Related Research Articles
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term capital refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing.
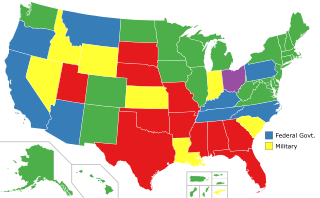
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty in 27 states, throughout the country at the federal level, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in the other 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 of them have authority to execute death sentences, with the other 7, as well as the federal government and military, subject to moratoriums.

Capital punishment has been completely abolished in all European countries except for Belarus and Russia, the latter of which has a moratorium and has not carried out an execution since September 1996. The complete ban on capital punishment is enshrined in both the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (EU) and two widely adopted protocols of the European Convention on Human Rights of the Council of Europe, and is thus considered a central value. Of all modern European countries, San Marino, Portugal, and the Netherlands were the first to abolish capital punishment, whereas only Belarus still practises capital punishment in some form or another. In 2012, Latvia became the last EU member state to abolish capital punishment in wartime.
In criminal law, a mitigating factor, also known as an extenuating circumstance, is any information or evidence presented to the court regarding the defendant or the circumstances of the crime that might result in reduced charges or a lesser sentence. Unlike a legal defense, the presentation of mitigating factors will not result in the acquittal of a defendant. The opposite of a mitigating factor is an aggravating factor.
Capital punishment in Georgia was completely abolished on 1 May 2000 when the country signed Protocol 6 to the ECHR. Later Georgia also adopted the Second Optional Protocol to the ICCPR. Capital punishment was replaced with life imprisonment.

Capital punishment in Latvia was abolished for ordinary crimes in 1999 and for crimes committed during wartime in 2012. Latvia is party to several international instruments which ban capital punishment.
Kvemo Barghebi is a village in Gali Municipality of Georgia. As is the case in the rest of the district its population is almost exclusively Georgian.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Cuba, however it is seldom resorted to. The last executions were carried out in 2003. National legislation provides for the death penalty for murder, threatening to commit murder, aggravated rape, terrorism, hijacking, piracy, drug trafficking and manufacturing, espionage, and treason. The typical method is execution by firing squad.
Death with reprieve is a criminal punishment found in chapter 5, sections 48, 50 and 51 of the criminal law of the People's Republic of China. It is a two-year suspended sentence where the execution is only carried out if the convicted commits further crimes during the suspension period. After the period the sentence is automatically reduced to life imprisonment, or to a fixed-term based on meritorious behavior. The reprieve is integrated into the sentence, unlike a pardon which occurs after the sentence.

Capital punishment in Luxembourg was abolished for all crimes in 1979.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the Federation of St. Kitts and Nevis, and is carried out by hanging at His Majesty's Prison in Basseterre. The death penalty can only be applied for aggravated murder and treason.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Algeria. Despite its legality, the last executions in the country were carried out in 1993, of seven unnamed Islamic terrorists. Due to its prolonged moratorium on executions, Algeria is considered to be "Abolitionist in Practice."
Capital punishment in Chile is legally sanctioned, albeit with significant limitations. Since its abolition for civilian offenses in 2001, its application has been restricted to military personnel convicted of war crimes and crimes against humanity committed during wartime. This places Chile among the seven countries globally that have abolished capital punishment solely for ordinary crimes.
Capital punishment in Oman is a legal penalty. Under Omani law, capital offenses are murder, drug trafficking, arson, piracy, terrorism, kidnapping, recidivism of aggravated offenses punishable by life imprisonment, leading an armed group that engages in spreading disorder, espionage, treason and perjury causing wrongful execution. Oman's last executions occurred in 2021. Oman voted against the United Nations moratorium on the death penalty in 2007, 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014, 2016, 2018, and 2020. Capital punishment in Oman is usually carried out by firing squad, however hanging is also permitted.
Capital punishment was a legal penalty in Zambia until 2022. Despite its former legality, the country had not carried out any execution since 1997. Zambia was considered "Abolitionist in Practice".
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Ghana only for high treason. Ghana last executed a criminal in 1993. The method of execution is by firing squad. It is considered "abolitionist in practice." Capital punishment was a mandatory sentence for certain ordinary criminal offenses until 2023.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Mauritania. However, the country is considered "Abolitionist in Practice" due to having a moratorium on executions since 1987. Mauritania last executed in 1987.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Tanzania. Tanzania has two capital offences: treason and murder. The death penalty is the mandatory sentence for murder.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Libya. Libya is classified as a "retentionist" state. Its last known executions were carried out in 2010. The execution method is shooting.
Capital punishment was abolished in Namibia in 1990. The last execution was carried out in 1988, under the rule of South Africa.