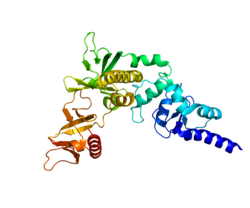
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis; a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene INSR, from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon combination are ultimately capable of homo or hetero-dimerisation to produce the ≈320 kDa disulfide-linked transmembrane insulin receptor.
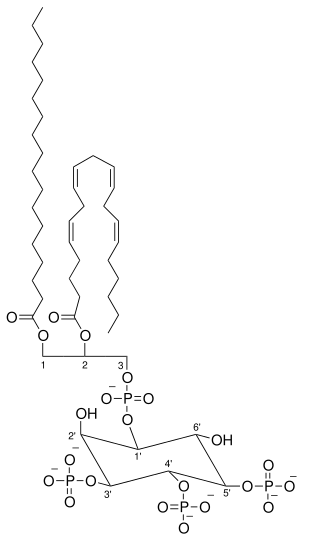
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3), abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases' (PI 3-kinases) phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is a phospholipid that resides on the plasma membrane.
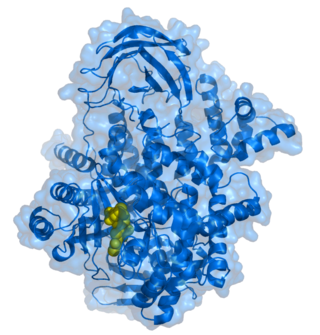
The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha, also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is encoded by the PIK3CA gene.
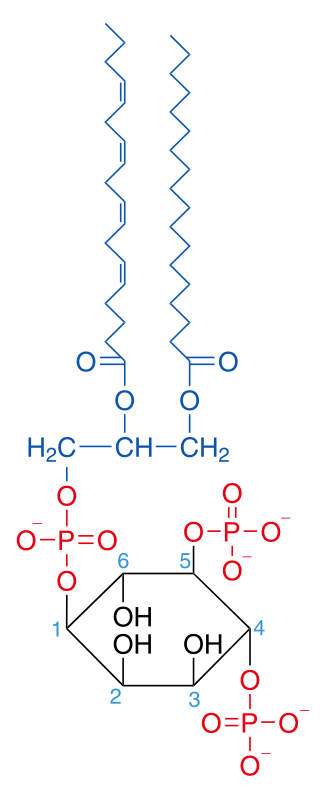
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.
Prostaglandin receptors or prostanoid receptors represent a sub-class of cell surface membrane receptors that are regarded as the primary receptors for one or more of the classical, naturally occurring prostanoids viz., prostaglandin D2,, PGE2, PGF2alpha, prostacyclin (PGI2), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and PGH2. They are named based on the prostanoid to which they preferentially bind and respond, e.g. the receptor responsive to PGI2 at lower concentrations than any other prostanoid is named the Prostacyclin receptor (IP). One exception to this rule is the receptor for thromboxane A2 (TP) which binds and responds to PGH2 and TXA2 equally well.

Nucleolin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCL gene.

Protein kinase C iota type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCI gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase D1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKD1 gene.

Src homology 2 (SH2) domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 1(SHIP1) is an enzyme with phosphatase activity. SHIP1 is structured by multiple domain and is encoded by the INPP5D gene in humans. SHIP1 is expressed predominantly by hematopoietic cells but also, for example, by osteoblasts and endothelial cells. This phosphatase is important for the regulation of cellular activation. Not only catalytic but also adaptor activities of this protein are involved in this process. Its movement from the cytosol to the cytoplasmic membrane, where predominantly performs its function, is mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation of the intracellular chains of cell surface receptors that SHIP1 binds. Insufficient regulation of SHIP1 leads to different pathologies.

High-mobility group protein B2 also known as high-mobility group protein 2 (HMG-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMGB2 gene.

Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 14A also known as CPI-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R14A gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RASA3 gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchanger 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PREX1 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3B2 gene.

Arf-GAP with dual PH domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADAP2 gene.
Casein kinase I isoform alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CSNK1A1 gene.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.
Leonard (Len) R Stephens FRS is a molecular biologist, senior group leader and associate director at the Babraham Institute.

RAS p21 protein activator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASA2 gene.