
Politics of Cape Verde takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Cape Verde is the head of government and the President of the Republic of Cape Verde is the head of state, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the President and the Government. Legislative power is vested in both the Government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The constitution first approved in 1980 and substantially revised in 1992 forms the basis of government organization. It declares that the government is the "organ that defines, leads, and executes the general internal and external policy of the country" and is responsible to the National Assembly.

The recorded history of Cape Verde begins with Portuguese discovery in 1456. Possible early references go back around 2000 years.

Pedro de Verona Rodrigues Pires was the President of Cape Verde from March 2001 to September 2011. Before becoming President, he was Prime Minister from 1975 to 1991.

José Maria Pereira Neves is a Cape Verdean politician who was Prime Minister of Cape Verde from 2001 to 2016. He is a member of the African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (PAICV).

The African Party of Independence of Cape Verde is a former socialist party and currently a social-democratic political party in Cape Verde. Its members are nicknamed "os tambarinas" in Portuguese, and they identify themselves with the color yellow.

Elections in Guinea-Bissau take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a semi-presidential system. Both the President and the National People's Assembly are directly elected by voters.
Carlos Alberto Wahnon de Carvalho Veiga is a Cape Verdean politician. He was Prime Minister of Cape Verde from April 4, 1991 to July 29, 2000.

The unicameral National Assembly is the legislative body of the Republic of Cape Verde.
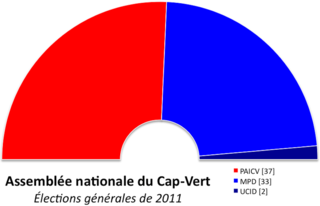
Parliamentary elections were held Cape Verde on 6 February 2011. The result was a victory for the ruling African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (PAICV), led by Prime Minister Jose Maria Neves, which won 38 of the 72 seats in the National Assembly.

General elections were held in Guinea-Bissau on 3 July 1994, with a second round for the presidential election on 7 August. They were the first multi-party elections since independence, and also the first time the president had been directly elected, as previously the post had been elected by the National People's Assembly. In the presidential election, the result was a victory for incumbent João Bernardo Vieira of the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC), who defeated Kumba Ialá of Social Renewal Party in the second round. In the Assembly election, 1,136 candidates ran for the 100 seats, of which the PAIGC won 62.

General elections were held in Guinea-Bissau on 28 November 1999, with a second round for the presidential election on 16 January 2000. The presidential election resulted in a victory for opposition leader Kumba Ialá of the Party for Social Renewal (PRS), who defeated Malam Bacai Sanhá of the ruling African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde. The PRS were also victorious in the National People's Assembly election, winning 38 of the 102 seats.

Indirect parliamentary elections were held in Guinea-Bissau on 15 June 1989. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde as the sole legal party. Voter turnout was 53.2%, and around 60% of the Assembly members were elected for the first time. The Assembly re-elected João Bernardo Vieira to the post of President on 19 June.

Indirect parliamentary elections were held in Guinea-Bissau on 31 March 1984. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde as the sole legal party. The Assembly elected João Bernardo Vieira to the post of President on 16 May 1984.

Indirect parliamentary elections were held in Guinea-Bissau between 19 December 1976 and mid-January 1977, the first since independence from Portugal. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) as the sole legal party. A single, official list of PAIGC candidates was presented to voters, although in some areas people voted for unofficial candidates, who achieved almost 20% of the national vote. The Assembly elected Luís Cabral to the post of President on 13 March 1977.

Indirect elections to a National Assembly were held in the parts of Portuguese Guinea held by the rebel African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) between August and October 1972, but not in the Portuguese-controlled areas of Bissau, Bolama, the Bissagos Islands and Bafatá.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cape Verde on 7 December 1980. The country was a one-party state at the time, with the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) as the sole legal party. Its leader was Aristides Pereira. The PAIGC presented a list of 63 candidates and three substitutes to voters to approve. Ultimately 93.0% of votes were cast for the PAIGC list, the others being blank or void. Voter turnout was 75.0%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cape Verde on 7 December 1985. The country was a one-party state at the time, with the African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (PAICV) as the sole legal party. The PAICV presented a list of 83 candidates to voters to approve. The list was approved by 94.0% of voters, with a turnout of 68.9%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cape Verde on 13 January 1991, the country's first multi-party elections, having previously been a one-party state with the African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (PAICV) as the sole legal party. The number of seats was reduced from 83 to 79. The result was a victory for the Movement for Democracy, which won 56 of the 79 seats. Voter turnout was 75.3%.

Presidential elections were held for the first time in Cape Verde on 17 February 1991, as previously the National Assembly had elected the President. The result was a victory for António Mascarenhas Monteiro of the Movement for Democracy, which had also won the parliamentary elections the previous month. He defeated incumbent Aristides Pereira of the African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde. Voter turnout was 61.4%.
Parliamentary elections were held in Cape Verde on 20 March 2016. The ruling African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (PAICV), led by Janira Hopffer Almada, was defeated by the Movement for Democracy (MpD), led by Ulisses Correia e Silva.













