
The Aspidodiadematidae are a family of sea urchins.

The Diadematidae are a family of sea urchins. Their tests are either rigid or flexible and their spines are long and hollow.

Centrostephanus coronatus, also known as crowned sea urchin, is a species of sea urchin in the family Diadematidae. It was first described to science by Yale zoology Professor Addison Emery Verrill in 1867.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms.

Heterocentrotus mamillatus, commonly known as the slate pencil urchin, red slate pencil urchin, or red pencil urchin, is a species of tropical sea urchin from the Indo-Pacific region.

The Echinacea are a superorder of sea urchins. They are distinguished by the presence of a rigid test, with ten buccal plates around the mouth, and solid spines. Unlike some other sea urchins, they also possess gills. The group is a large one, with species found worldwide.

The Camarodonta are an order of globular sea urchins in the class Echinoidea. The fossil record shows that camarodonts have been in existence since the Lower Cretaceous.
Agassizia excentrica is a species of sea urchin of the family Prenasteridae. The species was first scientifically described in 1869 by Alexander Agassiz.

Amphipneustes davidi is a species of sea urchin. Their armour is covered with spines. It is placed in the genus Amphipneustes and lives in the sea. Amphipneustes davidi was first scientifically described in 2010 by Madon-Senez.

Aporocidaris usarpi is a species of sea urchin of the family Ctenocidaridae. Their armour is covered with spines. It is placed in the genus Aporocidaris and lives in the sea. Aporocidaris usarpi was first scientifically described in 2000 by Mooi, David, Fell & Choné.

Echinometra is a genus of sea urchins in the family Echinometridae.

Asterechinus elegans is a species of sea urchin of the family Trigonocidaridae. Their armour is covered with spines. It is the only species in the genus Asterechinus and lives in the sea. Asterechinus elegans was first scientifically described in 1942 by Ole Theodor Jensen Mortensen.

Astriclypeus mannii is a species of sea urchin of the family Astriclypeidae. Their armour is covered with spines. It is placed in the genus Astriclypeus and lives in the sea. Astriclypeus mannii was first scientifically described in 1867 by Verrill.

Centrostephanus longispinus, the hatpin urchin, is a species of sea urchin in the family Diadematidae. There are two subspecies, Centrostephanus l. longispinus, found in the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea and Centrostephanus l. rubricingulus, found in the western Atlantic.
Centrostephanus nitidus is a species of sea urchin of the family Diadematidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Centrostephanus nitidus was first scientifically described in 1927 by Koehler.

Centrostephanus longispinus rubricingulus is a subspecies of sea urchins of the Family Diadematidae. Their armour is covered with spines. C. l. rubricingulus was first scientifically described in 1921 by Hubert Lyman Clark.
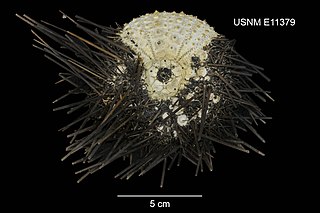
Centrostephanus sylviae is a species of sea urchins of the family Diadematidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Centrostephanus sylviae was first scientifically described in 1975 by Koehler.

Scutellidae is a family of sand dollars in the superfamily Scutellidea. All genera except Scaphechinus are extinct.

The infraclassis Carinacea includes most living species of regular sea urchin, and fossil forms going back as far as the Triassic.
Sophronica bimaculipennis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1955, originally under the genus Sophronisca. It is known from Ghana, the Ivory Coast, and Guinea. It contains the varietas Sophronica bimaculipennis var. besnardi.















