Related Research Articles

Emissions trading is a market-oriented approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). One prominent example is carbon emission trading for CO2 and other greenhouse gases which is a tool for climate change mitigation. Other schemes include sulfur dioxide and other pollutants.
Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

John Edward Sununu is an American politician who served as a member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1997 to 2003 and the U.S. Senate representing New Hampshire from 2003 to 2009. Sununu was the youngest member of the Senate for his entire six-year term. He also remains the only Salvadoran American ever elected to the U.S. Congress.
The Clear Skies Act of 2003 was a proposed federal law of the United States. The official title as introduced is "a bill to amend the Clean Air Act to reduce air pollution through expansion of cap-and-trade programs, to provide an alternative regulatory classification for units subject to the cap and trade program, and for other purposes."
The American Coalition for Clean Coal Electricity is a U.S. non-profit advocacy group representing major American coal producers, utility companies and railroads. The organization seeks to influence public opinion and legislation in favor of coal-generated electricity in the United States, placing emphasis on the development and deployment of clean coal technologies.
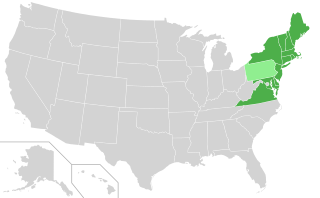
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 11-state region. Pennsylvania's participation in the RGGI cooperative was ruled unconstitutional on November 1, 2023, although that decision has been appealed. North Carolina's entrance into RGGI has been blocked by the enactment of the state's fiscal year 2023–25 budget.
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, or Assembly Bill (AB) 32, is a California state law that fights global warming by establishing a comprehensive program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all sources throughout the state. AB32 was co-authored by Assemblymember Fran Pavley and Speaker of the California Assembly Fabian Nunez and signed into law by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on September 27, 2006.

Joe Lieberman was an American politician who served as a United States Senator from Connecticut from 1989 to 2013. A former member of the Democratic Party, he was the party's nominee for Vice President in the 2000 election. He was an Independent prior to his death.

Frances J. "Fran" Pavley is an American politician who served two terms in the California State Senate and three terms in the California State Assembly. A Democrat, she last represented the 27th Senate District, which encompasses the Conejo Valley, and portions of the San Fernando and Santa Clarita Valleys. Due to term limits in California, Senator Pavley completed her legislative career in 2016. She is currently working as the Environmental Policy Director for the USC Schwarzenegger Institute.

The Global Warming Pollution Reduction Act of 2007 (S. 309) was a bill proposed to amend the 1963 Clean Air Act, a bill that aimed to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). U.S. Senator, Bernie Sanders (I-VT), introduced the resolution in the 110th United States Congress on January 16, 2007. The bill was referred to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works but was not enacted into law.
The America's Climate Security Act of 2007 was a global warming bill that was considered by the United States Senate to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted in the United States. Also known as the Lieberman–Warner bill, bill number S. 2191, the legislation was introduced by Sens. Joseph Lieberman (I-CT) and John Warner (R-VA) on October 18, 2007. The bill was approved by the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works in December 2007, and was debated in the Senate during the week of June 2. The bill would create a national cap-and-trade scheme for greenhouse gas emissions, in which polluters would mostly be allocated right-to-emit credits based on how much greenhouse gas they currently emit. The cap would get tighter over time, until by 2050, emissions would be reduced to 63% below 2005 levels. Several environmental groups expressed their encouragement at the progress in legislation on the global warming issue while at the same time expressing disappointment that the bill did not reduce emissions enough. On June 6, 2008, the bill was killed by Senate Republicans over worries that it would damage the economy.

Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose is to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. Carbon emissions trading is a common method that countries use to attempt to meet their pledges under the Paris Agreement, with schemes operational in China, the European Union, and other countries.

John McCain ran for U.S. president in the 2000 presidential election, but failed to gain the Republican Party nomination, losing to George W. Bush in a campaign that included a bitter battle during the South Carolina primary. He resumed his role representing Arizona in the U.S. Senate in 2001, and Bush won the election. Bush was President of the United States from 2001 to 2009. McCain won re-election to the Senate in 2004, 2010 and 2016.

