
Chaetomium is a genus of fungi in the Chaetomiaceae family. It is a dematiaceous (dark-walled) mold normally found in soil, air, cellulose and plant debris. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, there are about 95 species in the widespread genus.

The Arthoniales is the second largest order of mainly crustose lichens, but fruticose lichens are present as well. The order contains around 1500 species, while the largest order with lichenized fungi, the Lecanorales, contains more than 14000 species.

Coprophilous fungi are a type of saprobic fungi that grow on animal dung. The hardy spores of coprophilous species are unwittingly consumed by herbivores from vegetation, and are excreted along with the plant matter. The fungi then flourish in the feces, before releasing their spores to the surrounding area.

Parmelinella is a genus of lichen belonging to the family Parmeliaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1987 by John Elix and Mason Hale as a segregate of Parmelina, from which it differs in having larger ascospores and containing salazinic acid. Although the genus had been assumed to be well-defined morphologically, a 2021 molecular phylogenetic study suggests that the generic delimitations need to be revised.
Sagiolechia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Sagiolechiaceae. The genus was circumscribed by lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1854, who assigned Sagiolechia protuberans as the type species. The family Sagiolechiaceae was proposed in 2010 to contain Sagiolechia as the type genus, and genus Rhexophiale; molecular phylogenetic analysis showed that these two genera formed a distinct clade in the Ostropales.
Farrowia is a genus of fungi within the Chaetomiaceae family.

Chaetomium globosum is a well-known mesophilic member of the mold family Chaetomiaceae. It is a saprophytic fungus that primarily resides on plants, soil, straw, and dung. Endophytic C. globosum assists in cellulose decomposition of plant cells. They are found in habitats ranging from forest plants to mountain soils across various biomes. C. globosum colonies can also be found indoors and on wooden products.
Chaetomium atrobrunneum is a darkly pigmented mould affiliated with the fungal division, Ascomycota. This species is predominantly saprotrophic, although it has been known to infect animals including humans, showing a proclivity for the tissues of the central nervous system. Chaetomium atrobrunneum was described in 1949 from a mouldy military mattress cover obtained from the island of Guadalcanal.
Chaetomium undulatulum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. globosum.
Chaetomium rectangulare is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. elatum.
Chaetomium interruptum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. megalocarpum.
Chaetomium grande is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. It is closely related to C. megalocarpum.
Chaetomium truncatulum is a fungus species in the Chaetomium genus, first isolated from Iran. It shares features such as peridium structure, ascospore morphology and germ pore position with its cogenerates. This species in particular can be characterized by spirally coiled ascomatal hairs and fusiform ascospores.
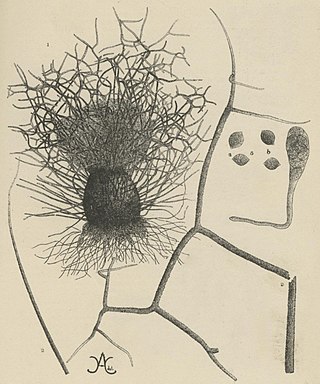
Chaetomium elatum is a very common and widely distributed saprotrophic fungus of the Chaetomiaceae family of molds which has been found to grow on many different substances all over the world. It was first established by Gustav Kunze after he observed it growing on dead leaves. Its defining features that distinguish it from other Chaetomium species are its extremely coarse terminal hairs and the lemon-shaped morphology of its ascospores. It produces many metabolites with potential biotechnology uses including one with promise against the rice blast disease fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. It shows very little pathogenic ability causing confirmed disease in only a few plant species.
Collariella bostrychodes is a fungal decomposer of lignin and carbohydrate in the family Chaetomiaceae commonly found in soil and dung. The fungus is distinguished by a darkened collar-like ostiole around the ostiolar pore, giving the fungus its name. The fungus is highly variable in shape and form, giving raise to the belief that there are two subclades in the species. The ascospores range from lemon-shaped to nearly spherical with slightly pointed ends. It can grow to be pale green and later turn pale bluish grey or olivaceous with age. The fungus produces the toxic secondary metabolite, chaetochromin.
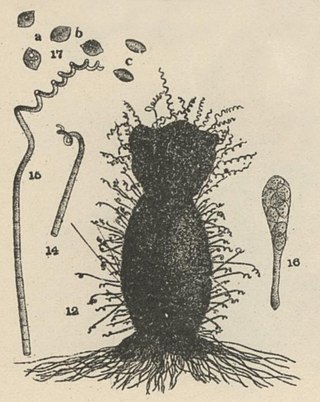
Chaetomium subspirale is a fungus from the phylum Ascomycota. It was described by A. H. Chivers in 1912 in America. The species has sexual fruiting bodies that are ornamented with characteristic, coiled hairs giving it a wooly appearance. C. subspirale colonies are brown, which the characteristic hairs are also responsible for. It is commonly found in various soil and dung samples. C. subspirale produces the mycotoxin, oxaspirodion, which inhibits inducible TNF-a expression and inhibits the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB.
Arcopilus aureus is a plant and soil fungus in the genus Arcopilus. It was first identified by A. H. Chivers in 1912, who named it Chaetomium aureum. It was later transferred to the genus Arcopilus by Wang and colleagues. The fungus has recently been recognized to have industrial use for the production of the metabolites resveratrol. and sclerotiorin Additionally, A. aureus has high lead tolerance and clearance, suggesting a potential role in environmental biotechnology.
Pyrenidium is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi. It is the only genus in the family Pyrenidiaceae. It has 13 species.

Nigrovothelium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Trypetheliaceae. It has three species. The genus was circumscribed in 2016 by lichenologists Robert Lücking, Matthew Nelsen, and André Aptroot, to contain species formerly in the Trypethelium tropicum species group. The type species, Nigrovothelium tropicum, was originally described by Erik Acharius in 1810, as a species of Verrucaria.
Gossypiothallon is a fungal genus of uncertain familial placement in the order Arthoniales. It contains the single species Gossypiothallon appendisporum, a corticolous (bark-dwelling), crustose lichen found in South Solomons. Both the genus and species were described as new to science in 2014 by Dutch lichenologist André Aptroot. The type specimen was collected from Kolombangara island at an altitude of 700 m (2,300 ft), where it was found growing on bark.







