
The alveolates are a group of protists, considered a major clade and superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria into the SAR supergroup.
The plagiopylids are a small order of ciliates, including a few forms common in anaerobic habitats.

Blepharisma is a genus of unicellular ciliate protists found in fresh and salt water. The group includes about 40 accepted species, and many sub-varieties and strains. While species vary considerably in size and shape, most are easily identified by their red or pinkish color, which is caused by granules of the pigment blepharismin.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.

Stephanopogon is a genus of flagellated marine protist that superficially resembles a ciliate.

Protozoa are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals".

Coleps is a genus of ciliates in the class Prostomatea with barrel-shaped bodies surrounded by regularly arranged plates composed of calcium carbonate.

Colpoda is a genus of ciliates in the class Colpodea, order Colpodida, and family Colpodidae.
Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, Loxodes, is found in freshwater.
''''' is a of karyorelictean ciliates, belonging to Loxodidae. It is the only known karyorelictean ciliate that lives in freshwater habitats.
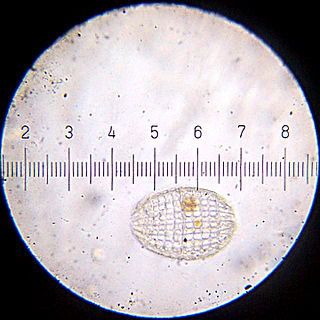
Prostomatea is a class of ciliates. It includes the genera Coleps and Pelagothrix.

The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation.

Euplotes is a genus of ciliates in the subclass Euplotia. Species are widely distributed in marine and freshwater environments, as well as soil and moss. Most members of the genus are free-living, but two species have been recorded as commensal organisms in the digestive tracts of sea urchins.

Climacostomum is a genus of unicellular ciliates, belonging to the class Heterotrichea.

Dileptus is a genus of unicellular ciliates in the class Litostomatea. Species of Dileptus occur in fresh and salt water, as well as mosses and soils. Most are aggressive predators equipped with long, mobile proboscides lined with toxic extrusomes, with which they stun smaller organisms before consuming them. Thirteen species and subspecies of Dileptus are currently recognized.

Mesodinium rubrum is a species of ciliates. It constitutes a plankton community and is found throughout the year, most abundantly in spring and fall, in coastal areas. Although discovered in 1908, its scientific importance came into light in the late 1960s when it attracted scientists by the recurrent red colouration it caused by forming massive blooms, that cause red tides in the oceans.

Intramacronucleata is a subphylum of ciliates. The group is characterized by the manner in which division of the macronucleus is accomplished during binary fission of the cell. In ciliates of this subphylum, division of the macronucleus is achieved by the action of microtubules which are assembled inside the macronucleus itself. This is in contrast to heterotrich ciliates of the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora, in which division of the macronucleus relies on microtubules formed outside the macronuclear envelope.

Armophorea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Intramacronucleata. . It was first resolved in 2004 and comprises three orders: Metopida, Clevelandellida, and Armophorida. Previously members of this class were thought to be heterotrichs because of similarities in morphology, most notably a characteristic dense arrangement of cilia surrounding their oral structures. However, the development of genetic tools and subsequent incorporation of DNA sequence information has led to major revisions in the evolutionary relationships of many protists, including ciliates. Metopids, clevelandellids, and armophorids were grouped into this class based on similarities in their small subunit rRNA sequences, making them one of two so-called "riboclasses" of ciliates, however, recent analyses suggest that Armophorida may not be related to the other two orders.
Protocruziea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Intramacronucleata.
Parablepharismea is a class of free-living marine and brackish anaerobic ciliates that form a major clade of obligate anaerobes within the SAL group, together with the classes Muranotrichea and Armophorea.













