
Cathorops is a genus of catfishes in the family Ariidae found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. These species are found in the eastern and western Central and South America in brackish and freshwater habitats. This genus is a strongly supported clade of this family. It consists of a natural group in which the monophyly is well-defined by morphological and molecular evidence and the genus probably includes several unrecognized species from both American coasts.
Pouteria belizensis is a species of plant in the family Sapotaceae. It is found in Belize, Guatemala, and Mexico.
The estuarine sea catfish, also known as the Aguadulce sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Seth Eugene Meek in 1904, originally under the genus Galeichthys. It is a tropical fish which is known from Mexico to Guatemala, where it typically inhabits freshwater rivers, lagoons, and drainages, also sometimes dwelling in marine waters. It reaches a maximum standard length of 22.7 cm (8.9 in).

Cathorops taylori, the Taylor's sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in estuaries at depths below 20 m from Mexico to El Salvador in the Eastern Pacific. Maximum recorded body length is 28.3 cm.

Cathorops arenatus, the yellow sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in the western Atlantic from the Gulf of Paria in Venezuela to Maranhão in Brazil. Maximum recorded body length is 25 cm.
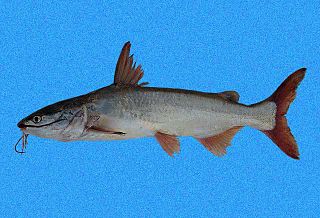
Cathorops wayuu, the Wayuu sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in shallow coastal and estuarine waters from Camarones in Colombia to the Gulf of Paria in Venezuela. Maximum recorded body length is 31.4 cm.

Cathorops tuyra, the Besudo sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in shallow coastal and estuarine waters of the eastern Pacific from Costa Rica to southern Peru. Maximum recorded body length is 29 cm.

Cathorops dasycephalus, the big-belly sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in clear waters at depth between 10 and 30 m in the eastern Pacific from central Mexico to Ecuador. Maximum recorded body length is 29 cm.

Cathorops fuerthii, the Congo sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in muddy and brackish waters at depths down to 20 m in the eastern Pacific from Mexico to Ecuador. Maximum recorded body length is 28 cm.

Cathorops higuchii, the Higuchi's sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is named after Horácio Higuchi, a scientist from Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi, Brazil. The species is found in estuaries and coastal waters of the western Atlantic from eastern Honduras to Colón, Panama. Maximum recorded body length is 35 cm.

Cathorops hypophthalmus, the gloomy sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish. It is found in coastal and estuarine waters of Costa Rica and Panama. Maximum recorded body length is 35 cm.

The Mapale sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It is a tropical fish which is known from Colombia to west Venezuela, where it typically inhabits freshwaters, brackish, in coastal lagoons and near-shore marine waters. It reaches a maximum standard length of 30.6 cm (12.0 in).
The Papillate sea catfish, also known as the Kailola's sea catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Alexandre Pires Marceniuk and Ricardo Betancur-Rodríguez in 2008. It is a tropical fresh and saltwater catfish which occurs in Central America. It reaches a standard length of 25.4 cm (10.0 in).
The Conguito sea catfish is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Susan Brown Bristol in 1897. It is a tropical, freshwater catfish which occurs in Mexico. It reaches a standard length of 19.7 cm (7.8 in).
The Dark sea catfish is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1864. It is a tropical, freshwater catfish which occurs in Guatemala. It reaches a total length of 23 cm (9.1 in).
The Box sea catfish is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1864. It is a tropical, marine catfish which occurs in Guatemala, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, Mexico, Nicaragua, Honduras, and Panama. It dwells at a maximum depth of 20 m (66 ft). It reaches a 30 cm (12 in).
The Orinoco sea catfish is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1864. It is a tropical, fresh and saltwater catfish which occurs between Venezuela and Guyana. It reaches a standard length of 24.5 cm (9.6 in).
The Curator sea catfish, also known as the Raredon's sea catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Alexandre Pires Marceniuk, Ricardo Betancur-Rodríguez and Arturo Acero Pizarro in 2009. It is a tropical, marine and freshwater-dwelling fish which occurs between Mexico and El Salvador.
The Madamango sea catfish, also known as the Raspfin sea catfish or the Spring cuirass, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Louis Agassiz in 1829. It is a tropical, marine and brackish water-dwelling catfish which occurs between Colombia and Brazil. It inhabits a depth range between 1 to 50 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 30 cm (12 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 20 cm (7.9 in).
The Steindachner's sea catfish is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert and Edwin Chapin Starks in 1904. It is a tropical, marine and freshwater-dwelling catfish which occurs between Costa Rica and Peru. It dwells at a maximum depth of 20 m (66 ft). It reaches a maximum total length of 36 cm (14 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 20 cm (7.9 in).












