Related Research Articles

Leishmania is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus Leishmania that is responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus Phlebotomus in the Old World, and of the genus Lutzomyia in the New World. At least 93 sandfly species are proven or probable vectors worldwide. Their primary hosts are vertebrates; Leishmania commonly infects hyraxes, canids, rodents, and humans.
Ehrlichiosis is a tick-borne disease of dogs usually caused by the rickettsial agent Ehrlichia canis. Ehrlichia canis is the pathogen of animals. Humans can become infected by E. canis and other species after tick exposure. German Shepherd Dogs are thought to be susceptible to a particularly severe form of the disease; other breeds generally have milder clinical signs. Cats can also be infected.
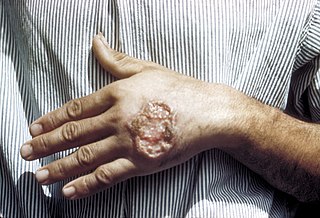
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus Leishmania. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, Phlebotomus and Lutzomyia, and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver.

Lutzomyia is a genus of phlebotomine sand flies consisting of nearly 400 species, at least 33 of which have medical importance as vectors of human disease. Species of the genus Lutzomyia are found only in the New World, distributed in southern areas of the Nearctic and throughout the Neotropical realm. Lutzomyia is one of the two genera of the subfamily Phlebotominae to transmit the Leishmania parasite, with the other being Phlebotomus, found only in the Old World. Lutzomyia sand flies also serve as vectors for the bacterial Carrion's disease and a number of arboviruses.

Phlebotomus is a genus of "sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance.
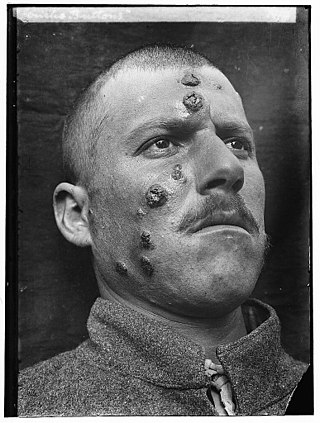
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.
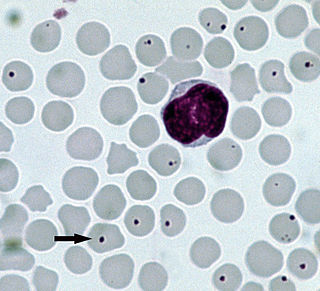
Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease affecting ruminants, dogs, and horses, and is caused by Anaplasma bacteria. Anaplasmosis is an infectious but not contagious disease. Anaplasmosis can be transmitted through mechanical and biological vector processes. Anaplasmosis can also be referred to as "yellow bag" or "yellow fever" because the infected animal can develop a jaundiced look. Other signs of infection include weight loss, diarrhea, paleness of the skin, aggressive behavior, and high fever.

Ehrlichiosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection, caused by bacteria of the family Anaplasmataceae, genera Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. These obligate intracellular bacteria infect and kill white blood cells.

The discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety.
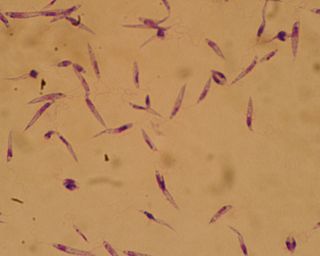
Leishmania major is a species of parasite found in the genus Leishmania, and is associated with the disease zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. L. major is an intracellular pathogen which infects the macrophages and dendritic cells of the immune system. Though Leishmania species are found on every continent aside from Antarctica, Leishmania major is found only in the Eastern Hemisphere, specifically in Northern Africa, the Middle East, Northwestern China, and Northwestern India.

In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking insects such as mosquitoes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected the stomach tissue of a mosquito.

Canine leishmaniasis (LEESH-ma-NIGH-ah-sis) is a zoonotic disease caused by Leishmania parasites transmitted by the bite of an infected phlebotomine sandfly. There have been no documented cases of leishmaniasis transmission from dogs to humans. Canine leishmaniasis was first identified in Europe in 1903, and in 1940, 40% of all dogs in Rome were determined to be positive for leishmaniasis. Traditionally thought of as a disease only found near the Mediterranean basin, 2008 research claims new findings are evidence that canine leishmaniasis is currently expanding in continental climate areas of northwestern Italy, far from the recognized disease-endemic areas along the Mediterranean coasts. Cases of leishmaniasis began appearing in North America in 2000, and, as of 2008, Leishmania-positive foxhounds have been reported in 22 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces.

