Bulgarian, is a South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of Bulgarians.

The Balkan Wars consisted of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan Peninsula in 1912 and 1913. Four Balkan states defeated the Ottoman Empire in the first war. In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria fought against all four original combatants of the first war along with facing a surprise attack from Romania from the north. The conflicts ended catastrophically for the Ottoman Empire, which lost the bulk of its territory in Europe. Austria-Hungary, although not a combatant, became relatively weaker as a much enlarged Serbia pushed for union of the South Slavic peoples. The war set the stage for the Balkan crisis of 1914 and thus served as a "prelude to the First World War".

The BalkansBAWL-kənz, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographic area in southeastern Europe with various definitions and meanings, including geopolitical and historical. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria from the Serbian-Bulgarian border to the Black Sea coast. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea on the northwest, the Ionian Sea on the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south and southeast, and the Black Sea on the east and northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

Macedonian is a South Slavic language spoken as a first language by around two million people, principally in North Macedonia and the Macedonian diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. It is the official language of North Macedonia and a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia.
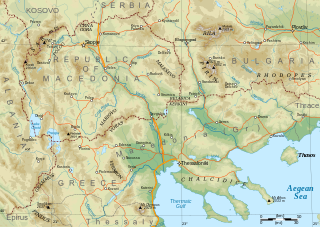
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of 4.76 million.
The history of Bulgaria can be traced from the first settlements on the lands of modern Bulgaria to its formation as a nation-state and includes the history of the Bulgarian people and their origin. The earliest evidence of hominid occupation discovered on what is today Bulgaria date from at least 1.4 million years ago. Around 5000 BC, a sophisticated civilization already existed and produced some of the first pottery and jewelry in the world. After 3000 BC, the Thracians appeared on the Balkan peninsula. In the late 6th century BC, most of what is nowadays Bulgaria came under the Persian Empire. In the 470s BC, the Thracians formed the powerful Odrysian Kingdom, probably after the Persian defeat in Greece, which subsequently declined and Thracian tribes fell under Macedonian, Celtic and Roman domination. This mixture of ancient peoples was assimilated by the Slavs, who permanently settled on the peninsula after 500 AD.

Sofia is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. The city is at the foot of Vitosha Mountain in the western part of the country. Being in the centre of the Balkans, it is midway between the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea, and closest to the Aegean Sea.
Bulgarians are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its immediate region.

Plovdiv is the second-largest city in Bulgaria after Sofia, with a city population of 346,893 as of 2018 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the culture capital of Bulgaria. It is an important economic, transport, cultural, and educational center. There is evidence of habitation in Plovdiv dating back to the 6th millennium BCE, when the first Neolithic settlements were established. It has been considered to be one of the oldest cities in the world.

The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 (O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counter-attacked, entering Bulgaria. With Bulgaria also having previously engaged in territorial disputes with Romania, this war provoked Romanian intervention against Bulgaria. The Ottoman Empire also took advantage of the situation to regain some lost territories from the previous war. When Romanian troops approached the capital Sofia, Bulgaria asked for an armistice, resulting in the Treaty of Bucharest, in which Bulgaria had to cede portions of its First Balkan War gains to Serbia, Greece and Romania. In the Treaty of Constantinople, it lost Edirne to the Ottomans.

The Bulgaria national football team represents Bulgaria in international football, and is administered by the Bulgarian Football Union, a member association of UEFA. The team's home stadium is the Vasil Levski Stadium in Sofia, and Krasimir Balakov is the current national team manager.

The Bulgarian Orthodox Church, legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria, is an autocephalous Orthodox Church. It is the oldest Slavic Orthodox Church with some 6 million members in the Republic of Bulgaria and between 1.5 and 2.0 million members in a number of European countries, the Americas, Australia, New Zealand and Asia. It was recognized as an independent Church by the Patriarchate of Constantinople in AD 870, becoming Patriarchate in 918/919.

The People's Republic of Bulgaria was the official name of Bulgaria, when it was a socialist republic.

The Second Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conquered by the Ottomans in the late 14th and early 15th centuries. It was succeeded by the Principality and later Kingdom of Bulgaria in 1878.

The First Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 681 when Bulgar tribes led by Asparuh moved to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeating – possibly with the help of local South Slavic tribes – the Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. At the height of its power, Bulgaria spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea.

The Kingdom of Bulgaria, also referred to as the Tsardom of Bulgaria and the Third Bulgarian Tsardom, was a constitutional monarchy in Eastern and Southeastern Europe, which was established on 5 October 1908, when the Bulgarian state was raised from a principality to a kingdom. Ferdinand I was crowned a Tsar at the Declaration of Independence, mainly because of his military plans and for seeking options for unification of all lands in the Balkans region with an ethnic Bulgarian majority.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in September 1991 under the name Republic of Macedonia. A landlocked country, North Macedonia has borders with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia, and is defined primarily by mountains, valleys, and rivers. The capital and largest city, Skopje, is home to roughly a quarter of the nation's 2.06 million inhabitants. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, and Aromanians.

Professional Football Club Ludogorets 1945 Razgrad, commonly known as Ludogorets Razgrad or simply Ludogorets, is a Bulgarian professional association football club based in Razgrad, which currently competes in the First Professional Football League, the top-tier of the Bulgarian football league system.

Tsar, also spelled csar, or tzar or czar, is a title used to designate East and South Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers of Eastern Europe, originally Bulgarian monarchs from 10th century onwards. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism. The term is derived from the Latin word Caesar, which was intended to mean "Emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official —but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to king, or to be somewhat in between a royal and imperial rank.