
Physcia stellaris is a species of lichen. It is pale grey, but darker in the centre, and lacks isidia, lobules, soredia and pruina.It tests positive K+ yellow upper cortex with a 10% potassium hydroxide solution. In North America, it is known colloquially as the fringed rosette lichen.
Irwin M. Brodo is an emeritus scientist at the Canadian Museum of Nature, in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He is an authority on the identification and biology of lichens. Irwin Brodo was honored in 1994 with an Acharius Medal presented to him by the International Association for Lichenology.

Soredia are common reproductive structures of lichens. Lichens reproduce asexually by employing simple fragmentation and production of soredia and isidia. Soredia are powdery propagules composed of fungal hyphae wrapped around cyanobacteria or green algae. These can be either scattered diffusely across the surface of the lichen's thallus, or produced in localized structures called soralia. Fungal hyphae make up the basic body structure of lichen. The soredia are released through openings in the upper cortex of the lichen structure. After their release, the soredia disperse to establish the lichen in a new location.

Chrysothrix candelaris, commonly known as the mustard powder lichen or gold dust lichen, is a species of leprose (powdery) lichen in the family Chrysothricaceae. It typically grows on tree bark, although it has also been recorded growing on rock. It does not show ascocarps or other reproductive structures, belonging to the group commonly known as the 'Fungi or lichens imperfecti' in the UK.

A foliose lichen is a lichen with flat, leaf-like lobes, which are generally not firmly bonded to the substrate on which it grows. It is one of the three most common growth forms of lichens. It typically has distinct upper and lower surfaces, each of which is usually covered with a cortex; some, however, lack a lower cortex. The photobiont layer lies just below the upper cortex. Where present, the lower cortex is usually dark, but occasionally white. Foliose lichens are attached to their substrate either by hyphae extending from the cortex or medulla, or by root-like structures called rhizines. The latter, which are found only in foliose lichens, come in a variety of shapes, the specifics of which can aid in species identification. Some foliose lichens attach only at a single stout peg called a holdfast, typically located near the lichen's centre. Lichens with this structure are called "umbilicate". In general, medium to large epiphytic foliose lichens are moderately sensitive to air pollution, while smaller or ground-dwelling foliose lichens are more tolerant. The term "foliose" derives from the Latin word foliosus, meaning "leafy".

Lasallia papulosa is an umbilicate lichen. It is in the family Umbilicariaceae.

Lichens are symbiotic organisms made up of multiple species: a fungus, one or more photobionts and sometimes a yeast. They are regularly grouped by their external appearance – a characteristic known as their growth form. This form, which is based on the appearance of vegetative part of the lichen, varies depending on the species and the environmental conditions it faces. Those who study lichens (lichenologists) have described a dozen of these forms: areolate, byssoid, calicioid, cladoniform, crustose, filamentous, foliose, fruticose, gelatinous, leprose, placoidioid and squamulose. Traditionally, crustose (flat), foliose (leafy) and fruticose (shrubby) are considered to be the three main forms. In addition to these more formalised, traditional growth types, there are a handful of informal types named for their resemblance to the lichens of specific genera. These include alectorioid, catapyrenioid, cetrarioid, hypogymnioid, parmelioid and usneoid.

Baeomyces rufus, commonly known as the brown beret lichen, is a fruticose lichen belonging to the cap lichen family, Baeomycetaceae. The species was first described by J.F Rebentisch in 1804. Like other lichens, it is a symbiosis between a fungus and an alga.

Physcia caesia, known colloquially as blue-gray rosette lichen and powder-back lichen, is a species of foliose lichenized fungus. First described by Georg Franz Hoffmann in 1784, it is common across much of Europe, North America and New Zealand, and more patchily distributed in South America, Asia, Australia and Antarctica. There are 2 subspecies: P. c. caesia and P. c. ventosa, as well as a number of distinct forms and varieties. Molecular studies suggest that the species as currently defined may be polyphyletic. It is typically pale gray shading to darker gray in the center, and grows in a small rosette, usually some 2–3 cm (0.79–1.18 in) across at maturity. It only rarely has apothecia, instead reproducing most often vegetatively via soredia, which are piled in round blue-gray mounds across the thallus's upper surface. It grows most often on rock—principally calcareous, but also basaltic and siliceous—and also occurs on bone, bark and soil. It is nitrophilic and is particularly common on substrates where birds perch.

