| Canton of Lugano Cantone Lugano | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canton of the Helvetic Republic | |||||||||||||||
| 1798–1803 | |||||||||||||||
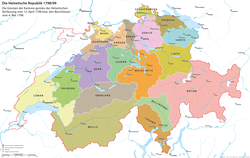 The Helvetic Republic, as at the constitution of 12 April 1798, showing the canton of Lugano in orange-brown, lower-centre. Bellinzona is shown immediately to Lugano's north, in green. | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Lugano | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
| 12 April 1798 | |||||||||||||||
• Canton established | 14 April 1798 | ||||||||||||||
| 19 February 1803 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Lugano was the name of a canton of the Helvetic Republic from 1798 to 1803, with its capital at Lugano. The canton unified the former Landvogteien of Lugano, Mendrisio, Locarno and Valmaggia.
As with the other cantons of the Helvetic Republic, the autonomy of Lugano was very limited, the republic having been founded by Napoleon in order to further centralise power in Switzerland. The canton was led by a Directory of five members, who appointed a "national préfet", the first of whom was Giacomo Buonvicini.
The canton was riven with dispute between "patriots", supporting the Cisalpine Republic, and traditionalist "aristocrats". The politics of the central government — the seizure of church property, the introduction of direct taxation, mandatory military service, an amnesty favouring Cisalpine patriots and a law regarding municipalities that rejected the secular tradition of communal autonomy — as well as the military occupation by the French Revolutionary Armies, with its associated violence and requisitions, all combined to maintain a level of hostility to the new régime within the local population, which eventually rose up against the régime.
In Lugano, during anti-French protests of 28 and 29 April 1799, the printer Agnelli's was looted and the abbot Giuseppe Lodovico Maria Vanelli and other Cisalpine patriots were killed; the préfet Francesco Capra, who succeeded Buonvicini earlier that year, fled and power passed to a provisional government sympathetic to the Habsburgs. Similar protests erupted in Mendrisio and Locarno. The arrival of Austro-Russian troops led to further requisition and pillage, leading to further shortages amongst the local population. French occupation was restored in 1800, with further consequences for the Luganese. Commissioner Heinrich Zschokke re-established the authority of the Helvetic Republic on his arrival; a new préfet was appointed, Giuseppe Giovanni Battista Franzoni.
After two abortive attempts to unite Lugano with Bellinzona in the first two years of the 19th century, popular discontent, combined with fiscal pressure and a disastrous economic situation, led to a revolt in Capriasca early in 1802, which led to the autumn pronunciamento of Pian Povrò, named for the location of a district general congress, between Massagno and Breganzona, which declared the independence of Lugano from the Helvetic client republic.
With the Act of Mediation, the following year, political agitation was finally quelled, as were the struggles between unionists and federalists; merger with Bellinzona was at last completed, creating the Ticino, which endures to the present day.