U.S. Senator John McCain, a Republican Party politician from Arizona who was a member of the U.S. Congress from 1983 until his death in office in 2018, a two-time U.S. presidential candidate, and the nominee of the Republican Party in the 2008 U.S. Presidential election, took positions on many political issues through his public comments, his presidential campaign statements, and his senatorial voting record.

The American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009 (ACES) was an energy bill in the 111th United States Congress that would have established a variant of an emissions trading plan similar to the European Union Emission Trading Scheme. The bill was approved by the House of Representatives on June 26, 2009, by a vote of 219–212. With no prospect of overcoming a threatened Republican filibuster, the bill was never brought to the floor of the Senate for discussion or a vote. The House passage of the bill was the "first time either house of Congress had approved a bill meant to curb the heat-trapping gases scientists have linked to climate change."
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.
California Senate Bill 535 is a California bill that was introduced by Senator Kevin De Leon of Los Angeles and signed into law on September 30, 2012 by Governor Jerry Brown. SB 535 is largely based on the actions introduced by Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, commonly known as AB 32. AB 32 was passed in 2006 and its goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in California. The process outlined by AB 32 resulted in the creation of a cap-and-trade system in California. Companies must purchase extra credits when they exceed their allotted amount for the cap and trade. Each year, the money generated from companies purchasing extra credits is expected to generate about $1 billion of state revenue. SB 535 requires that 25% of the fund is spent on projects that benefit disadvantaged communities, while at least 10% of the 25% is spent on projects located in disadvantaged communities. Cal Enviroscreen is a screening methodology that identifies disadvantaged communities that the funds will be directed into. The money will be spent on projects that have been approved by the Legislature.

The Energy Innovation and Carbon Dividend Act of 2019 is a bill in the United States House of Representatives that proposes a fee on carbon at the point of extraction to encourage market-driven innovation of clean energy technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The fees are recycled to citizens in monthly dividends. The act was originally introduced in 2018 with bipartisan support from six co-sponsors and died when the 115th congress ended on 3 January 2019. It is principally based on Citizens' Climate Lobby's carbon fee and dividend proposal, and this organization advocates for the bill.

The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) is a United States federal law which aims to reduce the federal government budget deficit, lower prescription drug prices, and invest in domestic energy production while promoting clean energy. It was passed by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 16, 2022.
References
- 1 2 "Summary of the Lieberman-McCain Climate Stewardship Act". Center for Climate and Energy Solutions. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05. Retrieved 2012-06-07.
- ↑ "All Information (Except Text) for S.139 - Climate Stewardship Act of 2003". U.S. Congress. 2003.
- ↑ "Jobs and the Climate Stewardship Act: How Curbing Global Warming Can Increase Employment" (PDF). Natural Resources Defense Council. Natural Resources Defense Council: 21. February 2005.
- ↑ Franta, Benjamin (2021). "Weaponizing economics: Big Oil, economic consultants, and climate policy delay". Environmental Politics. 31 (4): 555–575. doi: 10.1080/09644016.2021.1947636 . ISSN 0964-4016.
- ↑ "White House Left Out in the Cold on Warming". IPS. 2007-01-23. Archived from the original on 2007-02-14. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
- ↑ "Summary of The Lieberman-McCain Climate Stewardship Act of 2003". Center for Climate and Energy Solutions. 2003. Archived from the original on 2012-02-20. Retrieved 2020-01-21.
- ↑ "Vote On the McCain Amendment" . Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ↑ Moore, Patrick. "Nature, not Human Activity, Rules the Climate". Climate Change Credit. Retrieved 2020-01-21.
- ↑ "Lieberman, McCain Reintroduce Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act". Joe Lieberman, United States Senator. 2007-01-12. Archived from the original on 2008-04-20. Retrieved 2008-04-24.
- ↑ "Climate Stewardship and Innovation Act of 2007 (2007 - S. 280)". GovTrack.us. Retrieved 2020-01-21.