Rhipicephalus sanguineus, commonly called the brown dog tick, kennel tick, or pantropical dog tick, is a species of tick found worldwide, but more commonly in warmer climates. This species is unusual among ticks in that its entire lifecycle can be completed indoors. The brown dog tick is easily recognized by its reddish-brown color, elongated body shape, and hexagonal basis capituli. Adults are 2.28 to 3.18 mm in length and 1.11 to 1.68 mm in width. They do not have ornamentation on their backs.

Leishmania donovani is a species of intracellular parasites belonging to the genus Leishmania, a group of haemoflagellate kinetoplastids that cause the disease leishmaniasis. It is a human blood parasite responsible for visceral leishmaniasis or kala-azar, the most severe form of leishmaniasis. It infects the mononuclear phagocyte system including spleen, liver and bone marrow. Infection is transmitted by species of sandfly belonging to the genus Phlebotomus in Old World and Lutzomyia in New World. The species complex it represents is prevalent throughout tropical and temperate regions including Africa, China, India, Nepal, southern Europe, Russia and South America. The species complex is responsible for thousands of deaths every year and has spread to 88 countries, with 350 million people at constant risk of infection and 0.5 million new cases in a year.

Leishmania tropica is a flagellate parasite and the cause of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans. This parasite is restricted to Afro-Eurasia and is a common cause of infection in Afghanistan, Iran, Syria, Yemen, Algeria, Morocco, and northern India.
Leishmania braziliensis is a Leishmania species found in South America. It is associated with leishmaniasis.
Ehrlichia canis is an obligate intracellular bacterium that acts as the causative agent of ehrlichiosis, a disease most commonly affecting canine species. This pathogen is present throughout the United States, South America, Asia, Africa and recently in the Kimberley region of Australia. First defined in 1935, E. canis emerged in the United States in 1963 and its presence has since been found in all 48 contiguous United States. Reported primarily in dogs, E. canis has also been documented in felines and humans, where it is transferred most commonly via Rhipicephalus sanguineus, the brown dog tick.
Kala azar in India refers to the special circumstances of the disease kala azar as it exists in India. Kala azar is a major health problem in India with an estimated 146,700 new cases per year as of 2012. In the disease a parasite causes sickness after migrating to internal organs such as the liver, spleen and bone marrow. If left untreated the disease almost always results in the death. Signs and symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen.

A Leishmaniasis vaccine is a vaccine which would prevent leishmaniasis. As of 2017, no vaccine for humans was available. Currently some effective leishmaniasis vaccines for dogs exist.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Domenico Otranto, Filipe Dantas-Torres & Edward B. Breitschwerdt, Managing canine vector-borne diseases of zoonotic concern: part one, Trends in Parasitology Vol. 25, Issue 4, pp. 157–163 (April 2009).
- ↑ "First Canine Vector-Borne Disease Symposium in Billesley, UK" (Press release). Bayer HealthCare. April 2006. Archived from the original on 2006-10-18. Retrieved 2005-11-16.
- ↑ Beugnet, F., & Franc, M. (2012). Insecticide and acaricide molecules and/or combinations to prevent pet infestation by ectoparasites. Trends in parasitology, 28(7), 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2012.04.004
- ↑ Eisen, L., & Stafford, K. C. (2021). Barriers to Effective Tick Management and Tick-Bite Prevention in the United States (Acari: Ixodidae). Journal of medical entomology, 58(4), 1588–1600. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjaa079
- ↑ Palatnik-de-Sousa C. B. (2012). Vaccines for canine leishmaniasis. Frontiers in immunology, 3, 69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00069
- ↑ Reithinger, R., & Davies, C. R. (2002). Canine leishmaniasis: novel strategies for control. Trends in parasitology, 18(7), 289–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1471-4922(02)02296-1
- ↑ Stanneck, D., Kruedewagen, E. M., Fourie, J. J., Horak, I. G., Davis, W., & Krieger, K. J. (2012). Efficacy of an imidacloprid/flumethrin collar against fleas, ticks, mites and lice on dogs. Parasites & vectors, 5, 102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-102