
Aldolase A, also known as fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDOA gene on chromosome 16.
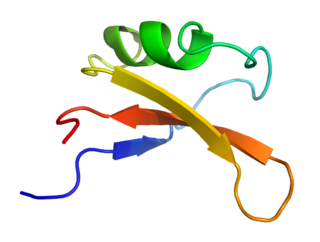
Brazzein is a sweet-tasting protein extracted from the West African fruit of the climbing plant Oubli. It was first isolated by the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1994.

Cathepsin A is an enzyme that is classified both as a cathepsin and a carboxypeptidase. In humans, it is encoded by the CTSA gene.

Mabinlins are sweet-tasting proteins extracted from the seed of mabinlang, a plant growing in Yunnan province of China. There are four homologues. Mabinlin-2 was first isolated in 1983 and characterised in 1993, and is the most extensively studied of the four. The other variants of mabinlin-1, -3 and -4 were discovered and characterised in 1994.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase (EC 1.3.7.9) is an enzyme found in some bacteria and archaea that catalyzes the chemical reaction

DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCM7 gene.

DNA replication licensing factor MCM3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCM3 gene.

DNA replication licensing factor MCM4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCM4 gene.
In enzymology, a dolichyl-phosphate beta-D-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases family (SDR) is a very large family of enzymes, most of which are known to be NAD- or NADP-dependent oxidoreductases. As the first member of this family to be characterised was Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase, this family used to be called 'insect-type', or 'short-chain' alcohol dehydrogenases. Most members of this family are proteins of about 250 to 300 amino acid residues. Most dehydrogenases possess at least 2 domains, the first binding the coenzyme, often NAD, and the second binding the substrate. This latter domain determines the substrate specificity and contains amino acids involved in catalysis. Little sequence similarity has been found in the coenzyme binding domain although there is a large degree of structural similarity, and it has therefore been suggested that the structure of dehydrogenases has arisen through gene fusion of a common ancestral coenzyme nucleotide sequence with various substrate specific domains.

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL6A1 gene.

Semenogelin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEMG1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is the predominant protein in semen. The encoded secreted protein is involved in the formation of a gel matrix that encases ejaculated spermatozoa. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) protease processes this protein into smaller peptides, with each possibly having a separate function. The proteolysis process breaks down the gel matrix and allows the spermatozoa to move more freely. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITIH1 gene.

Lithostathine-1-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the REG1B gene.

Heat-stable enterotoxins (STs) are secretory peptides produced by some bacterial strains, such as enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli which are in general toxic to animals.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K9 gene.

Myosin-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYH8 gene.
Sarcophaga peregrina is a species of flesh fly belonging to the family Sarcophagidae. They easily breed, multiply and spread in human habitation, from garbage, faeces and livestock manures. In many regions, they are health concerns as they are active vectors of infectious diseases such as myiasis in humans. Due to their close contact with human activities, they are considered as forensically important insects. They can be used for molecular analysis of the time of postmortem intervals. They are also occasionally parasitic in other invertebrates. They produce a group of antibacterial peptide called sarcotoxins. The first of such protein, sarcotoxin 1A, was determined in 1983 by Masayuki Okada and Shunji Natori at the University of Tokyo, Japan.















