
Cellulase is any of several enzymes produced chiefly by fungi, bacteria, and protozoans that catalyze cellulolysis, the decomposition of cellulose and of some related polysaccharides:
Candex is a dietary supplement manufactured by Pure Essence Laboratories. It is marketed as an enzymatic remedy to treat the yeast infection candida. Having the status of a dietary supplement, its efficiency has not been proven in scientifically controlled and peer-reviewed trials. Similar formulas exist, such as Candigest.

Chaetomium is a genus of fungi in the Chaetomiaceae family. It is a dematiaceous (dark-walled) mold normally found in soil, air, cellulose and plant debris. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, there are about 95 species in the widespread genus.
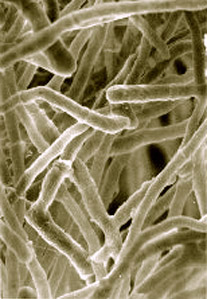
Trichoderma reesei is a mesophilic and filamentous fungus. It is an anamorph of the fungus Hypocrea jecorina. T. reesei can secrete large amounts of cellulolytic enzymes. Microbial cellulases have industrial application in the conversion of cellulose, a major component of plant biomass, into glucose.

Stone washing is a textile manufacturing process used to give a newly manufactured cloth garment a worn appearance. The process became popular in the 1980s, as acid jeans gained popularity; however, stone washing has roots going back to 1960s surfer apparel. Stone washing also helps to increase the softness and flexibility of otherwise stiff and rigid fabrics such as canvas and denim. Although stone washing increases a fabric's flexibility, it shortens the life-span of the jeans. The process of stone washing can be costly, as freshly stone washed jeans must be washed many times in order to remove the grit from the process. Along with high production costs, stone washing can be detrimental to the environment, due to the excess grit that is removed as fabric is being stone washed. This leads many manufacturers to pursue other methods to achieve a distressed appearance.

Coprophilous fungi are a type of saprobic fungi that grow on animal dung. The hardy spores of coprophilous species are unwittingly consumed by herbivores from vegetation, and are excreted along with the plant matter. The fungi then flourish in the feces, before releasing their spores to the surrounding area.
Chaetomium cupreum is a fungus in the family Chaetomiaceae. It is able to decay in manufactured cellulosic materials, and is known to antagonize a wide range of soil microorganisms. This species is component of the biocontrol agent, Ketomium, a commercial biofungicide. It has also been investigated for use in the production of natural dyes. Chaetomium cupreum is mesophilic and known to occur in harsh environments and can rapidly colonize organic substrates in soil. Laboratory cultures of C. cupreum can be propagated on a range of common growth media including potato dextrose at ambient or higher than ambient temperature producing cottony white colonies with a reddish reverse.

Chaetomium globosum is a well-known mesophilic member of the mold family Chaetomiaceae. It is a saprophytic fungus that primarily resides on plants, soil, straw, and dung. Endophytic C. globosum assists in cellulose decomposition of plant cells. They are found in habitats ranging from forest plants to mountain soils across various biomes. C. globosum colonies can also be found indoors and on wooden products.
Chaetomium atrobrunneum is a darkly pigmented mould affiliated with the fungal division, Ascomycota. This species is predominantly saprotrophic, although it has been known to infect animals including humans, showing a proclivity for the tissues of the central nervous system. Chaetomium atrobrunneum was described in 1949 from a mouldy military mattress cover obtained from the island of Guadalcanal.
Chaetomium rectangulare is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. elatum.
Chaetomium interruptum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. megalocarpum.
Chaetomium grande is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. megalocarpum.
Chaetomium iranianum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. This species in particular can be characterized by spirally coiled ascomatal hairs and fusiform ascospores.
Chaetomium truncatulum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. This species in particular can be characterized by spirally coiled ascomatal hairs and fusiform ascospores.
Botryotrichum murorum is a common soil and indoor fungus resembling members of the genus Chaetomium. The fungus has no known asexual state, and unlike many related fungi, is intolerant of high heat exhibiting limited growth when incubated at temperatures over 35 °C. In rare cases, the fungus is an opportunistic pathogen of marine animals and humans causing cutaneous and subcutaneous infection.
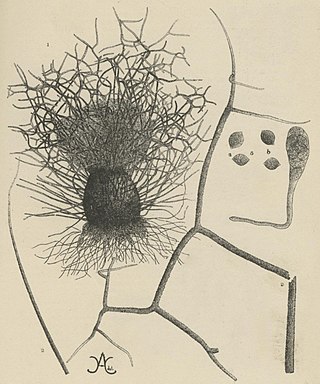
Chaetomium elatum is a very common and widely distributed saprotrophic fungus of the Chaetomiaceae family of molds which has been found to grow on many different substances all over the world. It was first established by Gustav Kunze after he observed it growing on dead leaves. Its defining features that distinguish it from other Chaetomium species are its extremely coarse terminal hairs and the lemon-shaped morphology of its ascospores. It produces many metabolites with potential biotechnology uses including one with promise against the rice blast disease fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. It shows very little pathogenic ability causing confirmed disease in only a few plant species.
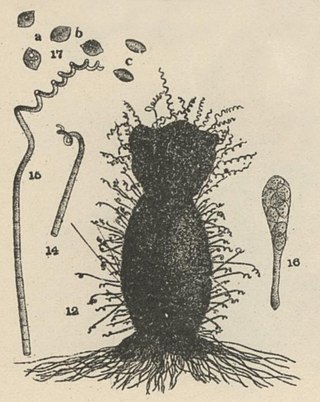
Chaetomium subspirale is a fungus from the phylum Ascomycota. It was described by A. H. Chivers in 1912 in America. The species has sexual fruiting bodies that are ornamented with characteristic, coiled hairs giving it a wooly appearance. C. subspirale colonies are brown, which the characteristic hairs are also responsible for. It is commonly found in various soil and dung samples. C. subspirale produces the mycotoxin, oxaspirodion, which inhibits inducible TNF-a expression and inhibits the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB.
Arcopilus aureus is a plant and soil fungus in the genus Arcopilus. It was first identified by A. H. Chivers in 1912, who named it Chaetomium aureum. It was later transferred to the genus Arcopilus by Wang and colleagues. The fungus has recently been recognized to have industrial use for the production of the metabolites resveratrol. and sclerotiorin Additionally, A. aureus has high lead tolerance and clearance, suggesting a potential role in environmental biotechnology.

Myxotrichum chartarum is a psychrophilic and cellulolytic fungus first discovered in Germany by Gustav Kunze in 1823. Its classification has changed many times over its history to better reflect the information available at the time. Currently, M. chartarum is known to be an ascomycete surrounded by a gymnothecium composed of ornate spines and releases asexual ascospores. The presence of cellulolytic processes are common in fungi within the family Myxotrichaceae. M. chartarum is one of many Myxotrichum species known to degrade paper and paper products. Evidence of M. chartarum "red spot" mold formation, especially on old books, can be found globally. As a result, this fungal species and other cellulolytic molds are endangering old works of art and books. Currently, there is no evidence that suggests that species within the family Myxotrichaceae are pathogenic.
Chaetomium perlucidum is a neurotropic dematiaceous fungus that is naturally found in the soil, including in agricultural soil, and in the stems of dead plants. The fungus can also be found on the feathers of birds, manure, seeds, and even paper. It is able to thrive at temperatures of 35 and 42 °C.








