
There are 459 properties and historic districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places in North Dakota. There are listings in 52 of North Dakota's 53 counties.

Hastings Methodist Episcopal Church is a church building located at 719 Vermillion Street in downtown Hastings, Minnesota, United States, listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It is significant for its Gothic Revival, Greek Revival, and Italianate architecture. The building exterior is clapboard with a characteristic tower including abat-sons and emphatic eaves supported by corbels. It is the oldest church building in Hastings, originally built in 1862 on 5th Street, it was moved to its present location in 1871; at that time the tower was added. The building is currently used by the Life Tabernacle Pentecostal Church.

The Church of the Advent built in 1872 is a historic Carpenter Gothic Episcopal church located at 412 Oak Street, in Farmington, Minnesota, in the United States. On December 31, 1979, it was added to the National Register of Historic Places.
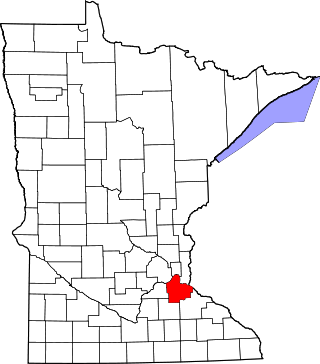
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Dakota County, Minnesota. It is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Dakota County, Minnesota, United States. Dakota County is located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Minnesota, bounded on the northeast side by the Upper Mississippi River and on the northwest by the Minnesota River. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.

The former Old Stone Church, also known as Calvary Episcopal Chapel, is an historic stone Late Gothic Revival-style Episcopal church building located at 206 North Wilcox Avenue in Buffalo, North Dakota. Built in 1885, it was designed by British architect George Hancock and built by Angus Beaton. Calvary Episcopal Chapel held its first services on October 15, 1886. In 1934, after years of many closings and reopenings, Calvary closed for the final time. In 1936, the building was bought by Buffalo Lodge No. 77 of the Ancient, Free & Accepted Masons. In the 1970s Buffalo No. 77 closed and in 1982 was merged with Casselton Lodge No. 3. In 1985, the Masons donated it to the Buffalo Historical Society, which 10 years later restored it. It is now called the Old Stone Church Heritage Center. On October 22, 1995, the Buffalo Historical Society received national recognition for its efforts from the National Trust for Historic Preservation. On March 29, 1996, the Old Stone Church was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

The former St. Stephen's Episcopal Church also known as St. Stephen's Church, is an historic stone Gothic Revival-style Episcopal church building located on the southeast corner of 3rd Avenue and 5th Street in Casselton, North Dakota, United States.

The Methodist Episcopal Church in Scotland, South Dakota is a former Methodist church located at 811 6th Street. It was built in 1872. In 1979 it was added to the National Register of Historic Places. As of that date, it was the Heritage Museum-Chapel.

St. John the Divine Episcopal Church, also known as St. John's Episcopal Church, is a church in Moorhead, Minnesota, United States. It was built 1898–99 in Shingle Style and is considered Moorhead's leading architectural landmark and one of Cass Gilbert's most interesting churches. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

George Hancock was an architect active in North Dakota, Montana and Minnesota.
Grace Episcopal Church is a historic Episcopal church building is located at 210 C Avenue, South, in Minnewaukan, Benson County, North Dakota.

Grace Episcopal Church is an historic Episcopal church building located at 405 2nd Avenue, North East, in Jamestown, Stutsman County, North Dakota. Designed in the Late Gothic Revival style of architecture by British-born Fargo architect George Hancock, it was built 1884 of local fieldstone exterior walls and a wooden roof. Early parish records contain several assertions that George Hancock modeled the church after Christ Episcopal Church which had been opened in 1881, but if he did, it was only in a very general, not specific way. Hancock's later work St. Stephen's Episcopal Church is much more closely related to Christ Church, Medway. On December 3, 1992, Grace Episcopal Church was added to the National Register of Historic Places.

Grace Episcopal Church is an historic Episcopal church building located at 152 Ramsey Street, West in Pembina, Pembina County, North Dakota. Designed in the Late Gothic Revival style of architecture by Fargo architect George Hancock, it was built in 1886. Unlike all the other churches in the Episcopal Churches of North Dakota Multiple Property Submission (MPS), it was built of brick instead of local fieldstone. The brick is yellow and was made locally by the Pembina Brick Company. The church building is one of only three extant building built of this brick. In 1937 Grace Church closed due to declining attendance and the building was sold by the Episcopal Diocese of North Dakota to the local Methodist congregation. Today it is the Pembina Pioneer Memorial United Methodist Church. On September 2, 1994, the building was added to the National Register of Historic Places as Grace Episcopal Church.

The Former North Dakota Executive Mansion, also or formerly known as Old Governor's Mansion or Asa Fisher House, at 320 Ave. B., E., in Bismarck, North Dakota, was built in 1893.

The Rudolf Hotel in Valley City, North Dakota is a three-story hotel building that was built in 1907. It was designed by John W. Ross in Classical Revival style. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983.

The Episcopal Church of the Advent-Guild Hall on 6th St. E. in Devil's Lake, North Dakota was built in 1886. It has also been known as Stone Church. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.
The High Butte Effigy and Village Site (32ME13) is an ancient Native American ceremonial site near the Garrison Dam and Riverdale, North Dakota. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. It is located atop a butte and includes a "turf cut turtle effigy." Items recovered from the site include 14 points, 24 body sherds, five rim sherds, and a grooved paddle.

Gethsemane Episcopal Cathedral is an Episcopal cathedral in Fargo, North Dakota, United States. It is the seat of the Diocese of North Dakota.

The St. James Episcopal Church and Rectory in Bozeman, Montana was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1987. The listing included two contributing buildings.

St. George's Episcopal Memorial Church, a historic Episcopal church in Bismarck, North Dakota's capital, is unique for its construction incorporating stained glass from English churches bombed in World War II into its own stained-glass windows. It is located in the Episcopal Diocese of North Dakota and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2021. The building, completed in 1949, replaced an early one dating to 1881 in the Dakota Territory, prior to statehood in 1889. The original building was built on railroad-donated land in the first decade of the city's growth. The church needed more space by the 1930s but was unable to erect a larger building until after World War II. The original building was moved and repurposed as a museum at Camp Hancock State Historic Site. The newer building is notable for being constructed of pumice concrete and its unique stained-glass windows. The windows were made in England by Barton, Kinder, and Alderson, and the majority of them contained pieces of glass that were salvaged from dozens of damaged churches in southeast England during World War II. The glass studio documented the lineage of each window, with some made with glass collected from churches built in the Middle Ages.




















