
Caspar Rudolph Ritter von Jhering was a German jurist. He is best known for his 1872 book Der Kampf ums Recht, as a legal scholar, and as the founder of a modern sociological and historical school of law. His ideas were important to the subsequent development of the "jurisprudence of interests" in Germany.

Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was a German naturalist, zoologist, botanist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. He is considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time.
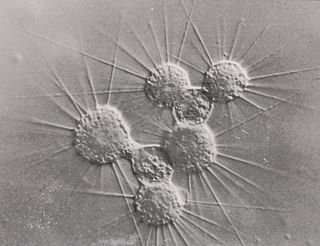
Actinophrys is a genus of heliozoa, amoeboid unicellular organisms with many axopodial filaments that radiate out of their cell. It contains one of the most common heliozoan species, Actinophrys sol. It is classified within the monotypic family Actinophryidae.

Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link was a German naturalist and botanist. The standard author abbreviation Link is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Johann Christoph Friedrich Klug, was a German entomologist. He described the butterflies and some other insects of Upper Egypt and Arabia in Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg and Wilhelm Friedrich Hemprich's Symbolæ Physicæ. He was professor of medicine and entomology in the University of Berlin where he curated the insect collections from 1810 to 1856. At the same time he directed the Botanic Garden in Berlin which contains his collections. Klug worked mainly on Hymenoptera and Coleoptera. The plant genus Klugia was named in his honour as well as the butterflies Geitoneura klugii and Heliophisma klugii.

The sebae anemone, also known as leathery sea anemone, long tentacle anemone, or purple tip anemone, is a species of sea anemone belonging to the family Stichodactylidae and native to the Indo-Pacific area.
Victor Ehrenberg was a German Jewish historian.
Gisela Bleibtreu-Ehrenberg is a German sociologist, ethnologist, sexologist, and writer further specializing into the fields of psychology, Indo-European studies, religious studies, and philosophy, since 1980 also increasingly anthropology. As Bleibtreu-Ehrenberg uses these approaches in research particularly in the fields of sexology, homophobia, and prejudice studies, the US Society of Lesbian and Gay Anthropologists of the American Anthropological Association ranked Bleibtreu-Ehrenberg's works on homophobia as internationally outstanding.

Herbert Ehrenberg was a German politician.
A small number of dinoflagellates contain an internal skeleton. One of the best known species is perhaps Actiniscus pentasterias, in which each cell contains a pair of siliceous five-armed stars surrounding the nucleus. This species was originally described by Ehrenberg. Although the description is incomplete and without illustrations, Ehrenberg described the skeletal elements but mentioned that the living cell was colorless and non-motile. Ehrenberg subsequently diagrammed the silicified skeletal elements (pentasters) from geological deposits in various parts of the world. These can be found as microfossils. Pentasters were studied from the Cenozoic South Pacific by Dumitrică http://deepseadrilling.org/21/volume/dsdp21_25.pdf Tappan gave a survey of dinoflagellates with internal skeletons. This included the first detailed description of the pentasters in Actiniscus pentasterias, based on scanning electron microscopy.

Acropora hemprichii is a species of acroporid coral that was first described by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1834. It lives in reefs at depths of 3 to 15 m for between 13 and 24 years. The species is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and has a decreasing population. It is common with a wide range, and is listed on Appendix II of CITES.
Gyrosmilia is a monotypic genus of large polyp stony coral. It is represented by a single species, Gyrosmilia interrupta. It was first described by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1834 as Manicina interrupta.
Anthopleura stellula is a species of sea anemone in the family Actiniidae. It was first described in 1834 by Wilhelm Hemprich and Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Actinia (Isacmaea) stellula. It is found in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, and is unusual among sea anemones in that it can divide itself in two transversely.

Heterodactyla hemprichii is a species of sea anemone in the family Thalassianthidae, and was first formally described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.
Surirella elegans is a species of freshwater diatoms in the family Surirellaceae.

Heterodactyla is a genus of sea anemones of the family Thalassianthidae. The genus was first described in 1834 by Wilhelm Hemprich and Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

Favites halicora is a species of coral belonging to the family Merulinidae. The species was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg as Astraea halicora.
Tubipora hemprichi is an organ coral in the family Tubiporidae. It was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg. The species name honours Wilhelm Hemprich, and was described from a specimen found in the Red Sea.

Tubipora chamissonis is an organ coral in the family Tubiporidae. It was first described in 1834 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, from a specimen collected near Radack Island.










