Related Research Articles

Capital punishment, also called the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as a punishment for a crime. It has historically been used in almost every part of the world. Since the mid-19th century many countries have abolished or discontinued the practice. In 2022, the five countries that executed the most people were, in descending order, China, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and the United States.

The president of Turkmenistan, officially the president and chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers of Turkmenistan, is the head of state and head of government of Turkmenistan. The president is also the supreme commander in chief of the Armed Forces of Turkmenistan and heads the State Security Council.

Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Belarus. At least one execution was carried out in the country in 2022.

Capital punishment in Sweden was last used in 1910, though it remained a legal sentence for at least some crimes until 1973. It is now outlawed by the Swedish Constitution, which states that capital punishment, corporal punishment, and torture are strictly prohibited. At the time of the abolition of the death penalty in Sweden, the legal method of execution was beheading. It was one of the last states in Europe to abolish the death penalty.

Capital punishment for murder was abolished in Cyprus on 15 December 1983. It was abolished for all crimes on 19 April 2002. The death penalty was replaced with life imprisonment. Cyprus is a signatory to the second optional protocol of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which provides for full abolition of capital punishment. Cyprus initially had a reservation on the second protocol, allowing execution for grave crimes in times of war, but subsequently withdrew this reservation. The Constitution of Cyprus was amended in 2016 to eliminate all forms of capital punishment.

The Constitution of Turkmenistan adopted on 18 May 1992 is the supreme law of Turkmenistan. In its preamble, the Constitution emphasizes self-determination for the Turkmen people, as well as the rule of law and rights for citizens..

Capital punishment in Armenia was a method of punishment that was implemented within Armenia's Criminal Code and Constitution until its eventual relinquishment in the 2003 modifications made to the Constitution. Capital punishment's origin in Armenia is unknown, yet it remained present in the Armenia Criminal Code of 1961, which was enforced and applied until 1999. Capital punishment was incorporated into Armenian legislation and effectuated for capital crimes, which were crimes that were classified to be punishable by death, including treason, espionage, first-degree murder, acts of terrorism and grave military crimes.

Capital punishment in Belgium was formally abolished on August 1, 1996, for all crimes, in both peacetime and wartime. The last execution for crimes committed in peacetime took place in July 1863, when in Ypres a farmer was executed for murder. The last execution for an ordinary crime took place on 26 March 1918 at Veurne Prison when Emile Ferfaille, a military officer found guilty of killing his pregnant girlfriend, was guillotined. This was the first execution to be carried out since 1863. The guillotine that was used had to be imported from France.
Capital punishment in Georgia was completely abolished on 1 May 2000 when the country signed Protocol 6 to the ECHR. Later Georgia also adopted the Second Optional Protocol to the ICCPR. Capital punishment was replaced with life imprisonment.

Capital punishment in modern Greece was carried out using the guillotine or by firing squad. It was last applied in 1972 during the military junta. The death penalty was abolished in stages between 1975 and 2005.

Capital punishment in Latvia was abolished for ordinary crimes in 1999 and for crimes committed during wartime in 2012. Latvia is party to several international instruments which ban capital punishment.
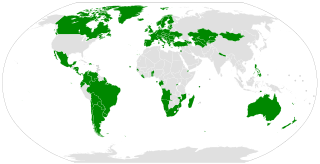
The Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, aiming at the abolition of the death penalty, is a subsidiary agreement to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. It was created on 15 December 1989 and entered into force on 11 July 1991. As of December 2024, the Optional Protocol has 92 state parties. The most recent country to ratify was Zambia, on 19 December 2024.

Capital punishment in Romania was abolished in 1990, and has been prohibited by the Constitution of Romania since 1991.
Capital punishment in Tajikistan is allowed by Article 18 of the 1999 Constitution of Tajikistan, which provides:
"Every person has the right to life. No person may be deprived of life except by the verdict of a court for a very serious crime."
Capital punishment is no longer applied in San Marino: the last execution was carried out in 1468 or in 1667, by hanging.
Capital punishment in Nauru was used prior to its independence in 1968. Prior to the abolition of capital punishment on 12 May 2016, with the passage of the Crimes Act 2016, Amnesty International categorised Nauru as a state that was abolitionist in practice.
Capital punishment in Angola was abolished by constitution in 1992. In 1977, the country carried out its last executions, which were of Nito Alves and many of his supporters, who were convicted of treason. The execution method in Angola was by firing squad. Angola signed the Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights on September 24, 2013, and ratified it on October 2, 2019. Angola voted in favor of the UN moratorium on the death penalty in 2007, 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014, 2016, 2018, and most recently in 2020.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in El Salvador. It was abolished in 1983 by Article 27 of the constitution, with an exception allowed for crimes committed under military law during a state of international war. Because of this, El Salvador is one of seven countries considered "Abolitionist for Ordinary Crimes," along with Brazil, Burkina Faso, Chile, Guatemala, Israel, and Peru. El Salvador last carried out an execution in 1973.
Capital punishment in Colombia was abolished by the 1910 constitution. In prohibiting the death penalty, the Colombian Constitution of 1991 states "The right to life is inviolable. There will be no death penalty."
Capital punishment has been abolished in Paraguay. It was abolished in the year 1992 by the constitution. The last execution was carried out in Paraguay in 1928.
References
- ↑ 1992 Constitution of Turkmenistan Archived 2015-04-14 at the Wayback Machine , unofficial English translation, University of Texas at Arlington, URL accessed 27 December 2006
- ↑ Abolition of capital punishment in Turkmenistan Archived 2016-11-26 at the Wayback Machine , Presidential Decree 3003, 28 December 1999 (in Russian)
- ↑ "Госсимволика - «Туркменистан: золотой век»". www.turkmenistan.gov.tm. Archived from the original on 20 October 2007. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ Ratification of Second Optional Protocol on abolition of death penalty