennine Mountains, it is the fifth-smallest country in the world, with a land area of just over 61 km2 and a population of 33,642, as of 2023.

The Republic of San Marino's public transport network consists of a local bus network and the Funivia di San Marino, an aerial cablecar system between Borgo Maggiore and the City of San Marino. Both means are operated by the Azienda Autonoma di Stato per i Servizi Pubblici, the Sammarinese state company for public transport.

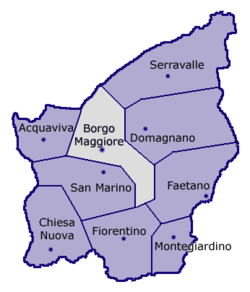
Borgo Maggiore is one of the nine castelli of San Marino. It lies at the foot of Monte Titano and has a population of 6,871, making it the second largest town of San Marino after Dogana.

S.P. Cailungo is a Sanmarinese football club, based in Cailungo, a civil parish of Borgo Maggiore. The club was founded in 1974. Cailungo currently plays in Girone A of Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio. The team's colors are red and green.

The Catholic Church in San Marino is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the leadership of the Pope in Rome.

Valdragone is a settlement in San Marino comprising two curazie, Valdragone di Sopra and Valdragone di Sotto, in the castello of Borgo Maggiore.
The 2008–09 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the twenty-fourth since its establishment. The season began with the first regular season games on 12 September 2008 and ended with the play-off final on 29 May 2009.

This page list topics related to San Marino.
The 2009–10 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the twenty-fifth since its establishment. The season began in September 2009 and ended with the playoff final in May 2010. Tre Fiori were the defending league champions, having won their fifth Sammarinese championship the previous season.
The 2010–11 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the twenty-sixth since its establishment. The season began with the first regular season games on 17 September 2010 and ended with the play-off final in May 2011. Tre Fiori are the league champions, having won their seventh Sammarinese championship and third-in-a-row last season.
The 2011–12 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the twenty-seventh since its establishment. The season began with the first regular season games on 17 September 2011 and ended with the play-off final in May 2012. Tre Fiori are the defending league champions, having won their seventh Sammarinese championship and third-in-a-row last season. The title was won by S.P. Tre Penne.
The 2012–13 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the twenty-eighth since its establishment. The league is the uppermost in San Marino, in which the country's top 15 amateur football clubs play. The season began on 14 September 2012 and ended with the play-off final in May 2013. Tre Penne are the defending league champions, having won their first ever Sammarinese championship last season. Tre Penne retained their title, defeating ten-man AC Libertas 5–3 on penalties in a repeat of the previous year's play-off final.
The 2014–15 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the thirtieth since its establishment. It is the highest level in San Marino, in which the country's top 15 amateur football clubs play. The season began on 12 September 2014 and ended with the play-off final on 26 May 2015.
The 2015–16 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the thirty-first since its establishment. It is the highest level in San Marino, in which the country's top 15 amateur football clubs play. The season began on 11 September 2015 and ended with the play-off final on 26 May 2016. Folgore/Falciano were the defending champions.

The San Marino cablecar system, also advertised as the San Marino Ropeway, is an aerial cablecar system in the Republic of San Marino. The line runs between a lower terminus of Borgo Maggiore to an upper terminus in the City of San Marino.
The 2016–17 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio season was the 32nd since its establishment. It is the only level in San Marino, in which all the country's 15 amateur football clubs play. The season began on 9 September 2016 and ended with the play-off final on 20 May 2017. Tre Penne were the defending champions. The fixtures and group compositions were announced on 27 August 2016.
The 2017–18 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio was the 33rd season since its establishment. It is the highest level in San Marino, in which the country's top 15 amateur football clubs played. The season begin on 8 September 2017 and concluded with the play-off final on 23 May 2018. La Fiorita were the defending champions from the previous season. The fixtures and group compositions were announced on 19 August 2017.

The Rimini–San Marino railway was a 31.5-kilometre (19.6-mile) electrified narrow-gauge railway that connected Rimini, Italy, with the City of San Marino, Republic of San Marino.
The 2004 San Marino local elections were held on 18 April to elect the mayor and the council of the municipalities of Borgo Maggiore, in San Marino, as the 2003 Sammarinese local elections was declared invalid, as the turnout quorum was not reached. Turnout in this election was 61.5%.
The 2021–22 Campionato Sammarinese di Calcio was the 37th season of league competition in San Marino, in which the country's top 15 amateur football teams competed. The season began on 18 September 2021 and ended on 26 May 2022. The winners of the league, La Fiorita qualified for a place in the 2022–23 UEFA Champions League. Runners-up, Tre Penne qualified for a place in the 2022–23 UEFA Europa Conference League.