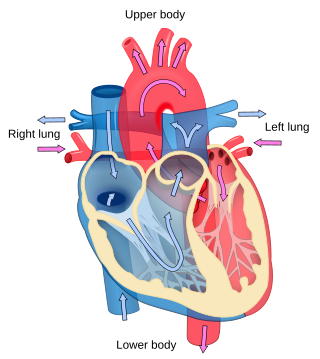
Cardiology is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a speciality of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a speciality of general surgery.

Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat.
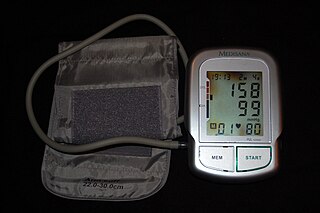
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. High blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.

Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases, stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis.

Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In severe cases of classic MVP, complications include mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, congestive heart failure, and, in rare circumstances, cardiac arrest.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems.

Nebivolol is a beta blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. As with other β-blockers, it is generally a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It may be used by itself or with other blood pressure medication. It is taken by mouth.
Avijit Lahiri is a researcher in cardiology in the UK.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "the sum of activity and interventions required to ensure the best possible physical, mental, and social conditions so that patients with chronic or post-acute cardiovascular disease may, by their own efforts, preserve or resume their proper place in society and lead an active life". CR is a comprehensive model of care delivering established core components, including structured exercise, patient education, psychosocial counselling, risk factor reduction and behaviour modification, with a goal of optimizing patient's quality of life and reducing the risk of future heart problems.

Celiprolol is a medication in the class of beta blockers, used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has a unique pharmacology: it is a selective β1 receptor antagonist, but a β2 receptor partial agonist. It is also a weak α2 receptor antagonist.

Valentín Fuster Carulla, 1st Marquess of Fuster is a Spanish cardiologist and aristocrat.
Annapoorna Kini is an American cardiologist. She is Professor of Cardiology and Interventional Director of Structural Heart Program at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.

A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest.

Complications of hypertension are clinical outcomes that result from persistent elevation of blood pressure. Hypertension is a risk factor for all clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis since it is a risk factor for atherosclerosis itself. It is an independent predisposing factor for heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, kidney disease, and peripheral arterial disease. It is the most important risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, in industrialized countries.
Jonathan L. Halperin is an American cardiologist and the author of Bypass (ISBN 0-89586-509-2), among the most comprehensive works on the subject of coronary artery bypass surgery. In addition, he is the Robert and Harriet Heilbrunn Professor of Medicine at The Mount Sinai School of Medicine as well as Director of Clinical Cardiology in the Zena and Michael A. Wierner Cardiovascular Institute at The Mount Sinai Medical Center, both in New York City. Halperin was the principal cardiologist responsible for both the design and execution of the multi-center Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation (SPAF) clinical trials, funded by the National Institutes of Health, which helped develop antithrombotic strategies to prevent stroke, and he subsequently directed the SPORTIF clinical trials, which evaluated the first oral direct thrombin inhibitor for prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Bococizumab is a drug that was in development by Pfizer targeting PCSK9 to reduce LDL cholesterol. Pfizer withdrew the drug from development in November 2016, determining that it was "not likely to provide value to patients, physicians or shareholders."

Stefan D. Anker is Head of Field “Tissue Homeostasis and Cachexia" at Charité University, Berlin, Germany. Previously, he was Professor of Innovative Clinical Trials at University Medical Center Göttingen in Germany. The main focus of the Innovative Clinical Trials department was research in the field of chronic heart failure, including the development and clinical testing of new therapies.

George (Rick) Stouffer M.D. is Chief of the Division of Cardiology at the University of North Carolina Medical Center, where he is a practicing interventional cardiologist. Stouffer was awarded the Ernest and Hazel Craige Distinguished Professorship of Medicine in 2018; prior to that he was the Henry A. Foscue Distinguished Professor of Medicine. Stouffer is also co-director of the McAllister Heart Institute. He is known for his research regarding inpatient ST elevation myocardial infarctions.

John A. Ambrose is an American physician who is an expert in coronary artery disease. He is one of the pioneers in acute coronary syndromes having published over 40 articles in the cardiology literature between 1985 and 2000 on their pathogenesis. He has also published on cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease. Working with his PhD candidate, Rajat Barua, utilizing a novel in vitro model, they described the effects of cigarette smoking on nitric oxide biosynthesis, endothelial function, and endothelial-derived fibrinolytic and antithrombotic factors. Their 2004 update on cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology has been referenced over 2,100 times as of 2020. Ambrose is a Professor of Clinical Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He was also a Director of the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory at Mount Sinai Hospital and received a National Leadership Award from the National Republican Congressional Committee.















