
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus Betula, in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech-oak family Fagaceae. The genus Betula contains 30 to 60 known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are a typically rather short-lived pioneer species widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates.

Larches are conifers in the genus Larix, of the family Pinaceae. Growing from 20 to 45 metres tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains further south. Larches are among the dominant plants in the boreal forests of Siberia and Canada. Although they are conifers, larches are deciduous trees that lose their needles in the autumn.

Larix gmelinii, the Dahurian larch or Gmelin larch, is a species of larch native to eastern Siberia and adjacent northeastern Mongolia, northeastern China (Heilongjiang) and North Korea.

Catocala is a generally Holarctic genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of Systema Naturae. The moths are commonly known as underwing moths or simply underwings. These terms are sometimes used for a few related moths, but usually – especially when used in plural, not as part of a species name – they are used to refer to Catocala only.

Plemyria rubiginata, the blue-bordered carpet, is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. The distribution area extends through western and central Europe including the British Isles, and continues through the temperate zone of the Palearctic to the Russian Far East Siberia and Japan. It rises to an elevation of 1500 metres in the Alps.

Catocala fraxini, the blue underwing or Clifden nonpareil, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Catocala fulminea, the yellow bands underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in his 1763 Entomologia Carniolica. It is found in central and southern Europe, east Asia and Siberia. The xarippe lineage has been proposed to be a distinct and valid species in its own right, instead of being only subspecifically distinct.

Catocala helena is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in Siberia and Manchuria.
Catocala bella is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. It is found in Russia, Korea, China and Japan.

Angelica dahurica, commonly known as Dahurian angelica, is a wildly grown species of angelica native to Siberia, Russia Far East, Mongolia, Northeastern China, Japan, Korea, and Taiwan. This species tend to grow near river banks, along streams and among rocky shrubs. The root of the plant is widely used for its medicinal properties and is known to contain furanocoumarins and angelicotoxin.
Catocala moltrechti is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Otto Bang-Haas in 1927. It is found in south-eastern Siberia.
Catocala aenigma is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Leo Sheljuzhko in 1943. It is found in south-eastern Siberia.
Catocala danilovi is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Otto Bang-Haas in 1927. It is found in south-eastern Siberia.
Catocala ella is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. It is found in south-eastern Siberia and Japan.
Catocala eminens is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Otto Staudinger in 1892. It is found in south-eastern Siberia.
Catocala koreana is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Staudinger in 1892. It is found in Japan, Korea and south-eastern Siberia.

Catocala lupina is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1851. It is found from south-eastern Europe to south-western Siberia, Asia Minor and Transcaucasia.
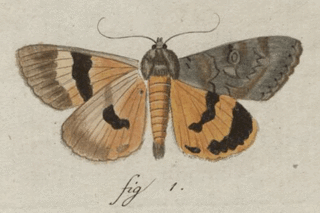
Catocala neonympha is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. It is found in south-western Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, eastern Turkey, Iraq, Armenia, Kurdistan, Afghanistan, the Altai Mountains and southern Siberia.
Catocala nymphaeoides is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1852. It is found in south-eastern Siberia.
Catocala thomsoni is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by A. E. Prout in 1924. It is found in northern China.









