The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure. Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner. Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.

Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites. This tumor most often occurs in the salivary glands, but it can also be found in many anatomic sites, including the breast, lacrimal gland, lung, brain, Bartholin gland, trachea, and the paranasal sinuses.
An oncocytoma is a tumor made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells characterized by an excessive amount of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. The cells and the tumor that they compose are often benign but sometimes may be premalignant or malignant.

Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers. It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, who described two cases in 1929.

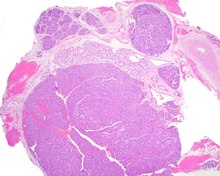
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance.

A perianal gland tumor is a type of tumor found near the anus in dogs that arises from specialized glandular tissue found in the perineum. It is also known as a hepatoid tumor because of the similarity in cell shape to hepatocytes. It is most commonly seen in intact dogs and is the third most common tumor type in intact male dogs. There are two types of perianal gland tumors, perianal gland adenomas, which are benign, and perianal gland adenocarcinomas, which are malignant. Both have receptors for testosterone. Perianal gland adenomas are three times more likely to be found in intact male dogs than females, and perianal gland adenocarcinomas are ten times more common in male dogs than females. The most commonly affected breeds for adenomas are the Siberian Husky, Cocker Spaniel, Pekingese, and Samoyed; for adenocarcinomas the most commonly affected breeds are the Siberian Husky, Bulldog, and Alaskan Malamute.
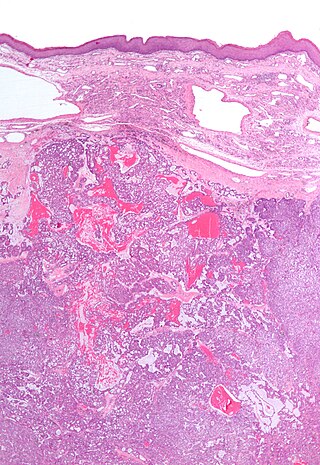
Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma (PLGA) is a rare, asymptomatic, slow-growing malignant salivary gland tumor. It is most commonly found in the palate.

Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor representing 2% of all salivary tumors. 90% of the time found in the parotid gland, 10% intraorally on buccal mucosa or palate. The disease presents as a slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness in 50% of the cases. Often appears pseudoencapsulated.

Salivary gland tumours, also known as mucous gland adenomas or neoplasms, are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800 to 1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity. Patients with these types of tumours may be asymptomatic.
A mixed tumor is a tumor that derives from multiple tissue types. A biplastic tumor or biphasic tumor has two tissue types.
Juxtaglomerular cell tumor is an extremely rare kidney tumour of the juxtaglomerular cells, with fewer than 100 cases reported in literature. This tumor typically secretes renin, hence the former name of reninoma. It often causes severe hypertension that is difficult to control, in adults and children, although among causes of secondary hypertension it is rare. It develops most commonly in young adults, but can be diagnosed much later in life. It is generally considered benign, but its malignant potential is uncertain.

Myoepithelioma of the head and neck, also myoepithelioma, is a salivary gland tumour of the head and neck that is usually benign. When malignant, which is exceedingly rare, they are known as malignant myoepithelioma or Myoepithelial carcinoma, and they account for 1% of the salivary tumors with poor prognosis.
A sialoblastoma is a low-grade salivary gland neoplasm that recapitulates primitive salivary gland anlage. It has previously been referred to as congenital basal cell adenoma, embryoma, or basaloid adenocarcinoma. It is an extremely rare tumor, with less than 100 cases reported worldwide.
A ceruminous adenoma is a benign glandular neoplasm which arises from the ceruminous glands located within the external auditory canal. These glands are found within the outer one third to one half of the external auditory canal, more common along the posterior surface; therefore, the tumor develops within a very specific location.
Neuroendocrine adenoma middle ear (NAME) is a tumor which arises from a specific anatomic site, the middle ear. NAME is a benign glandular neoplasm of middle ear showing histologic and immunohistochemical neuroendocrine and mucin-secreting differentiation.

Ceruminous adenocarcinoma is a malignant neoplasm derived from ceruminous glands of the external auditory canal. This tumor is rare, with several names used in the past. Synonyms have included cylindroma, ceruminoma, ceruminous adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS), ceruminous adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC), and ceruminous mucoepidermoid carcinoma.

Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma is a type of cancer typically found in the parotid gland. It arises from the benign tumour pleomorphic adenoma.

A parotidectomy is the surgical excision (removal) of the parotid gland, the major and largest of the salivary glands. The procedure is most typically performed due to neoplasms (tumors), which are growths of rapidly and abnormally dividing cells. Neoplasms can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The majority of parotid gland tumors are benign, however 20% of parotid tumors are found to be malignant. Parotidectomy is performed mostly by oral and maxillofacial surgeon and ENT surgeon.
Ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor (ECT) is a benign intraoral tumor with presumed origin from undifferentiated (ecto)mesenchymal cells. There are some who think it is a myoepithelial tumor type.