
Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

The brownspotted grouper, also known as the brown spotted reef cod, brown-spotted rockcod, coral grouper or honeycomb cod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It has an Indo-Pacific distribution but in the northern Indian Ocean this distribution is discontinuous. It forms part of a species complex with two closely related species in the genus Epinephelus.

The sharpbelly or wild carp, sharpbelly, or common sawbelly, is a tropical freshwater and brackish water fish belonging to the Cultrinae subfamily of the family Cyprinidae. It originates in large streams and reservoirs in China, Taiwan, Japan, Hong Kong, Korea, and the Amur River basin. It has become established as an exotic species in several other countries, including Iran, Afghanistan, and the former Soviet Union, where it has displaced local species. It was originally described as Culter leucisculus by S. Basilewsky in 1855, and has also been referred to as Chanodichthys leucisculus and Hemiculter leucisculus warpachowskii in scientific literature.

The spotfin goby cichlid is an African species of cichlid endemic to Lake Tanganyika where it is only known from the northern end of the lake. They live amongst pebbles in the surf-zone. This species can reach a length of 7 centimetres (2.8 in) TL. This species can also be found in the aquarium trade. Although presently considered the only species in the genus, another undescribed species is known from the Lukuga River.

The stone moroko, also known as the topmouth gudgeon, is a fish belonging to the Cyprinid family, native to Asia, but introduced and now considered an invasive species in Europe and North America. The fish's size is rarely above 8 cm and usually 2 to 7.5 cm long.
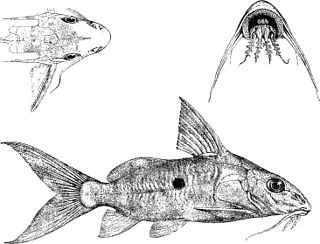
Synodontis nummifer, known as the two spot synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered in Léopoldville, Belgian Congo. The specific name "nummifer" comes from the Latin for "to bear a coin", which refers to the large spots on its sides.

Synodontis decorus is a species of upside-down catfish. Common names include clown catfish, clown synodontis, clown syno, clown squeaker, and barredtail squeaker.
Dactylogyrus is a genus of monogeneans in the Dactylogyridae family.
Cacatuocotyle is a genus of monogeneans.

Cichlidogyrus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Ancyrocephalidae. The type-species of the genus is Cichlidogyrus arthracanthusPaperna, 1960, by original designation. All the species of the genus are parasites on the gills of fish, namely African Cichlidae, Nandidae and Cyprinodontidae.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .
Pseudorhabdosynochus guitoe is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the Highfin grouper, Epinephelus maculatus. It has been described in 2007.
Plectanocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on the gills of marine fish.

Paradiplozoon hemiculteri is a species of monogenean of the family Diplozoidae. As in all species of this family, the bodies of the two hermaphroditic members of a couple are permanently fused for life.

Paradiplozoon yunnanense is a species of monogenean of the family Diplozoidae. As in all species of this family, the bodies of the two hermaphroditic members of a couple are permanently fused for life.

Cichlidogyrus jeanloujustinei is a species of monopisthocotylean monogenean in the family Ancyrocephalidae. It is a parasite of the gills of the fish Eretmodus marksmithi in Lake Tanganyika, Burundi.

Cichlidogyrus evikae is a species of monopisthocotylean monogenean in the family Ancyrocephalidae. It is a parasite of the gills of the fish Tanganicodus irsacae in Lake Tanganyika, Burundi.
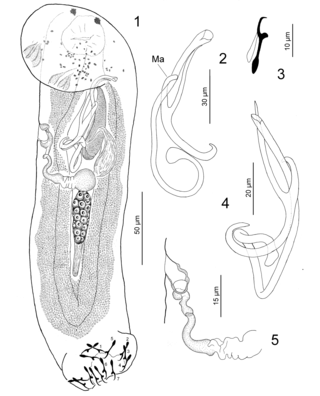
Paracolpenteron hubbsii is a species of dactylogyrid Monogenean. It is the single species of the genus Paracolpenteron. It is a parasite of the urinary bladder of the maya needlefish Strongylura hubbsi (Belonidae).
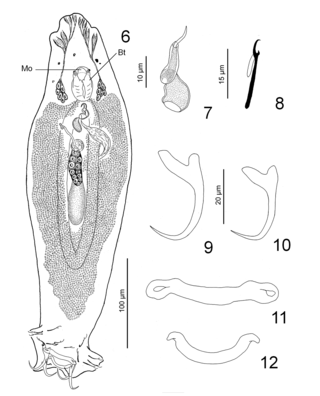
Ancyrocephalus chiapanensis is a species of ancyrocephalid monogenean. It is a parasite of the gills of the maya needlefish Strongylura hubbsi (Belonidae).
Rhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae.















