A satellite is a subviral agent that depends on the coinfection of a host cell with a helper virus for its replication. Satellites can be divided into two major classes: satellite viruses and satellite nucleic acids. Satellite viruses, which are most commonly associated with plants, are also found in mammals, arthropods, and bacteria. They encode structural proteins to enclose their genetic material, which are therefore distinct from the structural proteins of their helper viruses. Satellite nucleic acids, in contrast, do not encode their own structural proteins, but instead are encapsulated by proteins encoded by their helper viruses. The genomes of satellites range upward from 359 nucleotides in length for satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA (STobRV).
Tombusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Symptoms associated with this genus include mosaic. The name of the genus comes from Tomato bushy stunt virus.

Papaya ringspot virus (PRSV) is a pathogenic plant virus in the genus Potyvirus and the virus family Potyviridae which primarily infects the papaya tree.
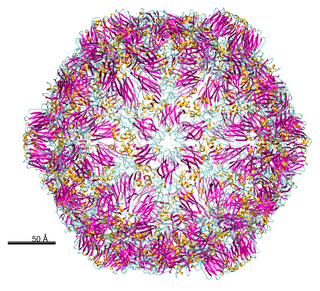
Nepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae, in the subfamily Comovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera in the subfamily Comovirinae, are transmitted by nematodes.
Dianthovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Dianthoviruses are plant viruses. There are three species in this genus. The virus probably has a worldwide distribution, and can be transmitted via nematodes, by mechanical inoculation, by grafting of plants and by contact between infected hosts with previously uninfected host.
Hydrangea ringspot virus (HRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Alphaflexiviridae.
Odontoglossum ringspot virus (ORSV) is a plant pathogenic virus that belongs to the family Virgaviridae. It is one of the most common viruses affecting cultivated orchids, perhaps second only to the Cymbidium mosaic virus. It causes spots on leaves and colored streaks on flowers. If a plant is also infected with the Cymbidium mosaic virus, it can lead to a condition called blossom brown necrotic streak.
Potato black ringspot virus (PBRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Comoviridae.

Prunus necrotic ringspot virus (PNRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing ring spot diseases affecting species of the genus Prunus, as well as other species such as rose and hops. PNRSV is found worldwide due to easy transmission through plant propagation methods and infected seed. The virus is in the family Bromoviridae and genus Ilarvirus. Synonyms of PNRSV include European plum line pattern virus, hop B virus, hop C virus, plum line pattern virus, sour cherry necrotic ringspot virus, and peach ringspot virus.

Tobacco rattle virus (TRV) is a pathogenic plant virus. Over 400 species of plants from 50 families are susceptible to infection.
Tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the plant virus family Secoviridae. It is the type species of the genus Nepovirus. Nepoviruses are transmitted between plants by nematodes, thrips, mites, grasshoppers, and flea beetles. TRSV is also easily transmitted by sap inoculation and transmission in seeds has been reported. In recent cases it has also been shown to appear in bees, but no transmission to plants from bees has been noted.
Tomato ringspot virus (ToRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It affects species of cucumber, tobacco, tomato, cowpea, among others. It causes ringspots in tobacco plants and raspberries, yellow bud mosaic in peaches, yellow vein in grapes, and stunted growth in gladiolus and Narcissus. Its range is in the temperate regions of North America, especially where its vector, Xiphinema americanum is present. Along with the adult and larval stages of this nematode, the virus is also spread by seed. This type of infection is more common in strawberries and soybeans than any other susceptible plant.
Raspberry ringspot virus (RRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It was first described by Cadman in 1958. It causes ringspots in raspberries and strawberries and can cause rasp-leaf symptoms in cherry. It also has been found in many other plants including those in the Vitis and Narcissus genera. There are many strains of the virus, the most important including the Scottish strain, the English strain, and the Lloyd George yellow blotch strain. The Scottish strain is the type virus.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.

Orthotospovirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses, in the family Tospoviridae of the order Bunyavirales, which infects plants. Tospoviruses take their name from the species Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) which was discovered in Australia in 1919. TSWV remained the only known member of the family until the early 1990s when genetic characterisation of plant viruses became more common. There are now at least twenty species in the genus with more being discovered on a regular basis. Member viruses infect over eight hundred plant species from 82 different families.

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Ringspot, a symptom of various plant viral infections, may refer to:

Betaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.
Carnation Italian ringspot virus is a virus that is a member of the Tombusviridae family. It can create C-shaped or doughnut-shaped structures that often join with other MVBs in the infected cell. It is found wherever carnations are grown by vegetative multiplication in temperate regions. It is isolated from apple, pear and sour cherry trees in the German Democratic Republic.