Peltigera venosa, commonly known as the fan lichen, is a species of foliose lichen in the family Peltigeraceae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1753 work Species Plantarum as Lichen venosus. German botanist Georg Franz Hoffmann transferred it to the genus Peltigera in 1789. P. venosa can be found in temperate and boreal regions of North America, Europe, and Asia, while occasionally being found in drier climates such as mountainous Arizona.

Bryoria nadvornikiana, commonly known as the spiny grey horsehair lichen or the blonde horsehair lichen, is a species of horsehair lichen in the family Parmeliaceae.

Cladonia coniocraea, commonly known as the common powderhorn or the powderhorn cup lichen, is a species of fruticose, cup lichen in the family Cladoniaceae. It was first described by Heinrich Gustav Flörke in 1821 under the name Cenomyce coniocraea, until Kurt Polycarp Joachim Sprengel reclassified it under the genus Cladonia in 1827.

Cladonia cervicornis is a species of cup lichen in the family Cladoniaceae. It was first described by Swedish lichenologist Erik Acharius in 1799 as Lichen cervicornis. Julius von Flotow transferred it to the genus Cladonia in 1849. In North America, it is colloquially known as the ladder lichen or elk's-horn cup lichen.

Cladonia incrassata or the powder-foot British soldiers cup lichen is a species of cup lichen in the family Cladoniaceae. Found in Europe and North America, it was formally described as a new species in 1828 by German botanist Heinrich Gustav Flörke. A colloquial name for the lichen is "powder-foot British soldiers".

Candelaria pacifica is a widely distributed corticolous (bark-dwelling), leprose lichen. It was formally described as a species in 2011.

Candelaria concolor, commonly known as the candleflame lichen or the lemon lichen, is an ascomycete of the genus Candelaria. It is a small foliose lichen dispersed globally.

The following outline provides an overview of and topical guide to lichens.
A bryophilous lichen is one that grows on a bryophyte – that is, on a moss or liverwort. Those which grow on mosses are known as muscicolous lichens, while those grow on liverworts are called hepaticolous lichens. Muscicolous derives from the Latin muscus meaning moss, while the suffix colous means "living or growing in or on". Lichens are slow-growing organisms, and so are far more likely to be overgrown by a bryophyte than to overgrow one. However, they are better able to compete if the bryophyte is sickly or decaying and they can be parasitic upon them. Some, rather than overgrowing the bryophyte, instead live among its branches. Bryophilous lichens are particularly common in heathland and arctic or alpine tundra. Because many are small and inconspicuous, they are easy to overlook.
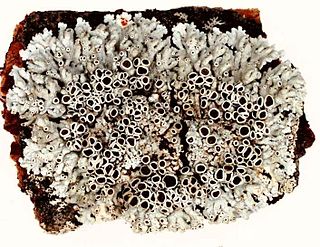
Physcia aipolia, commonly known as the Hoary rosette lichen, is a lichen species of fungus in the genus Physcia, and family Lecanoromycetes. Physcia aipolia is a species of lichen in the family Physciaceae. It has a worldwide distribution.Physcia aipolia is a known host species to the lichenicolous fungus species Muellerella lichenicola. It is characterized by the pale blue to gray thallus with many apothecia. Physcia aipolia is a common, widely distributed species, and can be found growing on a variety of trees and branches.
Opeltiella fibrosoides is a species of lichen-forming fungus in the family Candelariaceae. It is known to occur only in a single location in Peru, where lichen thrives in a high-altitude environment, specifically on shrubs and cacti in an open pasture land. It was formally described as a new species by Swedish lichenologists Martin Westberg and Patrik Frödén in 2007, first as a member of the genus Candelaria. Although it bears a striking resemblance to C. fibrosa on the surface, it is differentiated by its eight-spored asci and a thallus featuring an ecorticate lower surface. In 2020, Sergey Kondratyuk transferred the taxon to the newly circumscribed genus Opeltiella, following molecular phylogenetic-based analysis of the family Candelariaceae.

















